تلعب تفاوتات السماكة الدقيقة في ألواح الكوارتز دورًا حيويًا في قطاعات التكنولوجيا المتقدمة. تعتمد العديد من التطبيقات على الصفات الفريدة للوح الكوارتز، مثل معامل التمدد الحراري المنخفض والنقاء العالي. تساعد هذه الميزات في الحفاظ على الموثوقية والدقة في البيئات الصعبة. وتشمل تطبيقات تحمل دقة ألواح الكوارتز الأجهزة البصرية وأنظمة الليزر وتصنيع أشباه الموصلات والمعدات الطبية.
تقاوم صفيحة الكوارتز الصدمات الحرارية وتدعم الوضوح البصري الفائق عبر نطاق واسع من الأطوال الموجية، مما يجعلها ضرورية لنقل الصور بجودة عالية وإنتاج خالٍ من التلوث.
مجال التطبيق | تفاوت السُمك النموذجي |
|---|---|
صفيحة كوارتز مربعة الشكل | 2 مم إلى 10 مم |
صفيحة كوارتز مستطيلة الشكل | 2 مم إلى 15 مم |
الأدوات البصرية | 2 مم إلى 10 مم |
المعدات الطبية | 2 مم إلى 10 مم |
الأدوات الدقيقة | 1 مم إلى 10 مم |
المعدات الإلكترونية | حتى 15 مم |
صفيحة كوارتز تؤثر الدقة بشكل مباشر على الأداء والموثوقية والجودة في هذه الأنظمة.
الوجبات الرئيسية
تُعد التفاوتات الدقيقة للسماكة في ألواح الكوارتز ضرورية لتطبيقات مثل تصنيع أشباه الموصلات والأدوات البصرية والمعدات الطبية.
إن الحفاظ على التحكم الصارم في السماكة يمنع العيوب ويضمن أداءً ثابتًا في الأنظمة عالية التقنية، مما يعزز الموثوقية والكفاءة.
يجب على المهندسين مراعاة المتطلبات المحددة لكل تطبيق، مثل ثبات درجة الحرارة والوضوح البصري، عند اختيار ألواح الكوارتز.
يمكن أن يؤدي تفاوت السماكة المخصص إلى تحسين دقة القياس وجودة البيانات بشكل كبير في إعدادات البحث والمختبرات.
يساعد التشاور مع الموردين وتقييم التكلفة الإجمالية للملكية على ضمان أفضل النتائج عند اختيار ألواح الكوارتز للتطبيقات المتقدمة.
لماذا تتطلب تطبيقات معالجة رقاقات أشباه الموصلات التحكم في سمك الرقاقة ± 0.03-0.05 مم؟
يعتمد تصنيع أشباه الموصلات على تطبيقات تحمل دقة صفيحة الكوارتز لتحقيق أداء متسق للأجهزة. تؤثر سماكة لوح الكوارتز على التحكم في درجة الحرارة والتفاعلات الكيميائية وجودة الرقاقة في هذه الأنظمة. يستخدم المهندسون تفاوتات تحمل صارمة للحفاظ على الموثوقية والكفاءة في عمليات أشباه الموصلات المتقدمة.
حسابات اتساق الكتلة الحرارية لمكونات الكوارتز في مفاعل CVD
تلعب سماكة صفيحة الكوارتز دورًا حاسمًا في التحكم في الكتلة الحرارية أثناء ترسيب البخار الكيميائي (CVD). تضمن الكتلة الحرارية الموحدة بقاء درجة الحرارة مستقرة في جميع مناطق المفاعل، وهو أمر ضروري لإنتاج أشباه موصلات عالية الجودة. يمكن أن تتسبب الاختلافات في سمك صفيحة الكوارتز في تسخين غير متساوٍ، مما يؤدي إلى عيوب في طبقات الرقاقة.
يحسب المهندسون الكتلة الحرارية باستخدام المعادلة:
الكتلة الحرارية = الكثافة × الحجم × السعة الحرارية النوعية × السعة الحرارية النوعية
حتى الانحراف البسيط في سُمك الكوارتز يمكن أن يغير الكتلة الحرارية، مما يؤثر على تدرجات درجة الحرارة.
