Selecting the right quartz glass manufacturing method is a critical decision for engineers and buyers seeking reliable performance and cost efficiency.
Quartz glass manufacturing transforms high-purity silica into glass through melting, forming, annealing, and quality control. The choice of process—such as electric melting or flame fusion—directly impacts purity, cost, and suitability for advanced applications.
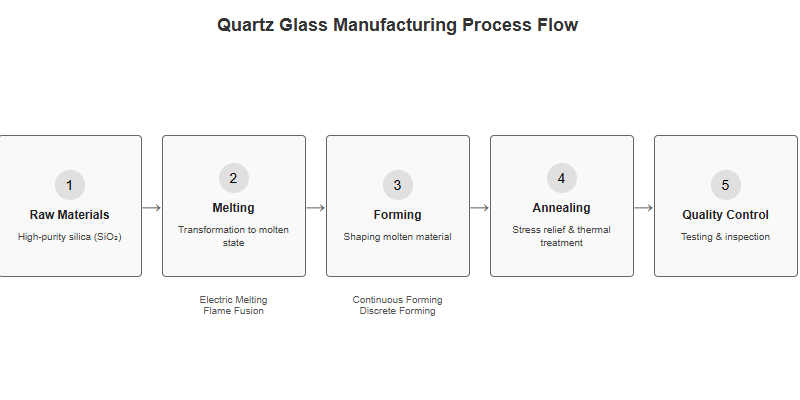
Understanding each step in the manufacturing process helps decision-makers align technical requirements with commercial objectives. The following guide breaks down every stage and provides a practical framework for method selection.
What Is Quartz Glass Manufacturing and Why Is It Critical for High-Tech Applications?
Quartz glass manufacturing is the process of converting high-purity silica into amorphous glass using controlled thermal and mechanical techniques. Its importance lies in enabling high-performance components for semiconductors, optics, photovoltaics, and laboratory equipment.
Quartz glass offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and optical clarity, making it indispensable for industries that demand precision and reliability.
Key Attributes of Quartz Glass for High-Tech Applications
| Attribute | Typical Value/Range | Application Context |
|---|---|---|
| SiO₂ Purity (%) | ≥99.995 | Semiconductor, optics |
| Working Temperature (°C) | 1,050–1,200 (continuous) | High-temp processing |
| UV Transmission (%) | >90 (at 200 nm, 1mm thick) | Lithography, UV optics |
| Thermal Expansion (1/K) | ~0.5 × 10⁻⁶ | Dimensional stability |
What Are the Key Raw Materials and Preparation Steps in Quartz Glass Manufacturing?
Raw material quality and preparation are foundational to quartz glass performance and yield.
High-purity silica is the primary input, but its source, form, and pre-processing directly affect the final product’s clarity and strength.
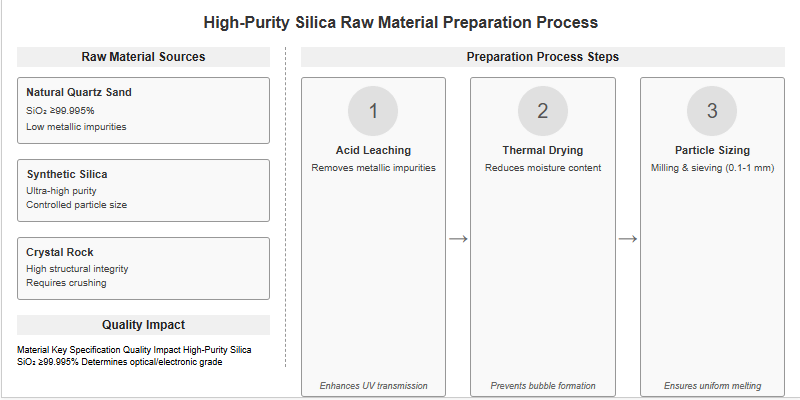
Essential Raw Materials for Quartz Glass Manufacturing
The core raw material is high-purity silica (SiO₂), typically sourced as natural quartz sand, synthetic silica, or crystal rock. Impurity levels—especially metallic contaminants—must be minimized to achieve optical and electronic grade glass.
