UV sınıfı erimiş kuvars ar kaplama diskleri, derin ultraviyole optik sistemlerde olağanüstü iletim ve dayanıklılık sağlar. Yüksek saflıkta kuvars ve gelişmiş kaplamalar, bu optiklerin çevresel bozulmaya direnmesini ve tutarlı performansı sürdürmesini sağlar. Optik cihazlar, nicel test yöntemleriyle gösterildiği gibi titiz malzeme seçimi ve kaplama teknolojisinden faydalanır:
Test Türü | Açıklama |
|---|---|
Optik Performans Testi | Dayanıklılık testinden önce ve sonra geçirgenlik, yansıtma ve bulanıklığı ölçer |
Temas Açısı Ölçümleri | Su ve yağ damlacıkları için yüzey iticiliğini ölçer |
Uzun Vadeli Performans Değerlendirmesi | Döngüsel kirlenme ve temizleme testleri ile kaplama ömrünü değerlendirir |
Optimize edilmiş uv sınıfı erimiş kuvars ar kaplama teknolojisine sahip kuvars diskler, zorlu ortamlarda güvenilir optikler için standardı belirler.
Önemli Çıkarımlar
UV sınıfı erimiş kuvars diskler, 200nm'de 85%'yi aşan yüksek iletim oranları sağlayarak derin UV uygulamaları için idealdir.
Kuvarsın düşük hidroksil içeriği emilim piklerinin oluşmasını engelleyerek ultraviyole optiklerde daha iyi performans sağlar.
Yansıma önleyici kaplamalar ışık iletimini artırır ve yansımayı azaltarak optik sistemlerin verimliliğini artırır.
Kaplanmış kuvars diskler lazer hasarına karşı güçlü bir direnç gösterir ve yüksek enerjili ortamlarda bile özelliklerini korur.
Düzenli bakım ve kontrollü koşullar UV AR kaplamalı kuvars disklerin ömrünü ve performansını uzatabilir.
UV-Grade Kaynaşmış Kuvars Disk Performansını Belirleyen Temel Malzeme Özellikleri Nelerdir?

UV sınıfı erimiş kuvars diskler benzersiz malzeme özellikleri sayesinde ultraviyole optiklerde olağanüstü performans sunar. Bu diskler, üstün iletim, dayanıklılık ve kararlılık elde etmek için yüksek saflıkta erimiş kuvarsı gelişmiş üretim standartlarıyla birleştirir. Mühendisler ve bilim insanları zorlu ortamlarda güvenilir çalışma sağlamak için bu özelliklere güvenmektedir.
Hidroksil İçeriğinin Derin UV İletimi Üzerindeki Etkisi
Hidroksil içeriği, kuvarsın derin ultraviyole ışığı nasıl ilettiğini belirlemede kritik bir rol oynar. Yarı iletken sınıfı erimiş kuvarstaki düşük hidroksil seviyeleri, aksi takdirde 300 nm'nin altındaki dalga boylarında iletimi azaltacak emilim zirvelerini önler. Üreticiler hidroksil içeriğini 10 ppm'den az olacak şekilde kontrol ederek yüksek saflıkta erimiş kuvars elde ederler, bu da iletim hızlarının 200nm'de 85%'yi aşmasını sağlar ve UV optiklerinde tutarlı performansı destekler.
Yüksek hidroksil içeriğine sahip kuvars, derin UV aralığında önemli iletim kaybı gösterir. Örneğin, 150-200 ppm hidroksil içeren kuvars 200nm'de sadece yaklaşık 40% iletirken, düşük OH kuvars çok daha yüksek iletimi korur. Bu fark, hidroksil gruplarının UV enerjisini absorbe etme şeklinden kaynaklanır, istenmeyen absorpsiyon bantları oluşturur ve optik bileşenlerin etkinliğini sınırlar.
Düşük hidroksil içeriği, kuvars disklerin şeffaf kalmasını ve derin UV uygulamaları için verimli olmasını sağlar.