النقاط الرئيسية:
كتلة حرارية موحدة يدعم الملامح المستقرة لدرجات الحرارة.
تحكم صارم في السماكة يمنع البقع الساخنة والمناطق الباردة.
تدفئة ثابتة تحسين إنتاجية الرقاقة وموثوقية الجهاز.
تساعد تطبيقات التحمل الدقيق للوح الكوارتز في مفاعلات التفريغ القابل للذوبان في البوليمرات القلبية الوسيطة في الحفاظ على استقرار العملية وجودة المنتج.
كيف يؤثر تباين السُمك على ملامح انتشار المنشطات في رقائق السيليكون
تؤثر سماكة صفيحة الكوارتز على كيفية انتشار المنشطات عبر رقائق السيليكون أثناء المعالجة بدرجة حرارة عالية. عندما تختلف سماكة الكوارتز، يتغير توزيع درجة الحرارة، مما يغير معدل وعمق انتشار المنشطات. ويمكن أن يؤدي ذلك إلى خصائص كهربائية غير متناسقة عبر الرقاقة.
المعلمة | المواصفات |
|---|---|
تباين السُمك | <10 ميكرومتر للرقائق ذات الدرجة البحثية |
تحمل القطر | ± 0.1 مم إلى ± 0.5 مم |
التسطيح (GBIR) | 1-10 ميكرومتر |
دقة التوجيه | ± 0.5 درجة إلى ± 0.1 درجة |
يضمن التحكم الدقيق في سُمك صفيحة الكوارتز سُمكًا دقيقًا لملامح المنشطات الموحدة، وهو أمر حيوي لإنتاج أجهزة أشباه موصلات موثوقة.
مواصفات التدرج في درجة الحرارة لتصنيع أشباه الموصلات ذات العقدة المتقدمة (أقل من 7 نانومتر)
تتطلب تطبيقات أشباه الموصلات المتقدمة، مثل تلك التي تقل عن 7 نانومتر، مواصفات تدرج درجة حرارة ضيقة للغاية. يجب أن تحافظ صفيحة الكوارتز على سمكها في حدود ± 0.03-0.05 مم لمنع التغيرات الحرارية غير المرغوب فيها. تستخدم هذه الأنظمة مستشعرات ليزر ومستشعرات بصرية لمراقبة درجة الحرارة وضمان التوحيد.
ملخص النقاط الرئيسية:
تفاوت السماكة الضيق تحافظ على تدرجات الحرارة ضمن الحدود الآمنة.
المراقبة بالليزر يكتشف التغيرات الصغيرة في سُمك صفيحة الكوارتز.
درجة حرارة موحدة يدعم التصنيع عالي الإنتاجية للعقد المتقدمة.
تتيح تطبيقات تحمل دقة ألواح الكوارتز إنتاج أشباه موصلات من الجيل التالي بأداء متسق.
ما هي تطبيقات قياس التداخل البصري التي تحتاج إلى تفاوتات سُمك ± 0.005-0.010 مم؟

قياس التداخل البصري تتطلب تحكمًا دقيقًا للغاية في سمك لوح الكوارتز. تعتمد هذه التطبيقات على تطبيقات تحمل دقة صفيحة الكوارتز لتحقيق قياسات دقيقة وأنماط تداخل واضحة. يستخدم المهندسون صفيحة الكوارتز في أنظمة قياس التداخل للحفاظ على جودة واجهة الموجة وتقليل الأخطاء.
ميزانيات الخطأ في واجهة الموجة المرسلة وتخصيص سماكة التحمل
تؤثر سماكة صفيحة الكوارتز بشكل مباشر على خطأ واجهة الموجة المرسلة في قياس التداخل البصري. يمكن أن تتسبب الانحرافات الصغيرة في السُمك في حدوث انزياحات في الطور، مما يقلل من وضوح هدب التداخل ويقلل من دقة القياس. يخصص المهندسون تفاوتًا صارمًا في السماكة للحفاظ على أخطاء واجهة الموجة ضمن الميزانية المطلوبة، وغالبًا ما يتراوح بين λ/4 و λ/10 عند 632.8 نانومتر، وهو ما يساوي 39.5-158 نانومتر.
