Certifications such as ISO 9001, ISO 12123, ASTM, and SEMI set the global benchmark for high-quality quartz tubes for industrial use. These standards demand strict controls over production, purity, and testing, which leads to consistent performance and fewer defects. When suppliers hold these certifications, they provide greater accountability and help ensure reliable supply chains.
Key Takeaways
ISO 9001 and ISO 12123 certifications ensure strict quality control in quartz tube manufacturing, leading to fewer defects.
Batch-specific purity certificates verify the quality of quartz tubes by documenting impurity levels, ensuring consistency.
ASTM and SEMI standards set clear benchmarks for testing and contamination control, crucial for semiconductor applications.
Automated inspection systems catch defects early, improving reliability and maintaining high quality in production.
Procurement teams should request essential documentation to confirm compliance and traceability, ensuring high-quality quartz tubes.
What Do ISO 9001 and ISO 12123 Standards Verify for Quartz Tube Manufacturing?

ISO 9001 and ISO 12123 set the foundation for reliable quartz tube production. These standards help manufacturers maintain strict controls over process and product quality. Companies that follow both standards deliver high-quality quartz tubes for industrial use with consistent performance.
ISO 9001 Requirements: Documentation and Process Control
ISO 9001 requires manufacturers to document every step of their production process. They must record incoming material inspections, monitor each stage of manufacturing, and test finished products. This approach reduces defect rates by 40-60% compared to uncertified suppliers.
Manufacturers use batch-specific documentation to track purity, dimensions, and thermal properties. They link each quartz tube to its production batch, which helps trace any issues back to their source. This traceability ensures that high-quality quartz tubes for industrial use meet strict customer requirements.
ISO 9001 also demands continuous improvement and corrective actions. Companies must train employees, prepare quality manuals, and address non-conformities quickly.
Summary Table: ISO 9001 Process Control
Requirement | Cause | Effect |
|---|---|---|
Documented Procedures | Systematic monitoring | Lower defect rates |
Batch Traceability | Linked records | Faster problem resolution |
Continuous Improvement | Employee training | Consistent product quality |
ISO 12123 Optical Testing: Transmission, Homogeneity, and Surface Quality
ISO 12123 sets strict criteria for optical transmission and homogeneity in quartz tubes. Manufacturers must test refractive index variation and transmission at specific wavelengths. These tests allow direct comparison of high-quality quartz tubes for industrial use from different suppliers.
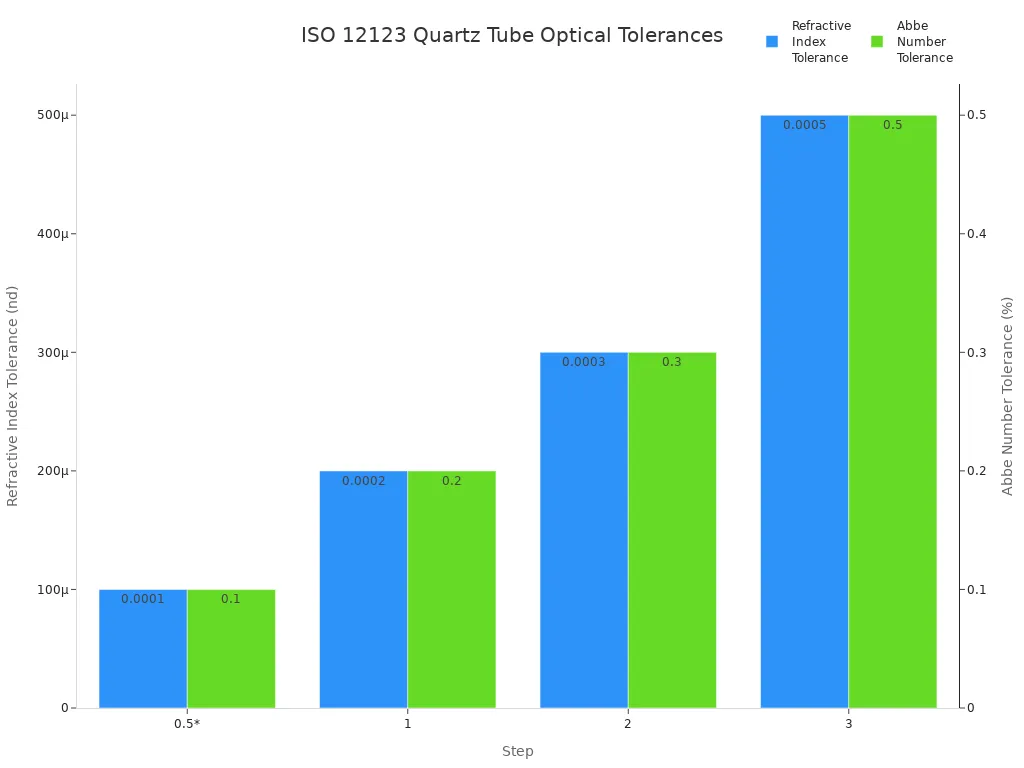
The standard defines tolerances for refractive index and Abbe number. For example, quality levels H4 and H5 specify maximum refractive index variations of 2 x 10^-6 and 1 x 10^-6, respectively. The table below shows how these tolerances affect optical performance.
