Quartz tubes deliver a broad optical transmission range, reaching from 190 nm to 2500 nm for UV-grade and extending up to 3500 nm for IR-grade material. This wide range supports UV, visible, and infrared spectroscopy, making quartz essential for precise measurements. Material purity, OH content, and adherence to certification standards all influence how quartz tubes optical applications perform across these wavelengths.
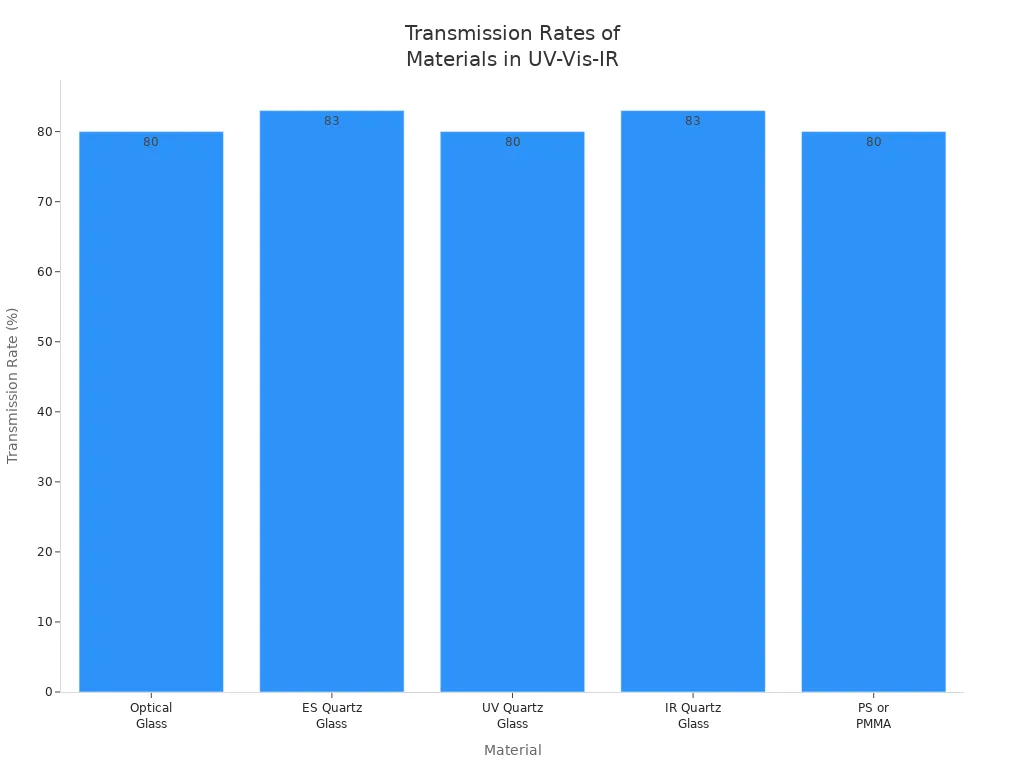
Material | Wavelength | Transmission Rate | Usage | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Optical Glass | 340-2,500nm | 80% at 350nm | Reusable | Visible |
ES Quartz Glass | 190-2,500nm | 83% at 220nm | Reusable | UV-visible |
UV Quartz Glass | 190-2,500nm | 80% at 220nm | Reusable | UV-visible |
IR Quartz Glass | 220-3,500nm | 83% at 2730nm | Reusable | UV-visible-IR |
PS or PMMA | 380-780nm | 80% at 400nm | Disposable | Visible (Optional UV) |
Key Takeaways
Quartz tubes provide a wide optical transmission range from 190 nm to 3500 nm, making them essential for UV, visible, and infrared spectroscopy.
High-purity quartz is crucial for deep UV applications, ensuring minimal absorption and high transmission efficiency above 80%.
Selecting the right quartz tube grade—UV or IR—depends on the specific wavelength needs of your application for optimal performance.
Controlling metallic impurities in quartz tubes is vital; even trace amounts can significantly affect transmission and measurement accuracy.
Always verify certification standards like ASTM E903 and ISO 10110-4 to ensure the quartz tubes meet the necessary quality for reliable optical measurements.
What Factors Define High-Performance Transmission for Optical Quartz Tubes?

High-performance optical quartz tubes must deliver consistent light transmission across a broad spectrum. The transmission range for these tubes typically spans from the deep UV to the near-infrared, supporting a wide variety of spectroscopy applications. Material purity, manufacturing standards, and impurity control all play critical roles in defining the optical performance of these tubes.