تساعد تطبيقات تحمل دقة ألواح الكوارتز في الحفاظ على سلامة القياسات البصرية. تستخدم الأنظمة أدوات قياس متقدمة لقياس السُمك والتوازي والتسطيح في نفس الوقت. تقوم وحدة قياس FTP بتقييم هذه المعلمات لضمان مراقبة الجودة في المكونات البصرية والميكانيكا الدقيقة.
يدعم التخصيص الدقيق للسُمك التصوير عالي الدقة والقياسات الطورية الموثوقة.
النقاط الرئيسية:
تحكم صارم في السماكة تحافظ على أخطاء واجهة الموجة أقل من العتبات الحرجة.
القياس المتزامن التسطيح والسمك والتوازي يحسن الجودة.
واجهات موجية متناسقة تمكين التحليل البصري الدقيق.
حساسية فرق المسار الضوئي (OPD) في مناطق الطول الموجي المختلفة (الأشعة فوق البنفسجية، والمرئية، والأشعة تحت الحمراء)
تلعب صفيحة الكوارتز دورًا حيويًا في التحكم في فرق المسار البصري (OPD) عبر مناطق الأشعة فوق البنفسجية والمرئية وتحت الحمراء. تزداد حساسية OPD مع انخفاض الطول الموجي، مما يجعل تفاوت السماكة أكثر أهمية لتطبيقات الأشعة فوق البنفسجية. على سبيل المثال، يمكن أن يتسبب تغيير السُمك بمقدار 0.01 مم في السُمك في حدوث انزياح طوري يزيد عن 15% في منطقة الأشعة فوق البنفسجية، مما يؤثر على دقة القياس.
يختار المهندسون صفيحة كوارتز ذات تفاوتات سماكة ضيقة لتقليل أخطاء OPD. تتطلب أنظمة الليزر وإعدادات الرنين OPD مستقرة للحفاظ على تماسك الحزمة وتقليل الضوضاء. تُظهر البيانات أن الحفاظ على السُمك في حدود ± 0.005-0.010 مم يحافظ على اختلافات OPD أقل من 5% لمعظم الأطوال الموجية الضوئية.
منطقة الطول الموجي | حساسية العيادة الخارجية | تفاوت السماكة الموصى به | التأثير على القياس |
|---|---|---|---|
الأشعة فوق البنفسجية (<400 نانومتر) | عالية | ± 0.005 مم | حاسم لدقة الطور |
مرئي (400-700 نانومتر) | متوسط | ± 0.008 مم | مهم لوضوح الصورة |
الأشعة تحت الحمراء (> 700 نانومتر) | منخفضة | ± 0.010 مم | يحافظ على استقرار خط الأساس |
يعتمد قياس التداخل بالليزر والتحليل البصري على هذه المواصفات لتقديم نتائج موثوقة.
المواصفات المجمعة: السُمك والتوازي والتسطيح للتطبيقات التداخلية
تتطلب تطبيقات قياس التداخل أن تفي ألواح الكوارتز بالمواصفات المجمعة للسمك والتوازي والتسطيح. تعمل المسطحات الضوئية كأسطح مرجعية لتوليد أهداب التداخل وتقييم جودة ألواح الكوارتز. تقوم وحدة قياس FTP بتقييم جميع المعلمات الثلاثة في وقت واحد، وهو أمر بالغ الأهمية لمراقبة الجودة في كل من الأنظمة البصرية والميكانيكية.
يجب أن تحافظ صفيحة الكوارتز على السماكة في حدود ± 0.005-0.010 مم، والتوازي أقل من 10 ثوانٍ قوسية، والتسطيح أقل من 0.2 ميكرومتر لضمان دقة القياسات. تمنع هذه المواصفات مجتمعة التشويه في أشعة الليزر والعدسات، مما يدعم التحليل عالي الدقة. يستخدم المهندسون هذه المعايير في صناعة الساعات وتصميم المرنان البصري والأبحاث المتقدمة.
يضمن استيفاء المواصفات المجمعة أداءً موثوقًا في التطبيقات البصرية الصعبة.