Quality Level | Maximum Refractive Index Variation (peak to valley) |
|---|---|
H4 | 2 x 10^-6 |
H5 | 1 x 10^-6 |
Step | Refractive Index Tolerance (nd) | Abbe Number Tolerance (νd) |
|---|---|---|
0.5* | ± 0.0001 | ± 0.1% |
1 | ± 0.0002 | ± 0.2% |
2 | ± 0.0003 | ± 0.3% |
3 | ± 0.0005 | ± 0.5% |
ISO 12123 also classifies surface quality, which impacts transmission and contamination risk.
Key Points:
Standardized optical testing enables fair supplier comparison
Strict tolerances ensure reliable performance
Surface quality affects both transmission and cleanliness
Verification Methods: Auditing Supplier Certifications
Auditing supplier certifications verifies compliance with ISO 9001 and ISO 12123. Procurement teams must review actual test data, calibration records, and traceability to ISO 17025 standards. This process confirms that suppliers deliver high-quality quartz tubes for industrial use.
Effective audits follow a structured approach. Teams prepare documentation, train auditors, and conduct on-site inspections. They use checklists to cover all relevant areas and document findings for future reference.
Tip: Always follow up on corrective actions after the audit to ensure continuous improvement.
Summary Table: Supplier Audit Steps and Outcomes
Audit Step | Action Taken | Result |
|---|---|---|
Review Test Data | Examine batch records | Confirm product meets specifications |
Inspect Calibration | Check equipment certificates | Validate measurement accuracy |
Traceability Verification | Link results to ISO 17025 | Ensure reliable and repeatable testing |
How Do Batch-Specific Purity Certificates Validate Material Quality?
Batch-specific purity certificates play a vital role in verifying the quality of industrial quartz tubes. These certificates document the actual levels of metallic impurities in each production batch, ensuring that tubes meet strict application requirements. Procurement teams rely on these certificates to confirm material consistency and traceability.
ICP-OES vs. GDMS: Analytical Technique Capabilities and Limitations
Industrial quartz tube suppliers use advanced analytical techniques to measure metallic impurities. ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy) and GDMS (Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometry) offer different detection limits and capabilities. ICP-OES provides accurate results for elements above 1 ppm, while GDMS achieves sub-ppm sensitivity for ultra-high-purity needs.
Manufacturers select the appropriate method based on the required purity level for each application. Semiconductor tubes often require GDMS to detect aluminum and iron below 0.1 ppm, while furnace tubes may use ICP-OES for higher impurity thresholds. The choice of technique affects both cost and quality assurance.
Method | Target Parameter | Detection Limit | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
ICP-OES | Metallic Impurities | <0.1 ppm | Furnace, chemical tubes |
GDMS | Trace Metals | <0.01 ppm | Semiconductor, optics |
Key points:
ICP-OES suits general industrial needs
GDMS enables ultra-high-purity verification
Detection limits drive application suitability
Critical Impurity Elements: Which Metals Impact Performance
Metal impurities such as iron and aluminum significantly affect quartz tube performance. At high temperatures, these metals react with silica, forming silicates that weaken the tube and reduce its lifespan. Even small amounts of iron can lower UV transmission, while excess aluminum accelerates devitrification.