Raw Material and Preparation Overview
| Material/Step | Purpose/Specification | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Silica | SiO₂ ≥99.995% | Determines optical/electronic grade |
| Acid Leaching | Removes metallic impurities | Enhances UV transmission |
| Thermal Drying | Reduces moisture content | Prevents bubble formation |
| Particle Sizing | 0.1–1 mm typical | Ensures uniform melting |
How Are Raw Materials Prepared for Quartz Glass Production?
Quartz glass production preparation involves washing, acid leaching, and thermal treatment1 to remove surface contaminants and moisture. Particle size is controlled through milling and sieving, ensuring uniform melting and reducing defect risk in the final product.
How Do Melting Methods in Quartz Glass Manufacturing Affect Purity and Cost?
The melting process is the heart of quartz glass manufacturing, dictating both material purity and production economics.
Different melting methods—electric melting and flame fusion—offer distinct trade-offs in terms of achievable purity, throughput, and operational cost.
How Does Electric Melting Influence Quartz Glass Purity and Cost?
Electric melting uses high-temperature resistance furnaces to liquefy silica. While efficient and cost-effective for large-scale production, this method may introduce trace metallic impurities from electrodes or furnace linings, slightly reducing optical clarity.
How Does Flame Fusion Impact Purity and Production Expenses?
Flame fusion (oxy-hydrogen or plasma torch2) achieves higher purity by melting silica in a contaminant-free flame. This method produces ultra-pure glass suitable for semiconductor and optical applications but comes with higher energy consumption and operational costs.
What Are the Comparative Advantages of Electric Melting and Flame Fusion?
Electric melting is preferred for bulk, industrial-grade quartz glass where cost efficiency is paramount. Flame fusion is chosen for applications demanding the highest purity, such as photomask blanks or UV optics, despite its premium price.
Melting Method Comparison
| Method | Purity (SiO₂, %) | Typical Cost Index | Main Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Melting | 99.95–99.995 | 1.0 (baseline) | Tubes, rods, general optics |
| Flame Fusion | ≥99.999 | 1.5–2.0 | Semiconductor, high-end optics |
How Are Forming and Shaping Processes Executed in Quartz Glass Manufacturing?
Forming and shaping determine the geometry, dimensional accuracy, and surface quality of quartz glass products.
Both continuous and discrete forming methods are used, followed by precision shaping to meet strict tolerances.

How Is Continuous Forming Applied in Quartz Glass Production?
Continuous forming extrudes molten quartz through dies to produce tubes, rods, or plates of consistent cross-section. This method is ideal for high-volume, standardized products.
How Is Discrete Forming Implemented in Manufacturing?
Discrete forming involves casting or pressing molten quartz into molds for custom shapes or large components. It is suitable for specialty items or low-volume production.
What Shaping Techniques Ensure Dimensional Precision in Quartz Glass?
Precision shaping includes grinding, lapping, and CNC machining. These techniques achieve tight tolerances and surface finishes required for optical and semiconductor applications.
Forming and Shaping Methods Overview
| Method/Technique | Typical Tolerance (mm) | Product Types | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Forming | ±0.2–0.5 | Tubes, rods, plates | High throughput |
| Discrete Forming | ±0.5–1.0 | Custom shapes, crucibles | Flexible, lower volume |
| CNC Machining | ±0.01–0.05 | Lenses, wafers, optics | High precision, post-forming |
Why Is Annealing and Stress Relief Essential in Quartz Glass Manufacturing?
Annealing and stress relief are critical to prevent cracking, warping, and internal defects in quartz glass products.
Controlled cooling relieves thermal stresses accumulated during melting and forming, ensuring long-term durability and dimensional stability.
