Quartz tube wavelength transmission spans from deep ultraviolet to mid-infrared, making these tubes essential in many scientific and industrial fields. Standard quartz tubes transmit nearly 100% of light at 185 nm in the ultraviolet, over 95% in the visible range around 550 nm, and maintain at least 85% in the infrared up to 2,500 nm. The following chart shows how transmission rates change across these regions:
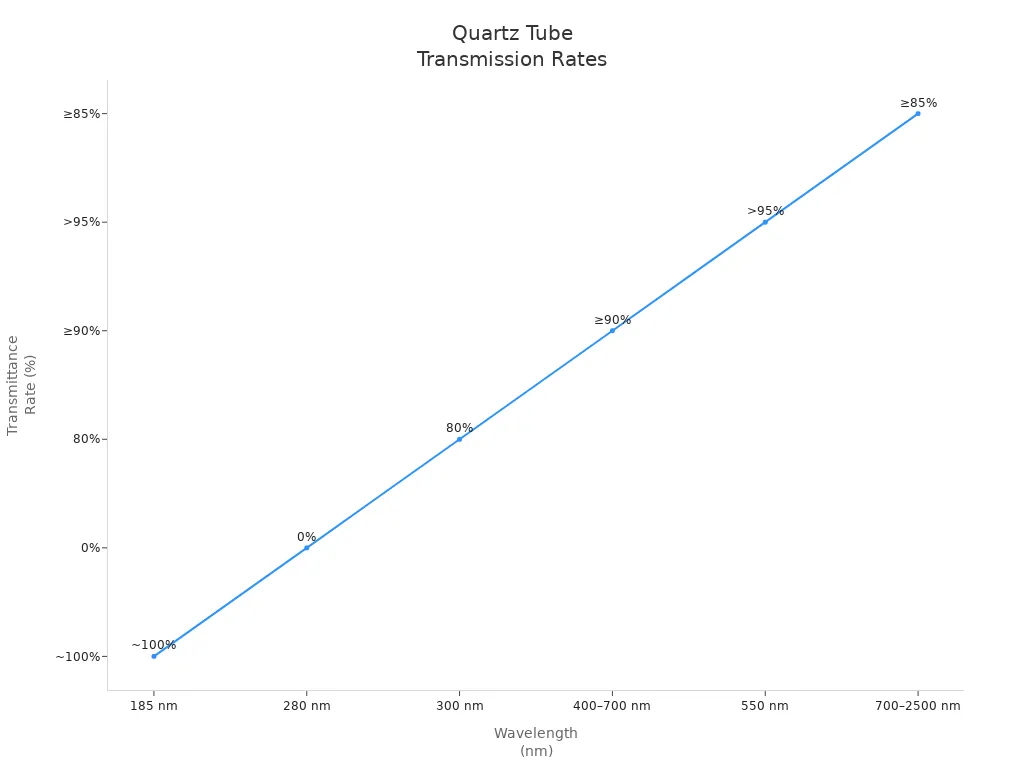
Engineers and buyers must consider grade, purity, and wall thickness, since these factors directly affect how much light passes through the tube at each wavelength.
Key Takeaways
Quartz tubes transmit light across a wide range, from deep ultraviolet to mid-infrared, making them vital for various scientific and industrial applications.
Different grades of quartz tubes (JGS-1, JGS-2, JGS-3) offer unique transmission properties, allowing engineers to select the right tube based on specific wavelength needs.
High-purity synthetic fused silica, like JGS-1, is ideal for UV applications, ensuring over 90% transmission at critical germicidal wavelengths.
Maintaining low OH content in quartz tubes enhances transmission efficiency, especially in infrared applications, ensuring accurate measurements and reliable performance.
Regular maintenance and careful selection of quartz tube grades help preserve transmission rates, ensuring long-term reliability in demanding environments.
What Is the Transmission Range of Different Quartz Tube Grades?

Quartz tube wavelength transmission depends on the grade of quartz, the manufacturing process, and the presence of hydroxyl (OH) groups. Each grade—JGS-1, JGS-2, and JGS-3—offers unique performance across the ultraviolet, visible, and infrared regions. Understanding these differences helps engineers and buyers select the right quartz tube for their specific wavelength range and application.
JGS-1 UV-Grade Quartz Tube
JGS-1 UV-grade quartz tube provides the highest transmission in the deep ultraviolet region. This grade uses synthetic fused silica, which allows light to pass through from 185 nm up to 2,500 nm with minimal absorption, making it ideal for applications that require strong UV penetration. The manufacturing process results in high purity and a typical OH content of 150-200 ppm, supporting over 90% transmission between 170 nm and 2,100 nm.