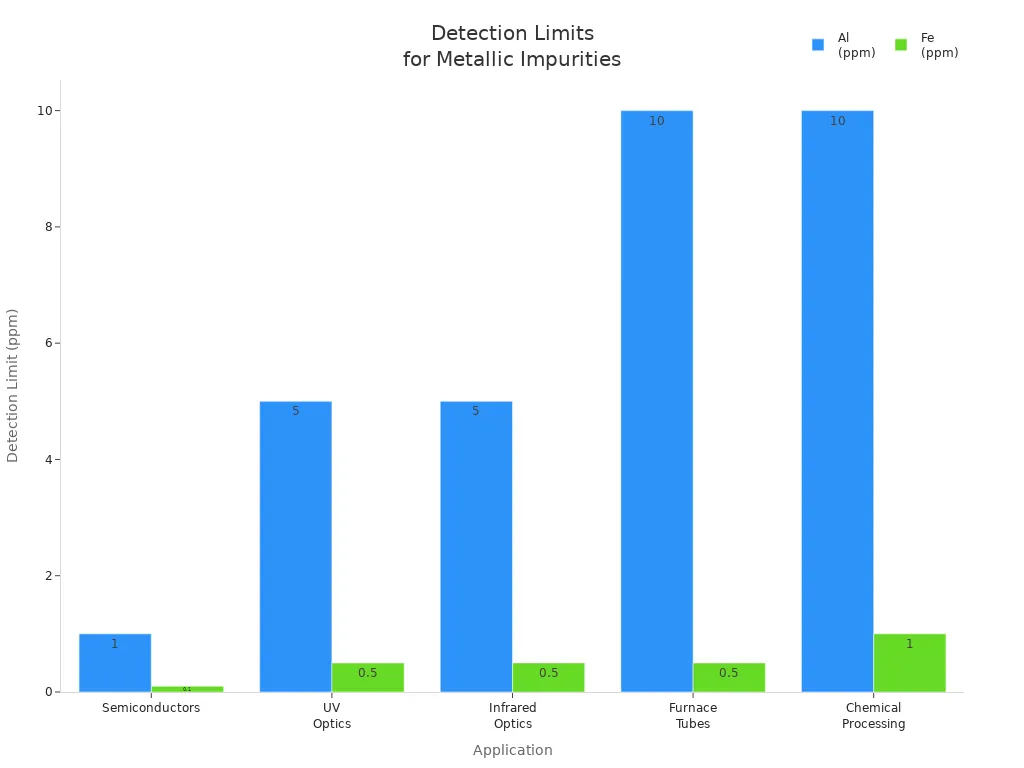
Different applications set strict impurity limits to protect material integrity. Semiconductor manufacturing demands less than 1 ppm aluminum and 0.1 ppm iron, while UV optics require low iron to maintain transmission. The table below shows how impurity thresholds vary by industry.
Application | SiO₂ (%) | Al (ppm) | Fe (ppm) | OH (ppm) | Particle Inclusion (pcs/cm³) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Semiconductors | >99.995 | <1 | <0.1 | <1 | <0.1 |
UV Optics | >99.99 | <5 | <0.5 | <10 | <1 |
Furnace Tubes | >99.95 | <10 | <0.5 | <10 | <5 |
Summary:
Iron and aluminum reduce tube stability
Strict impurity limits protect performance
Industry standards guide procurement choices
Certificate Verification: Validating Laboratory Accreditation
Procurement teams must verify the authenticity and accuracy of purity certificates. Accredited laboratories provide reliable test results, and each certificate should include batch-level traceability with unique material IDs. Third-party verification confirms compliance with industry standards and ensures consistent quality.
Quality assurance protocols include automated inspection reports, statistical process control data, and hydrofluoric acid etching tests for surface integrity. These measures help organizations track each batch and identify any deviations quickly. Reliable documentation reduces risk and supports long-term supplier relationships.
Quality Assurance Protocols | Description |
|---|---|
Batch-level traceability with unique material IDs | Ensures each batch can be tracked for quality |
Third-party verification of material certificates | Confirms compliance with industry standards |
Statistical process control data for dimensional tolerances | Ensures precision in manufacturing |
Automated optical inspection reports | Verifies the physical quality of the tubes |
Key points:
Accredited labs ensure certificate reliability
Traceability links certificates to specific batches
Verification protocols support consistent quality
Why Are ASTM and SEMI Standards Essential for Semiconductor Applications?
Semiconductor manufacturing demands strict control over material properties and contamination. ASTM and SEMI standards set clear benchmarks for testing, cleanliness, and reliability in quartz tubes. These standards help procurement teams select high-quality quartz tubes for industrial use that meet the most demanding requirements.