Hidroksil içeriği ve iletimi hakkında kilit noktalar:
Düşük hidroksil (85% iletim sağlar
Yüksek hidroksil (>150ppm) 200nm'de iletimi ~40%'ye düşürür
Kontrollü hidroksil seviyeleri UV sınıfı erimiş kuvars özellikleri için gereklidir
Düşük OH Kuvarsda Solarizasyon Direnç Mekanizmaları
Solarizasyon direnci, kuvarsın yoğun UV ışığına maruz kaldıktan sonra kalıcı iletim kaybına nasıl direndiğini açıklar. Düşük OH kuvars daha az safsızlık içerir, bu da ışığı emen ve performansı düşüren renk merkezlerinin oluşumunu önlemeye yardımcı olur. Bu özellik, lazer sistemleri ve litografi ekipmanı gibi yüksek etkili UV ortamlarında kullanılan optikler için hayati önem taşır.
Elektriksel füzyon süreçleriyle üretilen kuvars güçlü solarizasyon direnci gösterir. Testler, UV dereceli erimiş kuvarsın 10⁶ J/cm²'yi aşan kümülatif UV dozlarına önemli bir iletim kaybı olmadan dayanabildiğini göstermektedir. Malzemenin saflığı ve düşük hidroksil içeriği, aksi takdirde enerjiyi hapsedecek ve kuvarsı karartacak kusurların oluşumunu engellemek için birlikte çalışır.
Solarizasyon direnci, kuvars disklerin optik netliklerini ve işlevlerini uzun süreler boyunca korumalarını sağlar.
Mülkiyet | Neden | Performans Üzerindeki Etkisi |
|---|---|---|
Düşük hidroksil içeriği | Daha az kirlilik | Daha az renk merkezi oluşumu |
Elektriksel füzyon | Yüksek malzeme saflığı | Geliştirilmiş solarizasyon direnci |
Yüksek UV doz toleransı | İstikrarlı yapı | Zaman içinde iletimi korur |
UV Spektrumunda Kırılma İndisi ve Dağılım Özellikleri
Kuvarsın kırılma indisi ve dağılma özellikleri, ışığın malzemeden geçerken nasıl büküldüğünü ve yayıldığını belirler. UV sınıfı erimiş kuvars, 193nm'de yaklaşık 1,4585'lik bir kırılma indisine sahiptir ve bu da optik sistemlerde ışığın hassas kontrolünü destekler. Bu özellik, düşük termal genleşme ve yüksek homojenlik ile birleştiğinde, kuvarsı kararlı ve doğru ışık iletimi gerektiren uygulamalar için ideal hale getirir.
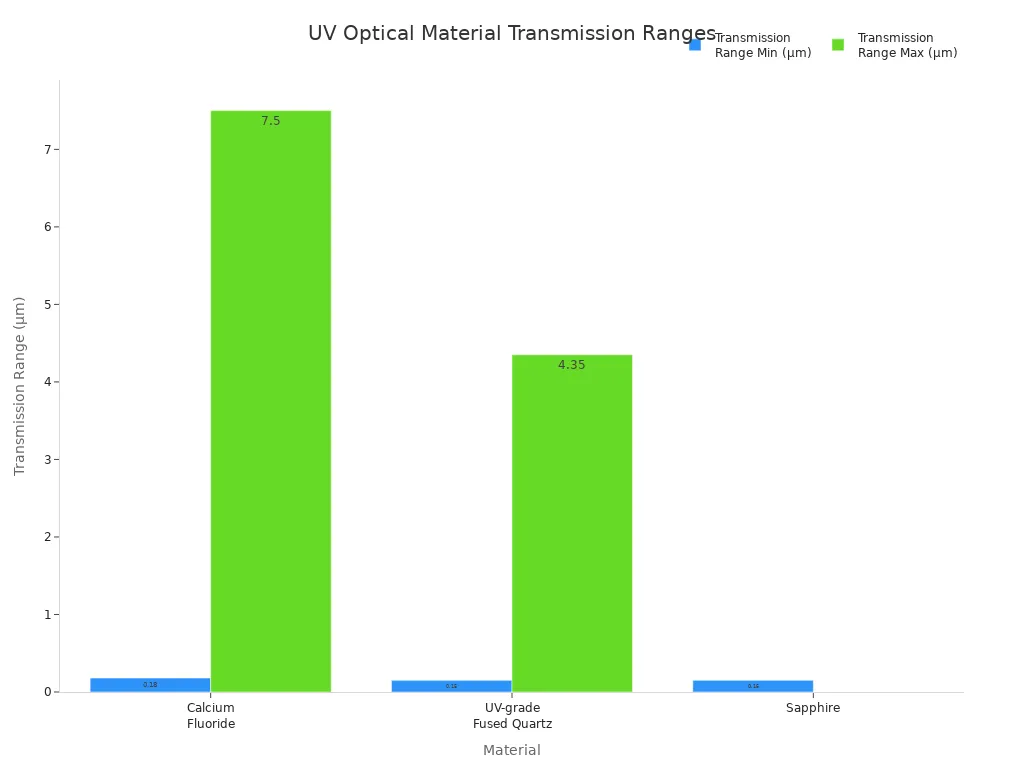
Diğer optik malzemelerle karşılaştırıldığında, kuvars geniş bir iletim aralığı ve düşük gerilimli çift kırılma sunar. Kalsiyum florür ve safir de UV ışığını iletir, ancak kuvars yüksek kırılma indisi homojenliği ve çevresel değişikliklere karşı direnci ile öne çıkar. Aşağıdaki tabloda yaygın UV optik malzemelerin iletim aralıkları gösterilmektedir:
Kuvarsın kırılma indisi kararlılığı ve düşük dispersiyonu UV optiklerinde tutarlı performans sağlar.