Deep UV Transmission Requirements (190-280nm)
Deep UV applications demand quartz tubes with exceptional clarity and minimal absorption. High-purity quartz achieves a transmission range starting at 190 nm, making it ideal for UV spectrophotometry and analytical chemistry. The ability to maintain high transmission in this region depends on both the absence of metallic impurities and strict adherence to industry standards.
Key factors for deep UV transmission:
High-purity quartz ensures minimal absorption below 250 nm
Transmission efficiency above 80% is required for UV-grade tubes
ASTM E903 and ISO standards set benchmarks for performance
For UV-C wavelengths (200–280 nm), filtering efficiency can exceed 99% in specialized uv-filtering quartz tubes, especially those with titanium doping. Laboratories rely on these tubes for applications such as protein quantification and nucleic acid analysis, where even trace iron can cause significant signal loss. Consistent performance in the deep UV region supports reliable, repeatable results in demanding scientific environments.
Visible-NIR Window Performance (400-2500nm)
Quartz tubes must also perform well across the visible and near-infrared spectrum. The transmission range for optical quartz tubes typically extends from 250 nm to 2500 nm, with some IR-grade materials reaching up to 3500 nm. The choice of tube grade directly impacts the transmission curve, especially in the NIR region.
Grade | UV Spectrum Transmission | NIR Spectrum Transmission | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
UV-grade | High, dips at 1.4µm, 2.2µm, 2.7µm | Lower | High OH- ion impurities, suitable for UV applications |
IR-grade | Lower | Higher | Reduced OH- ions, preferred for applications around 2µm |
UV-grade quartz tubes provide high transmission in the visible range but show dips in the NIR due to OH- absorption bands. IR-grade tubes, with reduced OH- content, offer superior performance for applications requiring extended NIR coverage, such as moisture analysis and pharmaceutical quality control. Selecting the right tube grade ensures optimal transmission range and measurement accuracy for each application.
Metallic Impurity Impact on Spectral Clarity
Metallic impurities can dramatically affect the spectral clarity of quartz tubes. Even trace amounts of iron or aluminum reduce transmission in the UV and visible regions, making high-purity quartz essential for sensitive optical measurements. The industry sets strict impurity limits to maintain high transmission range and prevent unwanted absorption peaks.
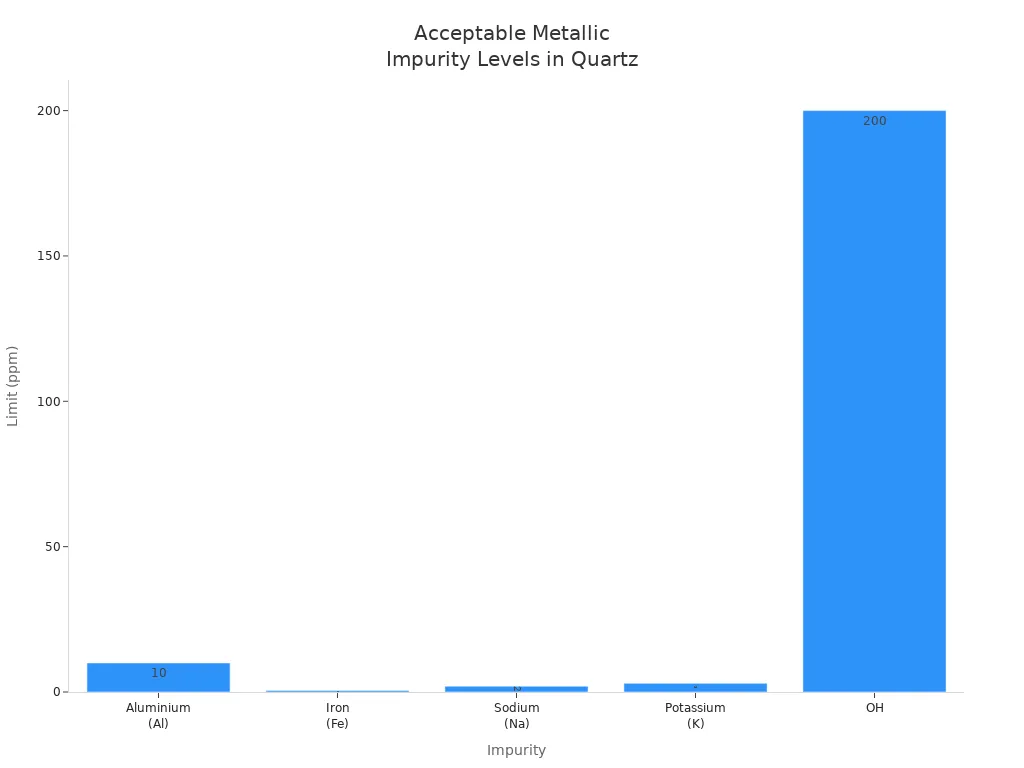
Impurity | Typical Limit (ppm) | Main Effect | Critical Application Concern |
|---|---|---|---|
Aluminium | <10 | Lowers devitrification temperature | Furnace tubes, high-temperature optics |
Iron | <0.5 | Increases UV absorption | UV optics, photolithography |
Sodium | <2 | Reduces electrical resistance | Semiconductor, high voltage |
Potassium | <3 | Similar to Na | Same as above |
OH | <1-200 | Affects IR absorption, stability | IR optics, high-temperature processing |
Summary of impurity impact:
Aluminum and alkali metals must remain low for stability
Ultrapure chemicals are required for high-performance uv-filtering quartz tubes
By controlling metallic impurities, manufacturers ensure that quartz tubes maintain a stable transmission range and deliver precise results in both research and industrial settings.