Understanding ASTM Testing Standards for Quartz Glass
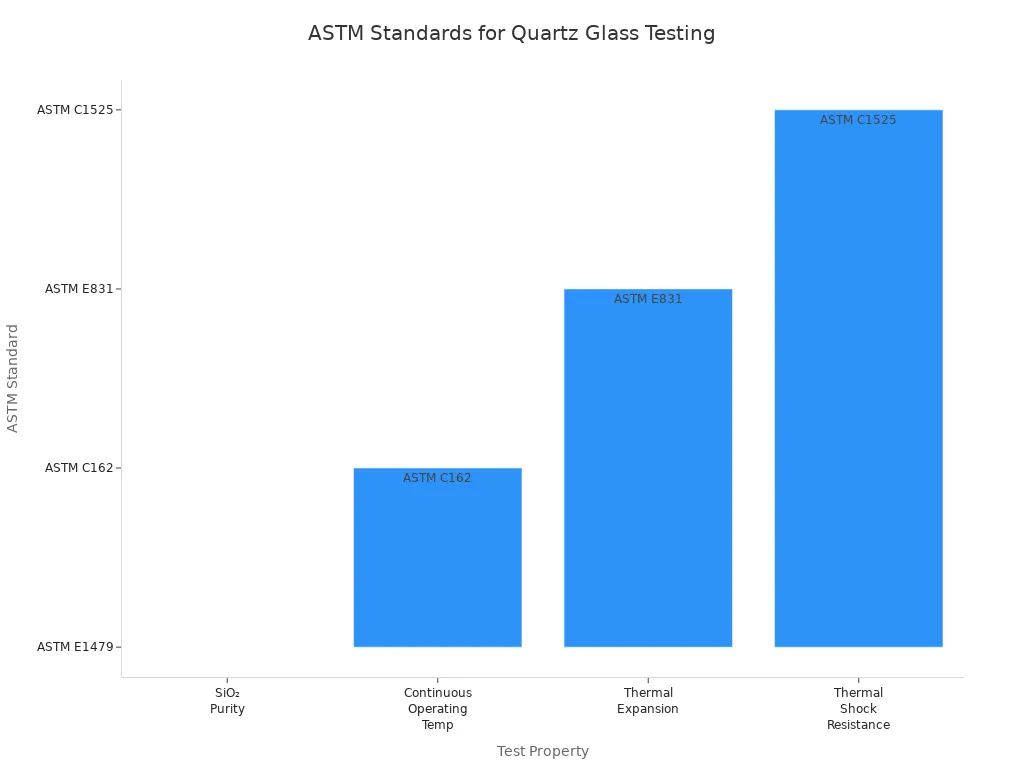
ASTM standards provide objective methods for measuring quartz glass properties. Manufacturers use ASTM C372 for thermal expansion, ASTM C693 for density, ASTM C1525 for thermal shock resistance, and ASTM E903 for optical transmission. These standards ensure that each tube performs reliably under extreme conditions.
The following table summarizes key ASTM standards and their relevance:
Property | Value/Range | Industry Standard (Test Method) | Contextual Note |
|---|---|---|---|
SiO₂ Purity (%) | ≥ 99.99 | ASTM E1479 | High purity eliminates weaker phase regions |
Continuous Operating Temp (°C) | 1050–1200 | ASTM C162 | Non-deforming, dimensional stability |
Thermal Expansion (×10⁻⁷/°C) | 5.0–5.5 | ASTM E831 | Reference: room temperature to 900°C |
Thermal Shock Resistance (ΔT, °C) | >1000 | ASTM C1525 | Withstands rapid, extreme temperature changes |
ASTM standards allow engineers to compare suppliers using identical criteria.
Note: Consistent testing reduces risk and improves yield in semiconductor processes.
SEMI F-78 Requirements: Contamination Control for Semiconductors
SEMI F-78 sets strict limits for contamination in quartz tubes. Manufacturers must control particle counts, metallic impurities, and outgassing to prevent defects in semiconductor wafers. Cleanroom handling and packaging procedures also play a critical role in maintaining tube cleanliness.
SEMI F-78 compliance reduces wafer contamination defects by up to 70%. This improvement can save manufacturers thousands of dollars per percentage point of yield.
Cleanroom protocols ensure that tubes remain uncontaminated from production to installation.