Kırılma indisi ve dağılma özelliklerinin özeti:
193nm'de kuvars kırılma indisi: 1.4585
Düşük dağılım hassas ışık kontrolünü destekler
Yüksek homojenlik ve düşük çift kırılma optik performansı artırır
Yansıma Önleyici Kaplamalar UV Dalga Boyu Aralığında Kuvars Disk Optik Performansını Nasıl Geliştirir?

Yansıma önleyici kaplamalar, ultraviyole optiklerde kullanılan kuvars disklerin performansını artırmada hayati bir rol oynar. Bu kaplamalar yansımayı azaltmaya ve iletimi artırmaya yardımcı olarak yüksek hassasiyetli optik sistemler için gerekli hale gelir. Mühendisler, ar kaplamalı camın zorlu UV ortamlarında güvenilir sonuçlar vermesini sağlamak için gelişmiş malzemeler ve tasarım stratejileri seçer.
UV Şeffaflığı için Geniş Bant Aralıklı Malzeme Seçimi
Geniş bant aralıklı malzemeler, etkili UV yansıma önleyici kaplamaların temelini oluşturur. Hafniyum oksit ve alüminyum oksit gibi bu malzemeler 300nm'nin altındaki dalga boylarında şeffaf kalarak kuvars disklerin daha fazla ultraviyole ışık geçirmesini sağlar. Bu malzemelerin seçimi, ar kaplamalı camın yüksek geçirgenliği korumasını ve yoğun UV maruziyetinden kaynaklanan hasara karşı direnç göstermesini sağlar.
Üreticiler, istenmeyen emilimi engelledikleri ve lazer hasarına karşı güçlü direnç sağladıkları için geniş bant aralıklı oksitler kullanmaktadır. Kuvars ve bu kaplamaların kombinasyonu, yüksek enerjili UV lazerlere maruz kalan optiklerde istikrarlı performansı destekler. Bu yaklaşım aynı zamanda optik kalite ve dayanıklılık için katı endüstri standartlarını da karşılamaktadır.
Geniş bant aralıklı malzemeler, kuvars disklerin UV uygulamalarında tutarlı optik performans sunmasını garanti eder.
Geniş bant aralıklı malzeme seçimi hakkında önemli noktalar:
Geniş bant aralıklı oksitler yüksek UV geçirgenliği sağlar
Hafniyum oksit ve alüminyum oksit gibi malzemeler lazer hasarına karşı dayanıklıdır
Doğru seçim optik standartlara uygunluğu sağlar
UV AR Kaplama Tasarımında Dispersiyon Yönetimi
UV spektrumu boyunca yüksek geçirgenliği korumak için dağılım yönetimi çok önemlidir. Tasarımcılar, ışığın kaplamayla nasıl etkileşime girdiğini kontrol etmek için silika ve daha yüksek indeksli oksitler gibi farklı kırılma indislerine sahip malzemelerin dönüşümlü katmanlarını kullanır. Bu katmanlama tekniği, ar kaplamalı camın geniş bir dalga boyu aralığında düşük yansıtıcılık elde etmesini sağlar.