How Does OH Content Determine Infrared vs Ultraviolet Performance in Quartz Tubes?
Hydroxyl (OH) content plays a critical role in the optical properties of quartz tubes. The amount of OH present directly influences how well these tubes transmit uv and infrared light. Understanding this relationship helps laboratories select the right material for their specific spectroscopy needs.
Hydroxyl Group Formation During Manufacturing
Manufacturers introduce hydroxyl groups into quartz during production. The formation of these groups depends on the melting process and the raw materials used. For example, electric melting often results in lower OH content, while gas refining with oxyhydrogen flames increases OH levels.
Hydroxyl groups can disrupt the Si-O bond network in quartz, leading to increased porosity and reduced stability. In electric melting, most hydroxyl groups come from fluid inclusions in high-purity quartz sand. Gas refining forms hydroxyl groups through reactions with hydrogen and oxygen, while plasma melting produces quartz with very low OH content, making it ideal for high-purity applications.
Key points about hydroxyl group formation:
Electric melting yields low OH content
Gas refining increases OH content
Plasma melting produces high-purity quartz
These differences in manufacturing impact the suitability of quartz tubes for uv or infrared applications.
Spectral Absorption Bands from OH Vibrations
Hydroxyl groups create distinct absorption bands in the infrared region. These bands occur at specific wavelengths and can significantly reduce transmission efficiency for certain applications. The most prominent absorption peak appears around 2730 nm, which is a signature of hydroxyl presence.
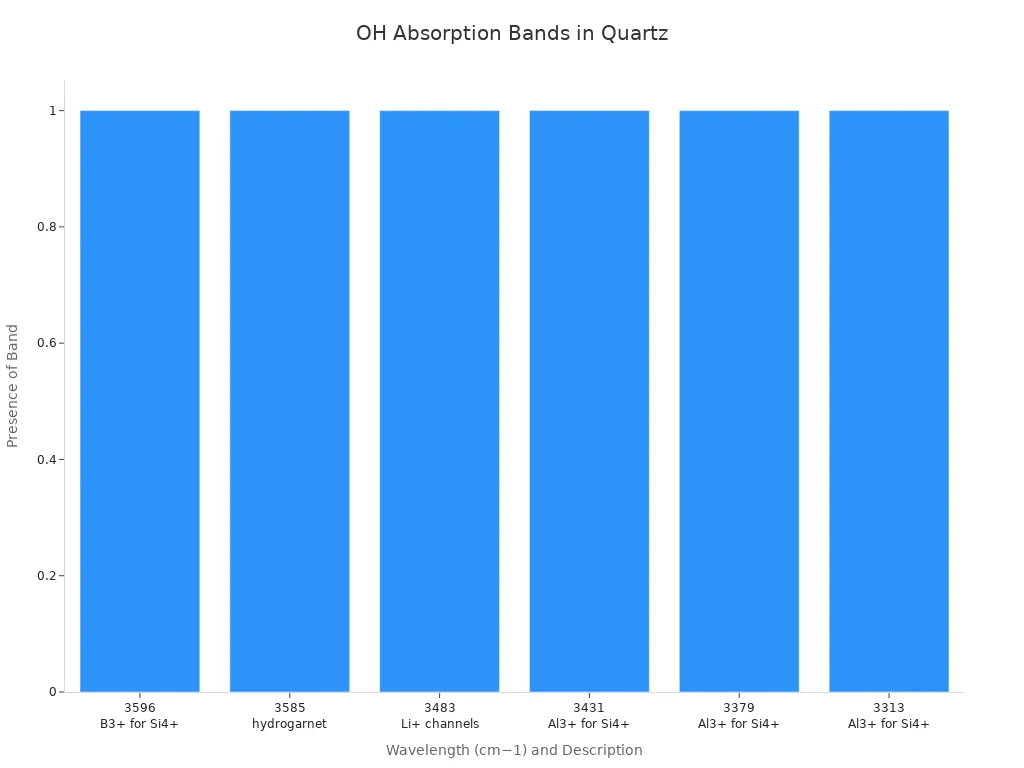
Wavelength (cm−1) | Description |
|---|---|
3596 | OH with B3+ for Si4+ substitution |
3585 | Hydrogarnet-type defects |
3483 | OH with Li+ ions in channels |
3431 | OH with Al3+ for Si4+ substitution |
3379 | OH with Al3+ for Si4+ substitution |
3313 | OH with Al3+ for Si4+ substitution |
These absorption bands limit the use of high-OH quartz tubes in infrared spectroscopy. In the uv region, hydroxyl groups influence the cutoff wavelength, shifting it depending on their concentration. Laboratories must consider these spectral features when choosing quartz tubes for multi-wavelength systems.
Application-Specific Grade Selection Criteria
Selecting the right quartz tube grade depends on the required transmission range. UV-grade tubes contain higher OH content, which supports deep uv transmission but limits performance in the infrared. IR-grade tubes have low OH content, enabling superior infrared transmission but raising the uv cutoff.
Grade Type | OH Content Level | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
UV-grade | >150 ppm | Deep uv spectroscopy |