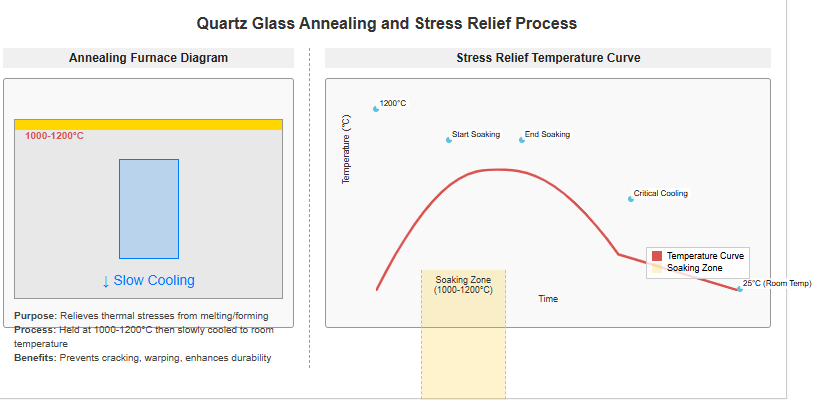
During annealing, products are held at specific temperatures (typically 1,000–1,200°C) and cooled slowly to room temperature. This process eliminates residual stresses and enhances mechanical strength.
How Is Quality Control and Testing Performed in Quartz Glass Manufacturing?
Quality control ensures that quartz glass meets stringent specifications for purity, geometry, and performance.
Testing includes visual inspection, dimensional measurement, spectrophotometry, and stress analysis.
Key standards include ISO 9001 for quality management, ASTM E438 for chemical composition, and ISO 10110 for optical components.
Quality Control and Testing Overview
| Test/Standard | Purpose/Parameter | Typical Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Surface defects, bubbles | No visible inclusions |
| Spectrophotometry | UV/visible transmission | >90% at 200 nm (1mm thick) |
| Dimensional Check | Tolerance, flatness | As per drawing/spec |
| Stress Analysis | Residual stress | <5 MPa |
How Should Engineers and Buyers Select the Right Quartz Glass Manufacturing Method?
Choosing the optimal manufacturing method requires balancing technical requirements, cost, and supplier capabilities.
A structured decision framework helps engineers and buyers minimize risk and maximize value.
What Decision Criteria Should Engineers Use for Method Selection?
Engineers should evaluate end-use requirements (purity, geometry, optical clarity), production volume, and tolerance needs. For example, semiconductor applications may demand flame fusion for ultra-high purity, while general labware may use electric melting.
How Can Buyers Balance Cost and Performance in Procurement?
Buyers should compare total cost of ownership, including initial price, yield rates, and long-term reliability. Higher upfront costs for premium methods may be justified by reduced failure rates and superior performance.
What Supplier Evaluation Steps Minimize Project Risk?
Supplier evaluation should include certification checks (ISO, ASTM), audit of production facilities, sample testing, and review of past project performance. Establishing clear quality agreements and communication channels further reduces risk.
Quartz Glass Manufacturing Method Selection Checklist
| Decision Factor | Key Questions to Ask | Action Point |
|---|---|---|
| Purity Requirements | What is the minimum acceptable purity? | Match method to application |
| Volume & Geometry | Is the product standard or custom? | Choose continuous or discrete |
| Cost Constraints | What is the total lifecycle cost? | Balance upfront and long-term cost |
| Supplier Capability | Are certifications and track record proven? | Conduct audits and sample tests |
Conclusion
Quartz glass manufacturing success depends on aligning process selection with technical and commercial goals.
Making the right choice in quartz glass manufacturing is a strategic challenge. Leverage TOQUARTZ’s direct factory supply, engineering support, and rapid delivery to ensure your project’s technical and commercial success—contact us for a custom solution today.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the difference between electric melting and flame fusion in quartz glass manufacturing?
Electric melting is cost-effective for bulk production but may introduce trace impurities, while flame fusion achieves higher purity at a higher cost, ideal for semiconductor and optical applications.
How can I ensure the quartz glass I purchase meets my technical requirements?
Request detailed material certificates, review supplier quality standards (ISO, ASTM), and, if possible, test samples for purity, transmission, and dimensional accuracy.
What are the most important factors when selecting a quartz glass supplier?
Key factors include technical capability, certification, production track record, responsiveness, and ability to provide custom solutions.
How does annealing improve the quality of quartz glass products?
Annealing relieves internal stresses, prevents cracking, and ensures long-term dimensional stability and mechanical strength.
References:





