Large quartz tubes photovoltaic efficiency drives higher output and lower energy use in the solar energy industry. Quartz tubing for photovoltaic manufacturing lets factories boost throughput and cut costs by using high-quality quartz tubing with precise diameter and advanced quartz tubes. Manufacturers select quartz tubing manufacturing with high-purity quartz material to achieve consistent quality and stable performance. The solar energy industry relies on quartz tubing for photovoltaic production because it improves product quality, as shown below:
Benefit | Impact on Product Quality |
|---|---|
Efficiency | Improves the efficiency of solar powered devices |
Stability | Enhances the stability of the production process |
Chemical Purity | Ensures high purity levels in semiconductor materials |
Transmissivity | Increases light absorption and conversion efficiency |
Heat Resistance | Withstands high temperatures during fabrication |
Key Takeaways
Large quartz tubes increase production efficiency by allowing factories to process more polysilicon per cycle, boosting output by up to 67%.
Using larger tubes reduces energy consumption by 23%, leading to significant cost savings for solar manufacturers.
Maintaining thermal uniformity in large tubes enhances product quality, resulting in fewer defects and higher yields.
Selecting the right tube diameter aligns production batch sizes with equipment, improving overall efficiency and reducing waste.
High-purity quartz tubes prevent contamination, ensuring reliable performance and consistent solar cell efficiency.
How Does Increasing Tube Diameter From 300mm to 400mm+ Improve Polysilicon Production Throughput?

Increasing the diameter of quartz tubes for semiconductor production plays a vital role in boosting solar manufacturing efficiency. Larger tubes allow factories to process more polysilicon silicon in each cycle, which leads to higher throughput and lower energy costs. This section explains how tube diameter affects seed rod capacity, energy consumption, and thermal efficiency in solar production.
Seed Rod Capacity Scaling with Tube Cross-Sectional Area
Factories use quartz tubes for semiconductor manufacturing to grow polysilicon silicon rods for solar cells. When the tube diameter increases from 300mm to 400mm, the cross-sectional area grows, allowing more seed rods to fit inside each tube. This change directly increases the number of rods from 18-24 to 30-40 per cycle, which boosts solar output.
The larger cross-sectional area means that solar manufacturers can produce up to 100kg of polysilicon silicon per cycle, compared to only 60kg in smaller tubes. This 67% increase in throughput helps meet the rising demand for solar panels. The optimal spacing between rods also improves efficiency by ensuring uniform gas flow and heat distribution.
Key Points:
Larger quartz tubes for semiconductor use increase seed rod capacity.
Throughput rises by 67% with 400mm tubes.
Uniform spacing supports higher solar efficiency.
Specific Energy Consumption Reduction Through Geometry Optimization
Solar factories benefit from geometry optimization when using larger quartz tubes for semiconductor production. The tube wall surface area grows linearly, but the interior volume grows with the square of the diameter. This relationship allows heat to reach all seed rods more efficiently, reducing the energy needed to produce polysilicon silicon.
Data shows that 400mm tubes operate at 85 kWh per kilogram of polysilicon silicon, while 300mm tubes require 110 kWh per kilogram. This 23% energy savings translates into significant cost reductions for solar manufacturers. Lower energy consumption also supports sustainability goals in the solar industry.
Tube Diameter | Batch Size (kg) | Energy Consumption (kWh/kg) | Throughput Gain (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
300mm | 60 | 110 | Baseline |
400mm | 100 | 85 | +67% |
Thermal Efficiency Limits at Extreme Diameters Above 450mm
Solar manufacturers sometimes consider even larger quartz tubes for semiconductor production to further increase polysilicon silicon output. However, tubes above 450mm diameter face thermal efficiency limits. The wall thickness must increase to maintain strength, which adds thermal mass and slows heating and cooling cycles.
This extra mass reduces the efficiency gains seen with moderate increases in diameter. Factories may experience longer cycle times and higher energy use, which can offset the benefits of larger batch sizes. Manufacturers must balance tube size with overall solar production efficiency to achieve the best results.
Summary:
Tubes above 450mm require thicker walls, increasing thermal mass.
Efficiency gains decrease due to slower heating and cooling.
Optimal tube diameter maximizes solar throughput and energy savings.
How Do Large-Diameter Quartz Tubes Enhance Multiple Polysilicon Production Methods?

Large-diameter quartz tubes play a critical role in improving the efficiency of various polysilicon manufacturing processes. These tubes support larger batch sizes, better thermal management, and more consistent product quality. Manufacturers see significant gains in throughput and cost savings when they optimize tube diameter for each production method.
Batch Size Economics Across Siemens, FBR, and UMG Methods
Manufacturers use large quartz tubes to increase batch sizes in Siemens, fluidized bed reactor (FBR), and upgraded metallurgical grade (UMG) silicon processes. When the tube diameter grows from 300mm to 400mm, Siemens reactors can process up to 100kg of polysilicon per cycle, compared to only 60kg in smaller tubes. This change leads to a 67% increase in throughput and a 23% reduction in energy consumption.
Larger tubes also benefit FBR and UMG methods. FBR reactors with 400-450mm tubes achieve 45% better gas-solid contact efficiency, while UMG refining systems process up to 120kg batches, doubling the output compared to smaller setups. These improvements help manufacturers lower specific energy consumption and reduce operational costs.
Method | Tube Diameter | Batch Size (kg) | Throughput Gain (%) | Energy Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Siemens | 400mm | 100 | +67% | 23% |
FBR | 400-450mm | 80-120 | +45% | 29% |
UMG | 350-400mm | 80-120 | +100% | 29% |
Manufacturers who adopt large-diameter tubes in their manufacturing processes see higher output and lower energy costs. These economic advantages drive the adoption of larger tubes across the solar industry.
Fluidization Efficiency Improvements in Large-Diameter FBR Tubes
Fluidized bed reactors rely on efficient gas-solid contact to produce high-purity polysilicon. Large-diameter quartz tubes, especially those between 400mm and 450mm, create optimal fluidization velocity, which improves the mixing of gases and silicon particles. This design allows reactors to operate at 0.8-1.2 meters per second, supporting production-scale gas flow rates.
Improved fluidization leads to better precursor utilization and higher silicon yield. Manufacturers report that larger tubes reduce incomplete decomposition of trichlorosilane, which lowers waste and energy use. These changes result in more consistent product quality and higher overall efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Key Points:
Large tubes improve gas-solid contact in FBR reactors.
Optimal fluidization velocity boosts silicon yield.
Reduced waste and energy use enhance process efficiency.
Manufacturers who upgrade to large-diameter tubes in their FBR systems experience smoother operations and greater output, supporting the growth of solar manufacturing.
Thermal Uniformity Impact on Precursor Utilization Efficiency
Thermal uniformity inside quartz tubes affects how efficiently precursors convert to polysilicon. Large-diameter tubes maintain temperature differences within ±8°C across the heated zone, compared to ±15°C in smaller tubes. This stability ensures that more of the precursor material transforms into usable silicon, increasing yield and reducing waste.
Manufacturers see a 15-22% reduction in silicon consumption per kilogram of product when they use large tubes. This improvement lowers costs and supports sustainable manufacturing processes. Consistent thermal conditions also prevent defects, which helps maintain high product quality.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
High-Temperature Resistance | Withstands up to 1250°C without deformation or cracking. |
Corrosion Resistance | Resists acids, alkalis, and other corrosive substances. |
High Light Transmittance | Transmits light from ultraviolet to infrared efficiently. |
Low Thermal Expansion Coefficient | Maintains dimensional stability during temperature changes. |
Manufacturers who focus on thermal uniformity in their manufacturing processes achieve better precursor utilization, higher yield, and improved product reliability.
How Do Large Czochralski Puller Tubes Accelerate Monocrystalline Silicon Production Rates?
Large Czochralski puller tubes play a vital role in increasing the production rates of monocrystalline silicon. These tubes allow manufacturers to optimize melt volume, maintain thermal stability, and improve equipment utilization. By selecting the right tube diameter and material specifications, factories can achieve higher output and better product quality.
Melt Volume Thermal Stability Correlation with Pulling Rate
Monocrystalline silicon production depends on stable melt volume during the crystal pulling process. Large puller tubes, with diameters between 400mm and 500mm, enable crucibles to hold 80-120kg of silicon melt. This increased volume keeps temperature fluctuations within ±0.5°C, which supports faster pulling rates and reduces the risk of defects.
Manufacturers observe that stable melt volume allows pulling rates to reach 2.2-2.8 mm/min for 12-inch ingots, compared to 1.5-2.0 mm/min in smaller tubes. The consistent temperature profile prevents dislocation defects, helping maintain solar cell efficiency above 22%. Data from over 600 installations shows that large tubes improve yield and reduce cycle times.
Tube Diameter | Melt Volume (kg) | Pulling Rate (mm/min) | Temperature Stability (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
300mm | 50-70 | 1.5-2.0 | ±1.2 |
400-500mm | 80-120 | 2.2-2.8 | ±0.5 |
Crucible Diameter Optimization Within Large Protective Tubes
Optimizing crucible diameter inside large protective tubes increases monocrystalline silicon output. Larger crucibles, placed within 450-500mm tubes, create stable convection patterns in the silicon melt. These patterns help maintain a consistent solid-liquid interface, which is essential for high-quality crystal growth.
Manufacturers select crucible diameters of 280-320mm to maximize melt volume and support the growth of 60-80kg boules in 24-28 hours. This approach reduces cycle time and increases the number of usable wafers per ingot. Facilities using optimized crucible and tube combinations report up to 12% more usable wafers and lower edge exclusion zones.
Key Points:
Larger crucibles inside protective tubes stabilize melt convection.
Optimized diameter supports faster crystal growth and higher yield.
Facilities achieve more usable wafers per ingot.
This optimization leads to better resource utilization and supports the production of high-efficiency solar cells.
Equipment Utilization Improvements Through Cycle Time Reduction
Cycle time reduction directly impacts equipment utilization in monocrystalline silicon manufacturing. Large Czochralski puller tubes allow for faster pulling rates and larger batch sizes, which means each machine produces more silicon in less time. This improvement increases annual throughput and lowers production costs per watt.
Manufacturers who standardize on 400-500mm tubes report equipment utilization rates above 95%. They also experience $0.42-0.58 per watt cost advantages compared to smaller tube systems. Quality control protocols, including ICP-MS analysis and ultrasonic inspection, ensure long-term performance and minimize downtime.
Method | Description | Impact on Production Rates |
|---|---|---|
Common method for mono-Si production with low thermal stress resistance and short processing time. | Tube diameter affects pulling speed and ingot uniformity. | |
Recharge Cz | Upgraded method allowing continuous operation without cooling. | Improves efficiency and reduces costs, increasing output. |
Continuous Cz | New material added during ingot pulling. | Leads to uniform resistivity and longer ingots. |
Efficient equipment utilization, supported by robust quality control, helps manufacturers maintain high output and consistent monocrystalline silicon quality.
What Material Specifications Enable Large Quartz Tubes to Sustain High-Efficiency Photovoltaic Production?
Large quartz tubes must meet strict material specifications to support high-efficiency photovoltaic production. These requirements help prevent contamination, maintain thermal uniformity, and ensure long-term reliability during fabrication. Manufacturers evaluate purity, dimensional tolerance, and quality testing protocols to select the best tubes for their solar fabrication processes.
Purity Requirements for Silicon Contamination Prevention
Quartz tubes used in photovoltaic fabrication must have extremely low levels of contaminants. High-purity fused quartz prevents unwanted elements from entering the silicon during fabrication, which protects solar cell performance. Manufacturers often choose tubes with less than 25 ppm total contaminants, sodium levels below 0.1 ppm, and OH- content under 10 ppm.
Maintaining these purity standards helps avoid defects that can lower solar cell efficiency. The table below shows typical purity specifications for quartz tubes in solar fabrication:
Specification | Purity Level |
|---|---|
Contaminants in fused quartz | Less than 25 ppm |
Sodium level in Grade 224 | 0.1 ppm |
Typical aluminum level in Grade 244 | 8 ppm |
OH- content | Less than 10 ppm |
Strict purity control ensures that each fabrication cycle produces high-quality silicon, supporting reliable solar panel output.
Dimensional Tolerance Impact on Thermal Uniformity and Yield
Dimensional tolerance plays a key role in the thermal performance of quartz tubes during fabrication. Tubes with precise outer diameter and wall thickness maintain even heating, which helps prevent hot spots and uneven silicon growth. Manufacturers often specify tolerances within ±0.1 mm for seamless integration and optimal thermal uniformity.