IR-grade | <10 ppm | Extended infrared applications |
Summary for grade selection:
UV-grade suits applications below 250 nm
IR-grade excels above 2000 nm
Match grade to your wavelength needs for best results
Careful selection ensures optimal performance in both uv and infrared regions, supporting accurate and reliable spectroscopy measurements.
What Refractive Index Homogeneity Standards Ensure Precision Optical Measurements?
Precision optical measurements depend on the uniformity of the refractive index in quartz tubes. Even small variations can cause distortion or measurement errors in UV-Vis-IR spectroscopy. Laboratories rely on strict standards and advanced testing methods to ensure consistent optical performance.
ISO 10110-4 Homogeneity Classification System
ISO 10110-4 sets the global benchmark for refractive index homogeneity in optical quartz tubes. This standard classifies material based on the presence and severity of striae, which are streaks or variations in the glass that affect light transmission. Manufacturers use these classes to guarantee that their quartz tubes meet the needs of high-precision optical systems.
The classification system uses optical path difference to define each class. Lower class numbers indicate fewer striae and better homogeneity, which is essential for applications like laser optics and spectrophotometry. The table below summarizes the ISO 10110-4 classes and their impact:
Class | Description of Striae | Optical Path Difference (nm) |
|---|---|---|
1 | Minor striae | < 0.5 |
2 | Moderate striae | 0.5 - 1.0 |
3 | Noticeable striae | 1.0 - 2.0 |
4 | Severe striae | 2.0 - 5.0 |
5 | Extreme striae | > 5.0 |
Quartz tubes with Class 1 or 2 homogeneity ensure minimal distortion and high measurement accuracy. Laboratories should always check for ISO 10110-4 certification when selecting tubes for sensitive optical applications.
Annealing Processes for Stress Reduction
Annealing removes internal stress from quartz tubes, which helps maintain refractive index homogeneity. High internal stress can cause optical distortion and reduce the lifespan of the tube. Manufacturers follow precise temperature schedules to achieve optimal results.
The annealing process involves several stages:
Heating Stage: Slowly heat the tube to 1100°C at a controlled rate.
Constant Temperature Stage: Hold at the highest temperature for uniform heating.
Cooling Stage: Gradually lower the temperature to minimize stress.
Natural Cooling Stage: Allow the tube to cool naturally below 450°C.
Key points for effective annealing:
Proper annealing eliminates up to 95% of internal stress
Controlled cooling prevents new stress from forming
Consistent process ensures reliable optical performance
Careful annealing ensures that quartz tubes maintain their optical clarity and meet the strictest homogeneity standards.
Interferometric Measurement Techniques
Interferometric techniques allow precise measurement of refractive index homogeneity in quartz tubes. These methods detect even the smallest variations that could affect optical performance. Laboratories use several advanced tools to verify quality.
Multiple-beam Fizeau fringes provide high-resolution mapping of refractive index variations.
Two-beam interference Pluta microscopes help visualize striae and inhomogeneities.
Manual and automatic variable wavelength systems offer flexibility and accuracy for different tube sizes.
Summary of interferometric methods:
Detects minute refractive index changes
Ensures compliance with ISO 10110-4
Supports high-precision spectroscopy and imaging
By using these techniques, manufacturers and laboratories can guarantee that their quartz tubes deliver the uniformity required for demanding optical applications.
What Quality Standards Validate Optical-Grade Quartz Tube Performance?
Laboratories depend on strict quality standards to ensure reliable optical measurements across the UV, visible, and IR spectrum. These standards help users select the right quartz tubes for their application wavelength needs. Certification, stability testing, and manufacturer qualifications all play a role in guaranteeing consistent transmission and performance.
Multi-Parameter Certification Requirements
Labs require quartz tubes to meet several certification parameters before use in spectroscopy. Each parameter directly affects transmission accuracy and long-term reliability. The following table summarizes the most important certification requirements and their impact:
Parameter | Typical Value | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
Path length tolerance | ±0.01–0.05 mm | Direct impact on absorbance accuracy |
Window parallelism | ≤5 arc minutes | Reduces baseline noise |
Optical polish | λ/4 or better | Prevents scatter |
Temperature limit | 150–1200 °C (molded) | Adhesives or seals set the limit |
Chemical resistance | Excellent, except HF and hot alkalis | Ensures long life |
Seal materials | PTFE, silicone, epoxy | Affects solvent compatibility |
These parameters ensure that each quartz tube delivers consistent transmission across the UV, visible, and IR range. Laboratories should always verify that tubes meet these values to avoid measurement errors and maximize performance.
Long-Term UV Stability Testing Protocols
Long-term UV stability testing ensures that quartz tubes maintain high transmission after extended exposure to intense UV and IR light. Labs simulate years of use by exposing tubes to high-intensity sources and monitoring for transmission loss or solarization. This process helps identify materials that resist degradation and maintain clarity in both the UV and infrared range.
Key takeaways from stability testing:
Consistent transmission after 1000+ hours of UV exposure
Minimal solarization or devitrification
Reliable performance for multi-year laboratory use
These protocols help labs compare UV-filtering quartz tubes to standard quartz. UV-filtering tubes often show superior resistance to solarization, making them ideal for demanding spectroscopy applications. Reliable stability data supports confident selection for critical measurements.
Manufacturer Qualification Frameworks
Manufacturer qualification frameworks validate the ability to produce quartz tubes with precise transmission and IR performance. Labs assess suppliers based on certification records, production consistency, and independent testing results. Qualified manufacturers demonstrate high purity, low defect rates, and adherence to international standards.
Summary of manufacturer qualification essentials:
Documented multi-parameter certification
Proven long-term stability in the infrared range
Consistent transmission across all batches
Transparent quality control and traceability
Selecting a qualified manufacturer ensures that each quartz tube meets the required standards for UV, visible, and IR applications. This decision framework helps laboratories achieve accurate, repeatable results in spectroscopy and analytical testing.
How Should Laboratories Select Quartz Tubes for Multi-Wavelength Optical Systems?
Selecting the right quartz tube for multi-wavelength optical systems requires careful planning. Laboratories must match the optical properties of the tube to the specific measurement needs. Understanding both the wavelength range and transmittance requirements ensures accurate and reliable results.
Wavelength Range Mapping for Application Requirements
Laboratories begin by mapping the wavelength range needed for each spectroscopy application. Each optical measurement, such as DNA quantification or enzyme kinetics, demands a specific tube design to maximize transmittance and minimize sample loss. The choice of tube directly affects the quality of data collected across the optical spectrum.
The table below summarizes common laboratory applications, recommended quartz tube types, and the reasons for each selection. This data-driven approach helps laboratories align their optical system with the required wavelength and transmittance performance.