The following table summarizes the key transmission properties of JGS-1 UV-grade quartz tube:
Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
Transmission Range | 185 nm - 2500 nm |
UV Cutoff | <160 nm |
Transmission Range (medium) | 0.17~2.10 um (Tavg>90%) |
Engineers often choose JGS-1 when their systems demand reliable quartz tube wavelength transmission in the deep ultraviolet, such as in sterilization or photolithography.
JGS-2 Optical-Grade Quartz Tube
JGS-2 optical-grade quartz tube offers balanced performance for both ultraviolet and visible light applications. This grade transmits light effectively from 220 nm to 2,500 nm, with an average transmission above 85% in the 260 nm to 2,100 nm range. The flame-fused manufacturing method introduces moderate OH content and some metal impurities, which can affect absorption, especially near the 2,730 nm region.
Manufacturers monitor both OH content and melting technique to optimize quartz tube wavelength transmission. The presence of hydroxyl groups creates absorption peaks, while metal impurities can reduce transmittance in the visible spectrum. These factors make JGS-2 a cost-effective choice for applications that do not require deep UV but still need high visible and near-infrared performance.
Key Points:
Transmission range: 220–2,500 nm, with Tavg >85% from 260–2,100 nm.
OH content and manufacturing process influence absorption and transmission.
Best suited for UV-A curing, visible spectroscopy, and general laboratory use.
JGS-2 quartz tube provides a practical solution for many industrial and scientific needs, balancing cost and performance.
JGS-3 IR-Grade Quartz Tube
JGS-3 IR-grade quartz tube specializes in infrared transmission, making it suitable for applications beyond the visible spectrum. This grade maintains high transparency from the ultraviolet edge through the mid-infrared, with no significant absorption bands in the visible range and excellent performance up to 4,000 nm. The electrical fusion process produces low OH content, typically around 5 ppm, which is crucial for minimizing absorption in the infrared region.
Wavelength Range | Transparency Characteristics |
|---|---|
185-250 nm | Absorption bands present |
Ultraviolet to IR | Transparent with outstanding optical properties |
Mid-Infrared (MIR) | No absorption bands noted in the visible range |
Low OH content in JGS-3 quartz tube enhances laser damage resistance and ensures stable quartz tube wavelength transmission for demanding IR applications.
What Wavelength Ranges Do UV Applications Require from Quartz Tubes?

UV applications depend on precise control of the wavelength range and transmission efficiency of quartz tubes. Engineers select quartz grades based on the specific ultraviolet wavelength range needed for germicidal, curing, or photolithography processes. The right choice ensures that systems transmit ultraviolet light efficiently, maximizing performance and reliability.
UV-C Germicidal Applications (200-280 nm) Transmission Requirements
UV-C germicidal systems require quartz tubes that transmit ultraviolet light in the 200-280 nm range. Low-pressure mercury vapor lamps emit strongly at 254 nm, which is the peak for disinfection and sterilization. Fused silica quartz tubes with high ultraviolet transmittance are essential for these applications because they allow more than 90% of the UV-C wavelength to pass through, ensuring effective microbial DNA disruption.
The purity of the quartz and the wall thickness both influence ultraviolet wavelength transmission. High-purity, synthetic fused silica (JGS-1) transmits UV below 200nm and maintains stable performance under intense UV-C exposure, which is critical for medical sterilization, water treatment, and air purification. Thicker walls can reduce transmission by up to 10%, so engineers must balance mechanical strength with optical efficiency.
Quartz tubes designed for UV-C must meet strict requirements for both transmission and durability.
Key Points:
High transmission (>90%) at 254 nm is vital for germicidal effectiveness.
JGS-1 synthetic fused silica is the preferred grade for UV-C applications.
Wall thickness and purity directly affect ultraviolet wavelength and intensity.
Applications include medical, water, and air disinfection.
UV-A Curing Systems (315-400 nm) Quartz Grade Selection
UV-A curing systems rely on quartz tubes that transmit ultraviolet light in the 315-400 nm range. These systems use UV-A LEDs or mercury lamps to cure adhesives, inks, and coatings, requiring consistent transmission across the ultraviolet wavelength range. High-purity quartz enhances curing efficiency by allowing more UV-A energy to reach the target material.