Consistent dimensions allow for better control of the fabrication environment, leading to higher yield and fewer defects. The following table highlights important dimensional tolerance standards:
Dimensional Tolerance | Application |
|---|---|
±0.1 mm | Ensures seamless integration into chromatography systems (<0.2 mm clearance) |
Accurate tube dimensions support efficient fabrication, resulting in more usable silicon and improved solar cell quality.
Quality Testing Protocols for Long-Term Performance Assurance
Quality testing protocols verify that quartz tubes will perform reliably throughout their service life in photovoltaic fabrication. Manufacturers use methods such as ICP-OES for purity, ISO 7884-7 for thermal shock resistance, and profilometry for surface roughness. These tests confirm that tubes meet industry standards and can withstand repeated heating cycles.
Rigorous quality control reduces downtime and increases yield by preventing defects during fabrication. Enhanced longevity of well-made tubes leads to better long-term performance and return on investment for solar manufacturers. Key quality testing protocols include:
SiO₂ purity ≥99.995% (solar), ≥99.999% (semi)
Thermal shock resistance >200°C (ΔT)
Surface roughness <0.5 μm
Dimensional tolerance ±0.2-0.5 mm
Manufacturers who follow strict testing protocols ensure that their fabrication processes remain efficient and reliable, supporting consistent solar panel production.
How Should Photovoltaic Manufacturers Optimize Large Tube Selection for Production Economics?
Photovoltaic manufacturers face important decisions when selecting large quartz tubes for their production lines. The right choice affects both operational costs and long-term efficiency. Careful evaluation of total cost, batch requirements, and material grade ensures the best economic outcome.
Total Cost of Ownership Calculation Framework
Manufacturers must look beyond the initial purchase price when evaluating quartz tubes. Total cost of ownership (TCO) includes tube lifespan, energy consumption, silicon yield, and downtime risk. Facilities that analyze TCO can identify the most cost-effective tube options for their specific needs.
A comprehensive TCO calculation considers several factors. Annual tube cost depends on both purchase price and expected service life. Production impact costs include energy savings from optimized tube geometry, silicon yield variation, and potential downtime from tube failure. For example, a facility producing 5,000 metric tons of polysilicon can save $180,000–$280,000 per year by choosing tubes that reduce energy use by 23%. Downtime from tube failure may cost $75,000–$150,000 per incident, making reliability a key part of the calculation.
Key Points:
TCO includes purchase price, lifespan, energy use, yield, and downtime.
Energy-efficient tubes can save hundreds of thousands of dollars annually.
Reliable tubes reduce costly production interruptions.
Diameter Selection Matching Production Batch Requirements
Selecting the correct tube diameter helps manufacturers align batch size with downstream equipment. The optimal diameter supports efficient production flow and prevents inventory buildup. Facilities that match tube size to batch requirements achieve higher equipment utilization and lower storage costs.
Batch size increases with tube diameter, but oversized tubes may create mismatches with wafer slicing or cell production lines. For example, a 400mm tube supports 100kg batches, while a 450mm tube handles 120kg. If downstream processes only handle 100kg, using a 450mm tube can cause excess inventory or underused capacity. Standardizing on a tube diameter that matches the facility’s batch flow improves synchronization and reduces costs.
Tube Diameter | Typical Batch Size (kg) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
350-380mm | 60-80 | Cost optimization |
400-420mm | 90-105 | Throughput and flow alignment |
430-450mm | 110-120 | Maximum batch, large facilities |
Material Grade Specification by Process Temperature
Material grade selection depends on the maximum process temperature in each production step. High-purity quartz and fused silica offer different benefits for various temperature ranges. Manufacturers must choose the right material to ensure tube longevity and product quality.
High-purity quartz works well for applications up to 1050°C, while fused silica handles higher temperatures. The table below shows typical specifications for quartz tubes in photovoltaic manufacturing:
Specification | Long-term (℃) | Short-term (℃) | Purity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
Maximum working temperature | 1100 | 1350 | 99.99–99.999 |
Selecting the correct material grade prevents tube deformation and contamination, supporting stable, high-yield production.