Application | Recommended Cuvette | Reason |
|---|---|---|
DNA measurement at 260 nm | Micro-volume quartz cuvette | Saves rare samples |
Protein absorbance at 280 nm | Semi-micro quartz cuvette | Uses less sample, keeps 10 mm path |
Enzyme kinetics | Flow-through quartz cell | Real-time data, no refilling |
Trace pollutant in water | Long-path quartz cuvette | Higher sensitivity |
Fluorescence spectroscopy | 4-window quartz cuvette with cap | Reduces background, prevents evaporation |
Teaching labs | Standard 10 mm quartz cuvette | Robust and universal |
Key takeaways for wavelength mapping:
Match tube type to optical measurement needs
Consider sample volume and sensitivity
Select for optimal transmittance at target wavelength
Grade Selection Decision Framework
Choosing between UV-grade and IR-grade quartz depends on the required optical performance. UV-grade quartz is essential for experiments below 250 nm, while IR-grade quartz covers a broader wavelength range, supporting both UV and IR measurements. Laboratories must evaluate the transmittance profile of each grade to ensure compatibility with their optical system.
The table below highlights the differences between UV and IR quartz, showing how each material supports specific wavelength and transmittance needs:
Material | Transmission Range | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
UV Quartz | 190 - 2,500 nm | Essential for UV experiments |
IR Quartz | 220 - 3,500 nm | Good for UV VIS measurements |
Summary of grade selection:
UV Quartz ensures high transmittance for UV optical applications
IR Quartz provides extended wavelength coverage for multi-wavelength systems
Select grade based on the primary wavelength and transmittance requirements
By following this decision framework, laboratories can confidently select the optimal quartz tube for their multi-wavelength optical systems, ensuring precise and reproducible results.
Quartz tubes optical applications deliver unmatched performance for uv vis measurements across the uv, visible, and IR spectrum. Laboratories choose cuvettes for uv vis because quartz remains transparent down to 190 nm, unlike optical glass cuvette or plastic. The uv quartz cuvette supports precise vis and uv control, while IR-grade cuvettes for uv vis extend the cut-off wavelength for broader applications. Selecting the right cuvette grade ensures optimal filtering efficiency and uv shielding. Certified cuvettes for uv vis maintain purity, homogeneity, and long-term stability, making them ideal for vis, uv, and visible light range studies. Laboratories rely on quartz tubes optical applications for consistent vis and uv vis measurements, accurate cut-off wavelength, and reliable filtering efficiency in optical devices.
Quartz cuvettes excel in uv transmission and vis clarity.
Chemically inert quartz supports thin-film and coating analysis.
High damage threshold and low autofluorescence benefit vis and uv vis measurements.
Uniform optical quality ensures accurate vis and uv vis results.
Long-term optical integrity reduces background noise in cuvettes for uv vis.
Laboratories should always consult transmission data and certification standards when selecting cuvettes for uv vis and other quartz tubes optical applications.
FAQ
What is the typical optical transmission range for UV-grade quartz tubes?
UV-grade quartz tubes transmit light from 190 nm to 2500 nm. This range covers deep ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions. Laboratories use these tubes for applications that require high transmission and minimal absorption in the UV spectrum.
Key facts:
Transmission range: 190–2500 nm
High UV clarity
Used in spectroscopy
What impurities most affect quartz tube transmission?
Iron and titanium impurities cause significant absorption below 250 nm. Even 0.5 ppm iron can reduce UV transmission by up to 15%. High-purity quartz eliminates these impurities, ensuring stable and accurate optical measurements.
Impurity | Effect | Critical Level |
|---|---|---|
Iron | UV absorption | <0.5 ppm |
Titanium | UV absorption | <10 ppm |
What standards certify quartz tubes for optical use?
ASTM E903 and ISO 10110-4 set the main standards. These standards define transmission efficiency, refractive index homogeneity, and bubble content. Certified tubes meet strict requirements for laboratory and industrial optical systems.
Main standards:
ASTM E903: Transmission
ISO 10110-4: Homogeneity
ISO 10110-3: Bubble content
What determines the choice between UV-grade and IR-grade quartz tubes?
OH content determines grade selection. UV-grade tubes have >150 ppm OH for deep UV work. IR-grade tubes have <10 ppm OH for extended infrared use. Laboratories select the grade based on their required wavelength range.
Grade | OH Content | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
UV-grade | >150 ppm | Below 250 nm |
IR-grade | <10 ppm | Above 2000 nm |
What makes quartz tubes better than glass or plastic for spectroscopy?
Quartz tubes transmit light down to 190 nm, while glass and plastic block UV below 340 nm. Quartz also resists chemicals and maintains clarity after long-term UV exposure. This makes quartz the preferred choice for accurate and repeatable spectroscopy.
Advantages:
Wider transmission range
Chemical resistance
Long-term stability