Synthetic quartz, produced from high-purity materials, offers superior ultraviolet transmittance and lower defect rates compared to natural quartz. JGS-2 optical-grade quartz tubes provide a cost-effective solution, delivering over 92% transmission in the UV-A band while maintaining excellent batch-to-batch consistency. Purity also reduces contamination risks, which is important for sensitive manufacturing environments.
Engineers select quartz tubes for UV-A curing based on both performance and cost.
Key Points:
JGS-2 optical-grade quartz is ideal for UV-A curing systems.
High-purity quartz improves ultraviolet wavelength transmission and reduces defects.
Consistent transmission ensures reliable curing results.
Lower cost compared to deep UV grades makes JGS-2 attractive for industrial use.
Deep UV Photolithography (<220 nm) Specialized Material Needs
Deep UV photolithography demands quartz tubes that transmit ultraviolet light at wavelengths below 220 nm. Semiconductor manufacturing uses excimer lasers at 193 nm and 248 nm, which require exceptional ultraviolet wavelength transmission and minimal fluorescence. Only high-purity synthetic fused silica, such as JGS-1, meets these strict requirements, providing over 90% transmission from 200 nm upward and very low fluorescence.
The shorter ultraviolet wavelength range used in photolithography places unique demands on material quality. JGS-1 quartz tubes offer a high laser damage threshold and excellent surface quality after precision polishing, which is essential for maintaining pattern accuracy and process stability. These properties support advanced applications like excimer laser optics, UV-grade windows, and scientific instrumentation for UV analysis.
The following table summarizes the specialized needs for deep UV photolithography:
Property | Details |
|---|---|
Wavelength Range | 185–2500 nm |
Core Advantage | Exceptional deep ultraviolet transmittance |
High Transmission | >90% from 200 nm upward |
Fluorescence | Very low |
Laser Damage Threshold | High for excimer laser wavelengths |
Surface Quality | Excellent after precision polishing |
Selecting the right quartz tube ensures reliable performance in advanced semiconductor and scientific applications.
What Wavelength Ranges Do Visible Light Applications Require from Quartz Tubes?
Quartz tubes play a vital role in applications that use visible light. Their ability to transmit light efficiently across the visible spectrum ensures accurate measurements and reliable performance in scientific and industrial systems. Engineers must consider purity, wall thickness, and grade to match quartz tube properties to specific needs.
Spectrophotometric Cuvettes and Flow Cells (400-800 nm) Requirements
Spectrophotometric cuvettes and flow cells require quartz tubes that deliver high and consistent transmission in the 400-800 nm range. High-purity quartz, with SiO₂ content of at least 99.98%, minimizes interference from impurities and supports precise measurements. Wall thickness also matters; thinner walls improve heat transfer and optical efficiency, while thicker walls provide greater mechanical strength but can reduce transmission.
Accurate spectrophotometric results depend on both the purity and the uniformity of the quartz material. Even small variations in wall thickness can affect the path length of light, which in turn impacts measurement accuracy. Engineers select quartz tubes with strict manufacturing tolerances to ensure consistent results.
Factor | Effect on Measurement |
|---|---|
High Purity | Reduces interference, improves accuracy |
Thin Wall | Enhances transmission, boosts efficiency |
Uniform Thickness | Ensures consistent path length |
Selecting the right quartz tube ensures reliable visible light spectrum transmission for laboratory analysis.
High-Intensity Lamp Envelopes Operating in Visible Spectrum
High-intensity lamp envelopes must maintain excellent visible light transmission while withstanding high temperatures. Quartz tubes used in these lamps provide over 93% transmission in the 400-700 nm range, which supports bright and stable illumination. The material’s thermal shock resistance and low expansion rate help prevent cracking during rapid temperature changes.
Engineers often choose JGS-2 or JGS-3 quartz grades for lamp envelopes because these grades combine high visible light transmission with strong mechanical properties. The choice of wall thickness balances the need for durability with the desire to maximize light output. Lamp performance and lifetime both depend on selecting the right combination of quartz grade and tube dimensions.
Key Points:
Over 93% visible light transmission supports bright illumination.
Thermal shock resistance prevents cracking in high-temperature environments.
Proper wall thickness extends lamp life and maintains efficiency.
Careful material selection ensures that high-intensity lamps deliver consistent performance throughout their service life.
Laser Beam Delivery and Optical Fiber Coupling Applications
Laser beam delivery and optical fiber coupling systems demand quartz tubes with high optical clarity and precise refractive index control. These applications rely on quartz tubes that maintain uniform transmission and minimal distortion across the visible spectrum. Even small variations in refractive index can cause beam steering or focal shifts, which affect system accuracy.