Katman kalınlığının hassas kontrolügenellikle dalga boyunun dörtte birine kadar, yansımayı azaltan yıkıcı girişim yaratır. Bu tasarımın etkinliği farklı geliş açılarında değişebilir, bu nedenle mühendisler her uygulama için yapıyı dikkatlice ayarlamalıdır. Destekleyici veriler, kalınlığın bir nanometreye kadar kontrol edilmesinin kritik UV lazer dalga boylarında yansımayı 0,5%'nin altında tutabileceğini göstermektedir.
Dispersiyon yönetimi, kuvars optiklerin çok dalga boylu UV sistemlerinde istikrarlı performans sağlamasına yardımcı olur.
Tasarım Özelliği | Neden | Performans Üzerindeki Etkisi |
|---|---|---|
Alternatif kırılma indisi | Silika ve oksitlerin katmanlaşması | Geniş dalga boyu kapsamı |
Hassas kalınlık kontrolü | Çeyrek dalga boylu katmanlar | Düşük yansıtıcılık |
Açı ayarı | Uygulamaya özel tasarım | Tutarlı iletim |
Yoğun UV Kaplamaların Nem Bariyeri Özellikleri
Yoğun UV kaplamalar kuvars diskleri zamanla optik performansı düşürebilecek nemden korur. Üreticiler neme karşı güçlü bariyerler oluşturmak için çok katmanlı yapılar ve hidrofobik işlemler kullanmaktadır. UV kürleme gibi gelişmiş kürleme yöntemleri, su nüfuzuna direnen ve kaplanmış camın özelliklerini koruyan kararlı ağlar oluşturmaya yardımcı olur.
Çevresel strese dayanıklılık bu kaplamaların bir diğer önemli özelliğidir. Bazı tasarımlar, küçük hasarlardan kurtulan ve kuvars optiklerin hizmet ömrünü uzatan kendi kendini iyileştiren bileşenler içerir. Bu stratejiler, kaplamanın zorlu dış mekan veya laboratuvar koşullarında bile etkinliğini korumasını sağlar.
Nem bariyeri özellikleri, kuvars disklerin kullanım ömürleri boyunca güvenilir optik performans sunmasını sağlar.
İşte nem bariyeri özelliklerinin bir özeti:
Kanıt Türü | Açıklama |
|---|---|
Çok Katmanlı Yapılar | Nem dayanıklılığını artırır, hassas malzemeleri nem hasarından korur |
Hidrofobik İşlemler | Su emilimini azaltır, optik ve yapışkan özellikleri korur |
Gelişmiş Kürleme Yöntemleri | Kararlı polimer ağları oluşturur, nemin nüfuz etmesine karşı direnç gösterir |
Çevresel Strese Dayanıklılık | Zaman içinde optik performansı koruyun |
Kendi Kendini İyileştiren Bileşenler | Hasarlardan kurtulun, hizmet ömrünü ve performansı uzatın |
Kaplamalı UV Kuvars Disk Performansını Karakterize Eden Kantitatif İletim ve Yansıtma Ölçütleri Nelerdir?
Mühendisler, kaplanmış UV kuvars disklerin gerçek dünya optiklerinde nasıl performans gösterdiğini değerlendirmek için nicel ölçütler kullanır. Bu ölçütler arasında geçirgenlik, yansıtma ve lazer hasarına karşı direnç yer alır. Bu özelliklerin anlaşılması, kullanıcıların zorlu optik uygulamalar için doğru kuvarsı seçmelerine yardımcı olur.
UV-A, UV-B, UV-C Aralıklarında Spektral İletim Özellikleri
Spektral geçirgenlik, farklı UV dalga boylarında kuvarsın içinden ne kadar ışık geçtiğini tanımlar. Yüksek kaliteli kuvars diskler UV-A ve UV-B aralıklarında 99%'nin üzerinde geçirgenlik gösterirken, UV-C aralığında 98%'nin üzerini korur. Bu özellikler kuvarsın saflığından ve yansıma önleyici kaplamaların etkinliğinden kaynaklanmaktadır.
Üreticiler, 190-400nm aralığında hassas veriler sağlayan spektrofotometreler kullanarak geçirgenliği ölçmektedir. Kuvars diskler üzerindeki kaplamalar yansımayı en aza indirir ve özellikle 248nm ve 355nm gibi kritik dalga boylarında geçen UV ışık miktarını en üst düzeye çıkarır. Bu yüksek geçirgenlik, spektroskopi ve litografide kullanılan hassas optikleri destekler.
Aşağıdaki tabloda kaplanmış kuvars için temel geçirgenlik özellikleri özetlenmektedir:
UV Aralığı | Tipik Geçirgenlik | Temel Mülkiyet Nedeni | Performans Üzerindeki Etkisi |
|---|---|---|---|
UV-A | >99% | Yüksek kuvars saflığı | Maksimum ışık çıkışı |
UV-B | >99% | Gelişmiş AR kaplamalar | Geliştirilmiş optik netlik |
UV-C | >98% | Düşük hidroksil içeriği | Güvenilir derin UV optikleri |
AR Kaplama Performansının Açısal Bağımlılığı
Işığın bir kuvars diske çarptığı açı, geçirgenlik özelliklerini etkiler. Normal geliş açısında, AR kaplamalar yansıtıcılığı düşük ve geçirgenliği yüksek tutar. Açı arttıkça, kaplamanın etkili kalınlığı değişir ve bu da geçirgenliği biraz azaltabilir.
Mühendisler 0°, 15° ve 30° gibi farklı açılarda geçirgenliği ölçerek açısal bağımlılığı test ederler. Veriler, kaplanmış kuvars disklerin 15°'ye kadar 1%'den daha az geçirgenlik kaybettiğini ve 30°'de sadece 3-5% kaybettiğini göstermektedir. Bu özellikler, kuvars optiklerin, ışık onlara tam olarak çarpmadığında bile yüksek performansı korumasını sağlar.
Açısal bağımlılıkla ilgili önemli noktalar şunlardır:
Normal gelişte düşük yansıtma
15°'ye kadar minimum geçirgenlik kaybı
Çok açılı sistemler için kararlı optik özellikler
Lazer Hasar Eşiği Ölçümü ve Sertifikasyonu
Lazer hasar eşiği, bir kuvars diskin özellikleri değişmeden önce ne kadar enerji kaldırabileceğini ölçer. Yüksek lazer hasar eşikleri, kuvarsın güçlü UV lazerlere bozulmadan dayanabileceği anlamına gelir. Bu özellik, yüksek akımlı ortamlarda kullanılan optikler için çok önemlidir.
Üreticiler ISO 21254-2 gibi standart testleri kullanarak lazer hasar eşiklerini onaylamaktadır. Kaplanmış kuvars diskler için sonuçlar genellikle 355nm'de 7 J/cm²'yi ve 266nm'de 10 J/cm²'yi aşmaktadır. Bu yüksek eşikler, kuvarsın tekrarlanan lazer maruziyetinden sonra bile geçirgenliğini ve optik özelliklerini koruduğunu doğrulamaktadır.
Aşağıdaki tablo, lazer hasar eşiği ile optik performans arasındaki ilişkiyi vurgulamaktadır:
Test Dalga Boyu | Lazer Hasar Eşiği | Temel Mülkiyet Nedeni | Performans Üzerindeki Etkisi |
|---|---|---|---|
355nm | >7 J/cm² | Yoğun AR kaplamalar | Uzun vadeli optik güvenilirlik |
266nm | >10 J/cm² | Geniş bant aralıklı malzemeler | Sürekli yüksek geçirgenlik |
Çevresel Koşullar ve Dalga Boyu Değişimleri Kuvars Disk UV AR Kaplama Stabilitesini Nasıl Etkiler?
Çevresel koşullar, kuvars diskler üzerindeki UV yansıma önleyici kaplamaların uzun vadeli stabilitesinde önemli bir rol oynamaktadır. Nem, sıcaklık değişiklikleri ve yoğun UV maruziyeti gibi faktörler bu kaplamaların optik özelliklerini ve dayanıklılığını etkileyebilir. Bu koşullar altında neler olduğunu anlamak, mühendislerin zorlu uygulamalar için doğru kuvarsı seçmelerine yardımcı olur.
Nem Kaynaklı İletim Bozulma Mekanizmaları
Nem, kuvars kaplamaların özelliklerinde önemli değişikliklere neden olabilir. Nem kaplamaya girdiğinde, özellikle UV maruziyeti altında emilimin artmasına ve iletimin düşmesine neden olabilir. Zamanla bu süreç optik sistemlerde kuvars diskin etkinliğini azaltabilir.
Araştırmacılar, nemli UV koşulları altında bazı kaplamaların kalınlığını kaybettiğini ve bunun da malzemenin bozulduğuna işaret ettiğini gözlemlemişlerdir. Örneğin, bir nanokompozit kaplama yaklaşık 45 mikrometre kalınlık kaybettiStandart bir polimer 50 mikrometre kaybederken, her ikisi de kuru UV koşullarında neredeyse hiç kayıp göstermemiştir. Bu fark, nemin bozunmayı nasıl hızlandırdığını ve kuvars yüzeyinin özelliklerini nasıl etkilediğini vurgulamaktadır.
Nemin kuvars kaplamalar üzerindeki etkilerini özetlemek için şu kilit noktaları göz önünde bulundurun:
Nem emilimi artırır ve iletimi azaltır
Nemli UV ortamlarında malzeme bozulması daha hızlıdır
Kuru koşullar kaplama özelliklerinin korunmasına yardımcı olur
Termal Döngünün Kaplamanın Yapışması ve Bütünlüğü Üzerindeki Etkileri
Termal döngü, kuvars kaplamaların tekrarlanan ısıtma ve soğutmaya dayanma kabiliyetini test eder. Hızlı sıcaklık değişimleri kaplama ile kuvars alt tabaka arasında stres yaratarak bazen çatlaklara veya yapışma kaybına yol açabilir. Bu değişiklikler optik özellikleri değiştirebilir ve kaplanmış kuvarsın ömrünü kısaltabilir.
Mühendisler, kaplamaların termal döngüye nasıl tepki verdiğini ölçmek için hızlandırılmış ömür testi protokollerini kullanır. ASTM G154 ve ISO 16474-3 gibi standartlar gerçek dünyadaki sıcaklık değişimlerini simüle ederken, ASTM D4060 ve ASTM D968 gibi diğer testler aşınma direncini kontrol eder. Bu yöntemler, hangi kaplamaların özelliklerini koruduğunu ve hangilerinin stres altında başarısız olabileceğini belirlemeye yardımcı olur.
Aşağıdaki tablo yaygın test protokollerini ve bunların odak noktalarını özetlemektedir:
Test Protokolü | Açıklama |
|---|---|
ASTM G154 | Dış mekan UV ve sıcaklık maruziyetini simüle eder |
ISO 16474-3 | Yüksek sıcaklıklarda UV ve neme odaklanır |
ASTM D4060 | Aşınma direncini ölçer |
ASTM D968 | Düşen kuma karşı direnci değerlendirir |
Yüksek Etkili UV Uygulamalarında Fotokimyasal Bozunma
Fotokimyasal bozulma, yoğun UV ışığına maruz kaldığında kuvars kaplamaların özelliklerini etkiler. Yüksek etkili UV, kaplamadaki kimyasal bağları kırarak renk değişikliklerine, iletimin azalmasına veya yüzey kirliliğine yol açabilir. Bu etkiler, lazerler veya açık hava güneş ışığı gibi güçlü UV kaynaklarının bulunduğu ortamlarda daha belirgin hale gelir.
UV radyasyonu da dahil olmak üzere çevresel yaşlanma ve yüzey kirliliği, kaplamaların gerçek dünyadaki performansını sınırlar. Kimyasal korozyon ve kirlenme de bir rol oynar ve bu faktörlere karşı güçlü direnç gösteren kaplamaların seçilmesini önemli hale getirir. Mühendisler, zorlu ortamlarda kuvars disklerin özelliklerini korumaya yardımcı olmak için genellikle koruyucu önlemler ve düzenli temizlik kullanırlar.
Fotokimyasal bozunmanın ana nedenlerini ve etkilerini gösteren özet bir tablo aşağıda verilmiştir:
Neden | Kuvars Özellikleri Üzerindeki Etkisi |
|---|---|
Yüksek etkili UV maruziyeti | Kimyasal bağ kırılması, renk değişiklikleri |
Yüzey kirliliği | Artan emilim, azalan berraklık |
Kimyasal korozyon | Kaplama kalınlığı kaybı, performans kaybı |
Mühendisler bu çevresel etkileri anlayarak kuvars disklerin özelliklerini daha iyi koruyabilir ve uzun vadeli optik performans sağlayabilirler.
Hangi Gerçek Dünya Uygulama Verileri UV AR Kaplamalı Kuvars Disk Performans Avantajlarını Doğruluyor?