النقاط الرئيسية:
تحكم متزامن السُمك والتوازي والتسطيح يضمن دقة القياس.
الأسطح المرجعية مثل المسطحات الضوئية للتحقق من جودة المكونات.
مراقبة الجودة يدعم أنظمة الليزر والبصريات عالية الأداء.
كيف تحدد أنظمة الليزر عالية الطاقة متطلبات توحيد السماكة؟
تتطلب تطبيقات الليزر عالية الطاقة تحكمًا استثنائيًا في سمك لوح الكوارتز لضمان التشغيل الآمن والموثوق. ويعتمد المهندسون على ألواح الكوارتز في تكنولوجيا الليزر لأن هذه المواد توفر نفاذية عالية ومقاومة قوية للتآكل ومقاومة عالية لدرجات الحرارة. يؤثر توحيد سُمك صفيحة الكوارتز بشكل مباشر على أداء المكونات الأساسية لليزر، بما في ذلك عدسات مرنان الليزر وعدسات تركيز الليزر.
الانكسار الناتج عن الإجهاد الناجم عن عدم انتظام السُمك في الحزم عالية الطاقة
يلعب تجانس سُمك صفيحة الكوارتز دورًا حاسمًا في تقليل الانكسار الناتج عن الإجهاد في أشعة الليزر عالية الطاقة. فعندما تختلف سماكة صفيحة الكوارتز يتركز الإجهاد الميكانيكي في مناطق معينة، مما يتسبب في تغيير خصائص الكوارتز البصرية. يمكن أن يؤدي هذا التأثير إلى تشويه حالة استقطاب الليزر، مما يقلل من كفاءة الإرسال وجودة الحزمة.
يقيس المهندسون الانكسار الثنائي الانكسار باستخدام قياس الاستقطاب، وغالبًا ما يجدون أن انحراف السُمك بمقدار 0.008 مم فقط يمكن أن يزيد من الانكسار الثنائي الانكسار بمقدار يصل إلى 251 تيرابايت 3 تيرابايت في أنظمة التركيز الليزري عالية الطاقة. تُظهر البيانات المستمدة من أنظمة الإرسال والتشكيل بالليزر الصناعية أن الحفاظ على تجانس السُمك في حدود ± 0.005 مم يحافظ على الانكسار الانكساري أقل من 0.002، وهو أمر ضروري لاستقرار تشغيل الليزر.
النقاط الرئيسية:
سمك موحد يقلل من الضغط والتشوه البصري.
انكسار انكسار منخفض يدعم نفاذية عالية واستقطاب شعاعي مستقر.
دقة التحمل في صفيحة كوارتز تضمن أداءً موثوقًا في تطبيقات الليزر عالية الطاقة.
ارتباط تأثيرات العدسات الحرارية وتدهور جودة الشعاع (عامل M²)
تحدث العدسة الحرارية عندما تقوم أشعة الليزر عالية الطاقة بتسخين ألواح الكوارتز بشكل غير متساوٍ، مما يسبب تغيرات في معامل الانكسار تعمل مثل العدسة. تؤثر سماكة صفيحة الكوارتز بشكل مباشر على مقدار تطور العدسات الحرارية، مما قد يؤدي إلى تدهور جودة الشعاع المقاسة بعامل M². تمتص المنطقة الأكثر سُمكًا المزيد من الطاقة، مما يؤدي إلى عدسة أقوى وانخفاض دقة التركيز.
تشير الدراسات إلى أنه في أنظمة مرنان الليزر، يمكن أن يؤدي تباين السُمك بمقدار 0.006 مم إلى زيادة عامل M² بمقدار 0.3، مما يؤدي إلى انخفاض دقة تركيز الشعاع بمقدار 15%. ويستخدم المهندسون ألواح كوارتز ذات تباين سمك إجمالي (TTV) أقل من 0.010 مم للحفاظ على الحد الأدنى من العدسات الحرارية والحفاظ على نفاذية عالية لعدسات التركيز الليزري.
اختبار عتبة التلف المستحث بالليزر (LIDT) وفقًا للمواصفة القياسية ISO 21254 للعينات المتغيرة السُمك
عتبة الضرر الناجم عن الليزر (LIDT) يحدد الحد الأقصى لكثافة الطاقة التي يمكن للوح الكوارتز تحملها قبل حدوث تلف. يقوم المهندسون باختبار LIDT وفقًا لمعايير ISO 21254 باستخدام ألواح كوارتز بسماكات مختلفة لتقييم الأداء. غالبًا ما تظهر المناطق الأرق قيم LIDT أقل بسبب زيادة التسخين والإجهاد المحلي.
تكشف البيانات المستمدة من تطبيقات الليزر عالية الطاقة أن انحراف السماكة بمقدار 0.007 مم يمكن أن يقلل من انحراف السماكة من 10 جول/سم² إلى أقل من 5 جول/سم² عند الطول الموجي 1064 نانومتر ومدة النبضة 10 نانومتر. يجب أن تحافظ ألواح الكوارتز في تكنولوجيا الليزر على سماكة صارمة لضمان مقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية ومقاومة التآكل القوية، وحماية المكونات الأساسية لليزر من التلف.
النقاط الرئيسية:
تحكم صارم في السماكة يزيد من LIDT وسلامة النظام.
اختبار الأيزو 21254 ISO 21254 تتحقق من موثوقية لوحة الكوارتز.
سمك متناسق يحمي مرنان الليزر وعدسات التركيز البؤري في الأنظمة عالية الطاقة.
ما هي مواصفات أجهزة التحليل الطيفي والتحليلية التي توازن بين الدقة والتكلفة؟
يجب أن يوازن مصممو أجهزة التحليل الطيفي والتحليل بين الحاجة إلى الدقة وحقائق تكلفة التصنيع. ويلعب تحمل سماكة لوح الكوارتز دورًا محوريًا في هذه العملية، حيث يؤثر بشكل مباشر على موثوقية القياس وأداء النظام. يختار المصنعون المواصفات التي تدعم كلاً من النتائج عالية الجودة والإنتاج الاقتصادي لمجموعة واسعة من التطبيقات.
متطلبات دقة قانون بير-لامبرت ومتطلبات دقة قانون بير-لامبرت واشتقاق تحمل طول المسار
يحدد تفاوت سُمك لوح الكوارتز طول المسار في الكوفيت، وهو أمر بالغ الأهمية لقياسات قانون بير-لامبرت. وتتطلب الكوفيتات عالية الدقة تفاوتًا قدره ± 0.01 مم، بينما تسمح الكوفيتات القياسية بـ ± 0.05 مم. يؤثر هذا الاختلاف على دقة قراءات الامتصاص في أنظمة القياس الدقيقة.
يجب على المصنعين النظر في المفاضلة بين التفاوتات الأكثر صرامة وزيادة تكاليف الإنتاج. يتطلب تشديد التفاوتات المسموح بها عمليات تصنيع متقدمة ومعدات متخصصة، مما قد يؤدي إلى زيادة التكاليف وتمديد المهل الزمنية. إذا تجاوزت التفاوتات المسموح بها قدرات التصنيع، فقد يحدث إهدار للمواد وإفراط في الإنتاج.
نوع الكوفيت | التسامح |
|---|---|
كوفيتات عالية الدقة | ± 0.01 مم |
الكوفيتات القياسية | ± 0.05 مم |
يضمن التحكم الدقيق في طول المسار نتائج قياس موثوقة في الأجهزة البصرية والأنظمة التحليلية.
مواصفات سُمك التحليل الطيفي للأشعة فوق البنفسجية (<250 نانومتر) لشفافية الأشعة فوق البنفسجية العميقة
يجب أن تفي صفيحة الكوارتز بمواصفات سمك صارمة لتحقيق شفافية الأشعة فوق البنفسجية العميقة تحت 250 نانومتر. وتعتمد العديد من الأدوات البصرية وأنظمة الليزر على الكوارتز بسماكات تتراوح بين 0.1 مم إلى 0.5 مم لتحقيق الأداء الأمثل للنقل البصري. تدعم هذه المواصفات مقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية والنقل المستقر في البيئات الصعبة.
تقدم الشركات المصنعة مجموعة متنوعة من منتجات الكوارتز للتحليل الطيفي بالأشعة فوق البنفسجية، ولكل منها نطاقات سماكة وأسعار مختلفة. يوضح الرسم البياني التالي الحد الأدنى والحد الأقصى لسماكات ألواح الكوارتز المستخدمة في التحليل الطيفي بالأشعة فوق البنفسجية تحت 250 نانومتر:
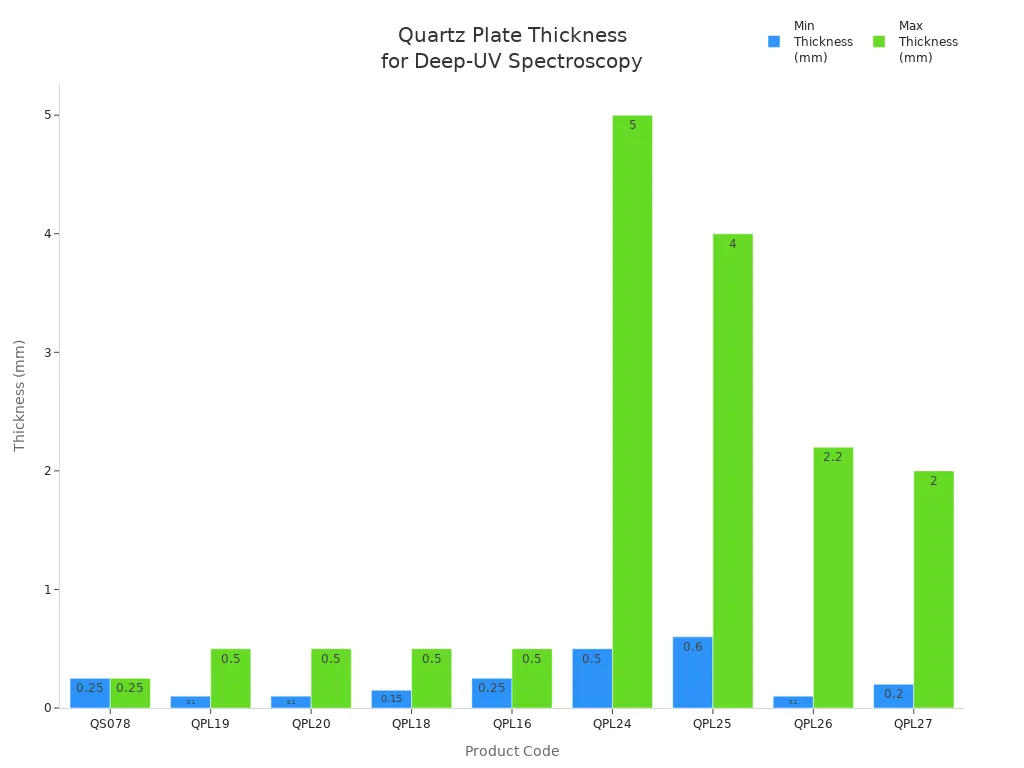
النقاط الرئيسية:
سمك صفيحة الكوارتز ما بين 0.1 مم و0.5 مم يدعم تطبيقات الأشعة فوق البنفسجية العميقة.
تنوع المنتجات تسمح للمستخدمين باختيار الأنسب لاحتياجات القياس الخاصة بهم.
أداء الإرسال البصري المستقر يضمن نتائج دقيقة في أنظمة الليزر والأنظمة البصرية.
يعتمد اختيار صفيحة الكوارتز للتحليل الطيفي بالأشعة فوق البنفسجية على كل من المتطلبات الفنية واعتبارات التكلفة.
تفاوتات التفاوتات القياسية المرجعية في الكوفيت (± 0.02 مم) لتطبيقات القياس
تضع الكوفيتات القياسية المرجعية المعيارية معيارًا للدقة في مختبرات القياس والمختبرات التحليلية. وتتطلب هذه الكوفيتات تفاوتات سماكة لوحة الكوارتز بدقة تصل إلى ± 0.02 مم لضمان طول مسار بصري متسق وقياس موثوق به. تعتمد الأدوات الدقيقة وعدسات الليزر على هذه المعايير للمعايرة ومراقبة الجودة.
يوازن المصنعون بين الدقة والتكلفة من خلال إعطاء الأولوية للكوارتز عالي النقاء، والمعدات المتقدمة، ومراقبة الجودة الصارمة. كما أنهم يديرون التكاليف من خلال التحسين الدقيق للعملية والالتزام بمعايير الصناعة. ويضمن هذا النهج أن تقدم الكوفيتات المرجعية أداءً عاليًا وقيمة اقتصادية.
المواصفات | التأثير |
|---|---|
تفاوت ± 0.02 مم | يضمن دقة القياس |
كوارتز عالي النقاء | يحسن أداء الإرسال البصري |
اختبار صارم | يحافظ على موثوقية النظام |
تلعب الكوفيتات القياسية المرجعية دورًا حيويًا في دعم دقة أنظمة القياس التحليلية والبصرية.
أين تحدد التطبيقات البحثية والمعملية تفاوتات السماكة المخصصة؟

غالبًا ما تتطلب التطبيقات البحثية والمعملية تفاوتات سماكة مخصصة للوح الكوارتز. يختار العلماء والمهندسون الكوارتز لتجانسها البصري وثباتها في البيئات الصعبة. تعتمد هذه الأنظمة على التحكم الدقيق لتحقيق نتائج دقيقة في الفحص المجهري وتحليل المواد والبصريات الكمية.
تطبيقات الفحص المجهري: تفاوت السماكة مقابل مفاضلة مسافة العمل
تعتمد تطبيقات الفحص المجهري على سُمك لوح الكوارتز للتحكم في مسافة العمل وجودة الصورة. ويستخدم الباحثون شرائح كوارتز ذات سماكة سماكة قياسية تبلغ ± 0.005 بوصة (127 ميكرومتر) للحفاظ على تركيز ووضوح متناسقين. يمكن أن يصل التباين على طول الشريحة الواحدة إلى 0.002 بوصة (51 ميكرومتر)، مما يؤثر على دقة صور المجهر.
تساعد لوحة الكوارتز ذات التفاوتات الضيقة العلماء على تحقيق نتائج قابلة للتكرار وصور واضحة. عندما تختلف السماكة، تتغير مسافة العمل، مما قد يقلل من دقة القياسات.
معدات توصيف المواد (XRD، XRF) مواصفات الركيزة (XRD، XRF)
تستخدم معدات توصيف المواد مثل XRD وXRF ركائز ألواح الكوارتز لدعم العينات أثناء التحليل. تحدد المختبرات تفاوتات مخصصة للطول والعرض والسماكة لضمان جمع بيانات موثوقة. يوفر الكوارتز درجة نقاء عالية وتوحيدًا بصريًا، مما يحسن من دقة القياسات القائمة على الليزر.
تدعم ألواح الكوارتز ذات الأبعاد الدقيقة النتائج المتسقة في تحليل المواد. تستفيد المختبرات من الركائز التي تقلل من أخطاء القياس وتزيد من قابلية التكرار.
متطلبات منصة أبحاث البصريات الكمومية والضوئيات الضوئية فائقة الدقة (± 0.01 مم)
تتطلب منصات أبحاث البصريات الكمية والضوئيات الضوئية تفاوتات فائقة الدقة للوحات الكوارتز. يستخدم العلماء الكوارتز بسماكة تحمل ضيقة تصل إلى ± 0.01 مم للحفاظ على مسارات بصرية مستقرة وتقليل انجراف خط الأساس في التجارب الحساسة. في أحد المختبرات، أدى التحول إلى ألواح الكوارتز عالية الدقة إلى التخلص من أخطاء الامتصاص بمقدار 5-101 تيرابايت في مقايسات البروتين.
النقاط الرئيسية:
صفيحة كوارتز فائقة الدقة يضمن نتائج مستقرة وقابلة للتكرار.
أنظمة الليزر تتطلب تفاوتات ضيقة لقياسات بصرية دقيقة.