Manufacturers use precision annealing and strict quality control to achieve refractive index homogeneity within ±0.0005. For most visible light applications, JGS-2 or JGS-3 grades provide the required transmission and optical properties. Engineers often specify anti-reflection coatings to further boost transmission by 2-4%, especially in systems where every percent of throughput matters.
Requirement | Impact on Application |
|---|---|
High Optical Clarity | Reduces distortion, improves focus |
Index Homogeneity | Prevents beam steering |
Anti-Reflection Coating | Increases transmission efficiency |
Matching quartz tube properties to laser and fiber optic needs ensures optimal system performance and long-term reliability.
What Wavelength Ranges Do Infrared Applications Require from Quartz Tubes?
Infrared applications require quartz tubes that maintain high transmission across both near-infrared and mid-infrared wavelengths. Engineers must select materials that minimize absorption and maximize intensity for accurate measurements and efficient heating. The right quartz grade and purity ensure reliable performance in demanding environments.
Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (700-2,500 nm) Material Selection
Near-infrared spectroscopy depends on quartz tubes that transmit light efficiently from 700 to 2,500 nm. Material selection focuses on maximizing intensity and minimizing absorption, as impurities and hydroxyl groups can create unwanted absorption bands that block infrared light and reduce measurement accuracy. Water-insoluble quartz and sapphire windows both serve as options, but quartz remains the standard due to its balance of cost and performance.
The presence of impurities in quartz tubes can lower intensity by introducing absorption bands, which block infrared light and reduce heating efficiency. Hydroxyl (OH) groups also increase infrared absorption, making it important to choose quartz with low impurity and OH content for optimal results. Engineers often compare materials using transmission capability tables to guide their decisions.
Material Type | Transmission Capability | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Water-insoluble Quartz | Up to 3000 nm | Effective for near-infrared spectroscopy, but qualitative data is limited. |
Sapphire Windows | Thin enough for NIR | Can also be used, similar limitations in qualitative information. |
Selecting the right quartz tube ensures high intensity and accurate results in near-infrared spectroscopy.
Mid-Infrared FTIR and Thermal Imaging (2,500-4,000 nm) Requirements
Mid-infrared FTIR and thermal imaging systems require quartz tubes that transmit light in the 2,500 to 4,000 nm range. Engineers look for materials that maintain high intensity and avoid absorption peaks, as these can interfere with thermal measurements and reduce system efficiency. JGS-3 IR-grade quartz, with its low OH content, provides excellent transmission and supports accurate temperature readings.
The intensity of infrared light passing through the tube directly affects the sensitivity of FTIR and thermal imaging devices. High OH content in quartz increases absorption, which lowers intensity and can cause errors in temperature or chemical analysis. Data shows that reducing OH content below 30 ppm enhances thermal stability and minimizes energy absorption, making JGS-3 the preferred choice.
Key Points:
Low OH content (<30 ppm) maximizes intensity and accuracy.
JGS-3 IR-grade quartz supports reliable thermal imaging.
High transmission in the mid-infrared range improves measurement sensitivity.
Choosing the correct quartz tube grade ensures consistent intensity and dependable results in mid-infrared applications.
OH Content Specifications for Infrared Transmission Optimization
OH content plays a critical role in optimizing infrared transmission in quartz tubes. Lowering the OH content below 30 ppm enhances intensity by reducing absorption bands associated with silanol groups, which typically appear between 3,800 and 3,200 cm⁻¹. Heating quartz to around 1,000°C during manufacturing helps diffuse out these groups, resulting in clearer IR transmission and improved thermal stability.
High OH content not only decreases intensity but also increases the risk of devitrification, which can compromise the tube’s structural integrity during high-temperature use. For high-temperature and high-intensity infrared applications, engineers specify quartz tubes with strict OH content limits to ensure maximum performance. The following table summarizes the impact of OH content on infrared transmission:
OH Content (ppm) | Infrared Transmission | Thermal Stability |
|---|---|---|
<30 | High | Enhanced |
>30 | Reduced | Lower, risk of devitrification |
Maintaining low OH content in quartz tubes guarantees high intensity and stable operation in infrared systems.
How Should Engineers Match Quartz Tube Wavelength Ranges to Specific Applications?
Engineers must match the transmission rate of quartz tubes to the needs of each application. This process involves identifying the critical wavelength range, calculating system-level transmission budgets, and considering how operating conditions affect performance. Careful planning ensures that the transmission rate is high enough for reliable results in every system.