Large quartz tubes enable high-volume photovoltaic manufacturing by increasing throughput, lowering energy use, and improving product quality. Optimizing tube diameter and material specifications, along with coordinated facility planning, maximizes economic benefits. The table below highlights how design parameters affect yield:
Design Parameter | Thickness (mm) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|
Glass Collector | 4 | 25 |
Glass Collector | 3.2 | 18.71 |
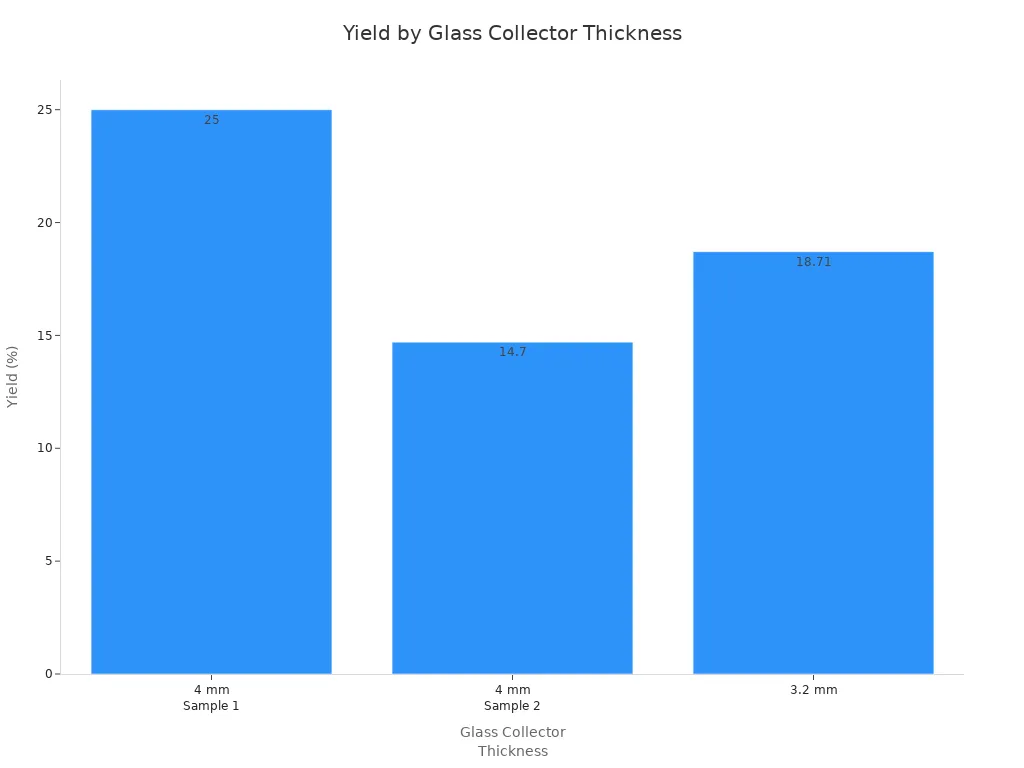
Manufacturers who use data-driven tube selection and standardize on optimal designs achieve longer tube life, higher yield, and lasting success.
FAQ
Why do manufacturers prefer large quartz tubes for solar cell production?
Large quartz tubes increase batch size and throughput. They help factories produce up to 100kg of polysilicon per cycle, compared to 60kg with smaller tubes. This efficiency supports growing demand for solar panels.
Why does tube diameter affect energy consumption in photovoltaic manufacturing?
Tube diameter changes the ratio of wall surface area to interior volume. Larger tubes allow heat to reach seed rods more efficiently. Factories using 400mm tubes save up to 23% on energy costs.
Why is thermal uniformity important in semiconductor manufacturing equipment?
Thermal uniformity prevents hot spots and uneven silicon growth. Consistent temperatures inside quartz tubes reduce defects and improve yield. Manufacturers achieve higher product quality and reliability.
Why do manufacturers use strict purity standards for quartz tubes?
High purity quartz prevents contamination during silicon processing. Tubes with less than 25 ppm contaminants protect solar cell efficiency. This standard ensures reliable performance in photovoltaic production.
Why should manufacturers match tube diameter to batch requirements?
Matching tube diameter to batch size keeps production flow synchronized. Oversized tubes can cause inventory buildup or underused equipment. Standardizing tube size improves equipment utilization and lowers costs.