تطبيقات مخصصة الاستفادة من تحسين جودة البيانات وقابلية التكرار التجريبي.
تدعم ألواح الكوارتز ذات التفاوتات فائقة الدقة الأبحاث المتقدمة في البصريات الكمية والضوئيات. يحقق العلماء قياسات موثوقة وبيانات عالية الجودة من خلال اختيار الكوارتز بالمواصفات المناسبة.
تدعم تفاوتات السُمك الدقيقة في الكوارتز التشغيل عالي الأداء والموثوق والآمن في العديد من الأنظمة المتقدمة. يعمل التحكم الدقيق في سُمك صفيحة الكوارتز على تحسين دقة القياس وإنتاجية الجهاز وسلامة النظام في تطبيقات أشباه الموصلات والبصريات والليزر. يوصي خبراء الصناعة المهندسين والمشترين التقنيين باتباع أفضل الممارسات التالية:
التوصية | الوصف |
|---|---|
تطابق درجة اللوحة وسُمكها | قم بمواءمة المواصفات مع التطبيق المحدد والطول الموجي. |
التشاور مع الموردين | ناقش متطلبات السُمك المخصص أو تشطيب السطح المخصص. |
تقييم التكلفة الإجمالية للملكية | ضع في اعتبارك تأثير النقاء العالي والتفاوتات الأكثر صرامة على الأداء والعمر الافتراضي مقابل التكاليف. |
التفاوض على الأسعار والمهل الزمنية | التعديل بناءً على حجم الطلب واحتياجات التخصيص. |
تحديد جودة السطح | استخدم معايير حفر الخدش (على سبيل المثال، 10-5 لكل MIL-PRF-13830B) لضمان جودة السطح العالية. |
طلب بيانات القياس | يجب على الموردين توفير البيانات والدعم للمعالجات السطحية المخصصة. |
يتيح الكوارتز نتائج دقيقة في الأبحاث والتصنيع وتقنية الليزر. يساعد المهندسون الذين يعطون الأولوية للتفاوتات الدقيقة في اختيار ألواح الكوارتز في ضمان أفضل النتائج لأنظمتهم.
الأسئلة الشائعة
ما هو تفاوت السماكة المعتاد لألواح الكوارتز في تصنيع أشباه الموصلات؟
وتتطلب معظم تطبيقات أشباه الموصلات ألواح كوارتز بسماكة سماكة تتراوح بين ± 0.03-0.05 مم. ويساعد هذا التحكم المحكم في الحفاظ على درجة حرارة موحدة وأداء جهاز متسق أثناء معالجة الرقاقة.
ما هي العوامل التي تحدد تفاوت السماكة المطلوب في التطبيقات البصرية؟
يأخذ المهندسون في الاعتبار الطول الموجي وخطأ واجهة الموجة وفرق المسار البصري. على سبيل المثال، يحتاج قياس التداخل في كثير من الأحيان إلى تفاوتات ضيقة تصل إلى ± 0.005 مم للحفاظ على أخطاء القياس أقل من 5%.
ماذا يحدث إذا اختلفت سماكة صفيحة الكوارتز كثيرًا في أنظمة الليزر؟
يمكن أن يتسبب التباين المفرط في السُمك في حدوث إجهاد وعدسة حرارية وانخفاض عتبات التلف الناتج عن الليزر. تُظهر البيانات أن انحرافًا بمقدار 0.007 مم قد يقلل من عتبة التلف بمقدار 50%.
ما هي سماكة السماكة التي تستخدمها كوفيتات الكوارتز القياسية للتحليل الطيفي؟
عادةً ما تكون كوفيتات الكوارتز القياسية ذات سماكة تحمل ± 0.05 مم. قد تستخدم الكوفيتات عالية الدقة ± 0.01 مم لقياسات امتصاص أكثر دقة.
ما هي تفاوتات السماكة المخصصة التي تطلبها مختبرات الأبحاث؟
غالبًا ما تطلب المعامل البحثية تفاوتات مخصصة تتراوح من ± 0.15 مم للشرائح العامة إلى ± 0.01 مم للبصريات الكمية. يعتمد الاختيار على احتياجات دقة التجربة.