Key Points:
SEMI F-78 limits particles and metals
Cleanroom handling prevents recontamination
Yield rates improve with strict compliance
Verification Infrastructure: Equipment Required for Compliance Testing
Manufacturers need specialized equipment to verify ASTM and SEMI compliance. Particle counters, TXRF analyzers, and outgassing test chambers measure contamination and purity. Dedicated laboratories use spectrophotometers and coordinate measuring machines for optical and dimensional checks.
Facilities with advanced testing infrastructure achieve higher first-pass yield rates. Automated inspection systems and statistical process control help maintain consistent quality across large batches.
Reliable verification ensures that high-quality quartz tubes for industrial use meet all semiconductor standards.
Verification Step | Required Equipment | Effect on Quality |
|---|---|---|
Particle Measurement | Particle Counter | Detects surface contamination |
Metal Impurity Analysis | TXRF Analyzer | Confirms purity levels |
Outgassing Test | Test Chamber | Prevents wafer defects |
How Do High-Volume Manufacturers Ensure Quality Consistency Across Large Production Batches?

High-volume quartz tube manufacturers must deliver consistent quality across thousands of units. They rely on advanced process controls, automated inspections, and mature production protocols. These methods help reduce defects and maintain uniformity from batch to batch.
Statistical Process Control Implementation in Quartz Production
Statistical process control (SPC) forms the backbone of quality management in large-scale quartz tube manufacturing. Manufacturers use SPC tools to monitor process variables and quickly detect any deviations. Six Sigma methodology often guides these efforts, focusing on reducing variation and eliminating defects.
SPC applies data-driven measurements at every stage, from raw material input to final inspection. Operators track key parameters like purity, diameter, and surface quality using control charts and real-time data analysis. This approach ensures that each production run meets strict quality standards.
Manufacturers who implement SPC and Six Sigma report higher yield rates and fewer field failures.
Summary Table: SPC in Quartz Tube Production
SPC Method | Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
Control Charts | Monitor process trends | Early detection of variation |
Six Sigma Analysis | Identify root causes | Fewer defects, higher consistency |
Real-Time Data | Immediate feedback | Faster corrective actions |
Automated Inspection Systems: Dimensional and Optical Verification
Automated inspection systems play a critical role in verifying both dimensional accuracy and optical properties. These systems use cameras, lasers, and sensors to check every tube for defects such as cracks, bubbles, or surface flaws. Automated checks provide objective, repeatable results that manual inspection cannot match.
Manufacturers program these systems to flag any tube that falls outside specification limits. The technology enables rapid sorting and reduces the risk of defective products reaching customers. Automated inspection also supports statistical sampling, which further improves process reliability.
These inspection systems help maintain high first-pass yield rates and support continuous improvement.
Key points:
Automated systems catch defects early
Objective measurements improve reliability
Statistical sampling supports process control
Production Volume as Quality Consistency Indicator
Production volume often signals a manufacturer’s ability to maintain quality over time. High-volume producers develop mature processes and invest in advanced quality control infrastructure. Consistency in large-scale production depends on rigorous protocols and ongoing process optimization.
Manufacturers with higher output typically show lower defect rates and better uniformity across batches. They track production history, yield rates, and customer returns to verify ongoing quality. Continuous improvement initiatives, such as Lean Manufacturing, further enhance consistency.
A review of industry data shows that large-scale producers achieve more uniform results and fewer defects.
Summary Table: Production Volume and Quality Consistency
Factor | Cause | Effect |
|---|---|---|
High Production Volume | Mature processes, more data | Greater consistency, fewer defects |
Rigorous QC Protocols | Standardized inspections | Uniformity across batches |
Continuous Improvement | Ongoing process optimization | Sustained high quality |
What Documentation Should Procurement Teams Require from Quartz Tube Suppliers?
Procurement teams need clear documentation to ensure quartz tubes meet all technical and quality requirements. The right paperwork supports traceability, compliance, and cost-effective sourcing. This section explains what documents matter most, how to verify them, and when to adjust requirements for specific applications.
Essential Documentation Checklist for Quartz Tube Procurement
Procurement teams should request six essential categories of documentation from suppliers. These categories include material certificates, dimensional inspection reports, optical and thermal test data, quality system certifications, and process documentation. Each document type plays a role in confirming that high-quality quartz tubes for industrial use meet strict standards.
A comprehensive checklist helps teams track supplier compliance and traceability. Preaward traceability documents confirm supplier history and pricing legitimacy, while postaward traceability ensures ownership and specification compliance. Acceptability criteria validate the authenticity and completeness of all traceability documentation.