Critical Wavelength Range Identification for Application Requirements
Every application has a specific wavelength range that determines system performance. Engineers first identify the minimum and maximum wavelengths that the quartz tube must transmit, then add a margin to account for spectral bandwidth and manufacturing tolerances. This step ensures that the transmission rate of quartz tubes meets or exceeds the requirements at all relevant wavelengths.
Selecting the correct range prevents unexpected losses in signal or process efficiency. For example, a UV-C disinfection system requires over 90% transmission at 254 nm, while a near-infrared spectrometer needs high transmission from 700 to 2,500 nm. Engineers use transmission curves to verify that the chosen quartz tube grade supports the full range needed for the application.
Tip:
Always specify the exact wavelength range and minimum required transmission rate of quartz tubes in procurement documents to avoid performance issues.
System-Level Transmission Budgets and Component Specification
System-level transmission budgets help engineers ensure that the transmission rate of quartz tubes supports the entire optical path. They calculate the total loss by adding up the losses from each component, such as the transmitter, connectors, fiber optic cables, and the receiver. The following table summarizes the most critical parameters:
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Minimum Transmitter Power | The least amount of power the transmitter will output in a worst-case scenario. |
Maximum Connector Insertion Loss | The highest loss expected from connectors in the system. |
Fiber Optic Cable Transmission Loss | The loss of signal strength as it travels through the fiber optic cable. |
Maximum Receiver Sensitivity | The minimum light level required by the receiver to function without errors. |
A high transmission rate of quartz tubes reduces the total system loss, allowing more light to reach the detector or target. Engineers select tubes with the highest possible transmission rate to maximize system efficiency and maintain signal quality. This approach ensures that the system meets its performance targets even when other components introduce losses.
Operating Condition Effects on Transmission Performance
Operating conditions can change the transmission rate of quartz tubes over time. High temperatures, UV exposure, and surface contamination may lower the transmission rate, affecting system reliability. Engineers must consider these factors when specifying quartz tubes for demanding environments.
For instance, a quartz tube exposed to temperatures above 800°C may experience a 3-8% drop in transmission rate, while UV aging can reduce transmission by up to 20% over the tube’s lifetime. Regular cleaning and proper installation help maintain a high transmission rate of quartz tubes in the field. Engineers should always factor in these real-world effects to ensure long-term system performance.
Key Points:
High temperatures and UV exposure can reduce the transmission rate of quartz tubes.
Surface contamination also lowers transmission and should be minimized.
Regular maintenance helps preserve a high transmission rate and system reliability.
By understanding these factors, engineers can select and maintain quartz tubes that deliver consistent performance throughout their service life.
Quartz tubes deliver good transmission rates across ultraviolet, visible, and infrared wavelengths. JGS-1, JGS-2, and JGS-3 grades each offer unique transmittance profiles. High purity silicon dioxide ensures high light transmittance and a high proportion of light passes through, especially in demanding applications. Engineers should always match the quality of quartz glass to the specific wavelength and transmittance needs. Specifying exact transmittance requirements and reviewing transmission curves helps achieve optimal system performance.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of using a quartz glass tube for UV applications?
A quartz glass tube transmits over 90% of UV-C light at 254 nm. This high transmission rate ensures effective sterilization in water, air, and surface disinfection systems. Most plastic or standard glass tubes block these wavelengths.
What wavelength range does a quartz glass tube typically cover?
A quartz glass tube covers wavelengths from 170 nm in the deep ultraviolet to 4,000 nm in the mid-infrared. This broad range supports applications in UV sterilization, visible light analysis, and infrared heating.
What factors affect the transmission rate of a quartz glass tube?
The transmission rate of a quartz glass tube depends on grade, purity, wall thickness, and OH content. For example, JGS-1 grade transmits over 90% at 185 nm, while JGS-3 grade excels above 2,500 nm due to low OH content.
What grade of quartz glass tube should engineers select for infrared applications?
Engineers should select JGS-3 grade quartz glass tube for infrared applications. This grade maintains over 85% transmission from 2,500 nm to 4,000 nm. Low OH content ensures minimal absorption in the mid-infrared region.
What maintenance helps preserve the transmission of a quartz glass tube?
Regular cleaning removes surface contamination that can reduce transmission by up to 15%. Engineers should also monitor for UV aging and high-temperature exposure, which may lower transmission by 3-20% over time.