Documentation Category | Description |
|---|---|
Material Certificates | Batch-specific purity analysis and chemical composition |
Dimensional Reports | CMM measurement data for tube dimensions |
Optical Test Data | Transmission and refractive index results at application wavelengths |
Thermal Test Data | Annealing records and thermal shock verification |
ISO 9001, ISO 12123, and other relevant standards | |
Process Documentation | Fusion method, annealing protocol, and surface finishing procedures |
This checklist ensures that procurement teams receive all necessary information for traceability and compliance.
Witness Testing Protocols: When and How to Implement
Witness testing protocols provide an extra layer of assurance during quartz tube procurement. A technical specialist should witness factory acceptance tests to confirm compliance with specifications. This process includes observing tests at both the component level and final inspection.
Teams review contract specifications, technical datasheets, and equipment drawings before testing. They observe acceptance tests to ensure adherence to protocols and documentation, and they perform non-conformance testing to identify any gaps in compliance. Witness testing helps organizations catch issues early and avoid costly rework.
Key points for witness testing:
Technical specialists confirm compliance
Testing occurs at multiple manufacturing stages
Review all specifications and observe acceptance tests
Non-conformance testing identifies gaps
These steps help procurement teams verify that suppliers deliver products that meet all requirements.
Balancing Documentation Requirements with Application Needs
Procurement teams must balance thorough documentation with the specific needs of each application. Material certification, hydroxyl content, thermal stability, and chemical resistance are critical for many uses. For laser applications, teams should ensure hydroxyl content is ≤5ppm to prevent absorption and signal loss.
Teams request OH content analysis and validate it with supplier documentation. They require ISO 9001 certification, batch-specific purity certificates, and process documentation for each order. For applications needing high thermal shock resistance or purity, teams prioritize tubes that meet ASTM E438 Type I/II or ISO 3290-1 standards.
Requirement | Cause | Effect |
|---|---|---|
Material Certification | Confirms chemical composition | Ensures suitability for application |
OH Content Analysis | Prevents absorption and signal loss | Maintains optical performance |
Batch-Specific Purity Certificates | Verifies impurity levels | Reduces risk of contamination |
Process Documentation | Details manufacturing protocols | Supports repeatable quality |
This approach allows teams to optimize documentation for both performance and cost.
Procurement teams who prioritize ISO, ASTM, and SEMI certifications, along with batch-specific documentation, consistently secure high-quality quartz tubes for industrial use. These standards help prevent defects, minimize impurities, and ensure accuracy for demanding industries. Teams should verify certifications and documentation to reduce risk and improve supplier transparency.
Long-term benefits include strict quality control, minimized impurities, and reliable performance.
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Fragmented Supplier Onboarding & Qualification | Slow onboarding can let poor suppliers slip through, risking quality. |
Lack of Real-Time Visibility & Monitoring | Without real-time data, quality issues may go unresolved. |
Poor Collaboration & Inconsistent Communication | Miscommunication leads to misaligned quality expectations. |
Certification | Description |
|---|---|
ISO 9001 | Ensures traceable manufacturing workflows with 100% batch testing for dimensional accuracy. |
Traceable Compliance | Provides material traceability for critical applications, reducing operational risks. |
FAQ
What is the difference between ISO 9001 and ISO 12123 for quartz tubes?
ISO 9001 focuses on quality management and process control. ISO 12123 sets standards for optical properties and surface quality.
Both certifications together ensure reliable manufacturing and consistent optical performance.
How do batch-specific purity certificates help in procurement?
Batch-specific purity certificates show actual impurity levels for each production lot. They help buyers confirm material quality and traceability.
Key points:
Confirms purity
Links to specific batches
Reduces risk of defects
Why are ASTM and SEMI standards important for semiconductor applications?
ASTM and SEMI standards set strict requirements for testing, cleanliness, and contamination control. They help manufacturers achieve higher yields and fewer defects.
Standard | Purpose |
|---|---|
ASTM | Verifies material quality |
SEMI | Controls contamination |
What documents should procurement teams always request from suppliers?
Procurement teams should request material certificates, dimensional reports, optical and thermal test data, quality system certifications, and process documentation.
These documents support traceability and ensure the quartz tubes meet all technical requirements.
Can automated inspection systems improve quartz tube quality?
Automated inspection systems detect defects quickly and provide objective measurements. They help manufacturers maintain high yield rates and consistent quality.
Benefits:
Early defect detection
Reliable measurements
Supports process control