Gerçek dünya verileri, UV AR kaplamalı kuvars disklerin gelişmiş optik sistemlerin özelliklerini nasıl geliştirdiğini göstermektedir. Litografi, spektroskopi ve lazer uygulamalarından elde edilen saha sonuçları, bu kaplamalarla elde edilen performans kazanımlarını vurgulamaktadır. Kullanıcılar verim, hassasiyet ve uzun vadeli maliyet tasarruflarında ölçülebilir faydalar görebilirler.
UV Litografi Sistemi Performans İyileştirmeleri
UV litografi sistemleri, hassas sonuçlar elde etmek için kuvarsın özelliklerine bağlıdır. Mühendisler AR kaplamalı kuvars kullandıklarında, yüksek hacimli yonga plakası işleme sırasında daha yüksek iletim ve daha kararlı optik özellikler gözlemlerler. Bu gelişmeler, yarı iletken yonga plakalarında daha fazla lazer gücü dağıtımına ve daha iyi desen doğruluğuna olanak tanır.
Üretim ortamlarında AR kaplamalı kuvars, kaplamasız alternatiflere kıyasla gofret verimini 8-10% artırır. Daha yüksek iletim, fotoreziste daha fazla UV enerjisinin ulaşması anlamına gelir, bu da daha hızlı pozlama sürelerini ve daha keskin özellik tanımını destekler. Bu da zaman içinde yarı iletken üretiminde daha az hata ve daha iyi verim sağlar.
Litografi sistemi verilerinden çıkarılacak önemli sonuçlar şunlardır:
Daha yüksek verim artan iletim nedeniyle
Geliştirilmiş desen doğruluğu kararlı optik özelliklerden
Azaltılmış kusur oranları yüksek hacimli üretimde
AR Kaplamalarla Spektroskopi Hassasiyetinin Artırılması
UV spektroskopisi, düşük analit konsantrasyonlarını tespit etmek için kuvarsın özelliklerine dayanır. Kuvars diskler üzerindeki AR kaplamalar, geçen UV ışık miktarını artırarak sistemin hassasiyetini ve sinyal-gürültü oranını yükseltir. Bu kaplamalar ayrıca yansıma kayıplarını en aza indirerek daha doğru ölçümler yapılmasını sağlar.
Laboratuvar testleri, AR kaplamalı kuvarsın minimum tespit edilebilir konsantrasyonu 1,3 ila 1,5 kat artırdığını göstermektedir. Kaplamalar bunu, paraziti azaltan ve ölçüm doğruluğunu artıran yüksek iletim ve düşük yansıtma sağlayarak başarıyor. Sonuç olarak, bilim insanları daha az miktarda maddeyi tespit edebilir ve daha net veriler elde edebilir.
Aşağıdaki tabloda ana özellikler ve bunların spektroskopi performansı üzerindeki etkileri özetlenmektedir:
Özellik | Açıklama |
|---|---|
Yüksek İletim | Daha fazla UV ışığının geçmesine izin vererek hassasiyeti artırır |
Düşük Yansıtma | Sinyal netliğini koruyarak ışık kaybını en aza indirir |
Geliştirilmiş Algılama | Ölçüm doğruluğunu artırır ve algılama limitlerini düşürür |
UV Optik Sistemler için Toplam Sahip Olma Maliyeti Analizi
UV optik sistemlerinin toplam sahip olma maliyeti kuvars bileşenlerin özelliklerine ve dayanıklılığına bağlıdır. AR kaplamalı kuvars diskler daha az sıklıkta değiştirme ve bakım gerektirir, bu da arıza süresini ve işletme giderlerini azaltır. Sistemin kullanım ömrü boyunca bu tasarruflar artar ve birinci sınıf kaplamalara yapılan ilk yatırımı haklı çıkarır.
Endüstriyel kurulumlardan elde edilen saha verileri, AR kaplı kuvarsın 1.000 saatlik hızlandırılmış UV maruziyetinden sonra ilk iletiminin 97%'den fazlasını koruduğunu göstermektedir. Buna karşılık, kaplanmamış kuvars yüzey kirlenmesi ve oksidasyon nedeniyle 85-88%'ye düşmektedir. Bu fark, birçok uygulamada AR kaplamalı optikler için 18-24 aylık bir geri ödeme süresine yol açmaktadır.
Maliyetle ilgili faydaların bir özeti aşağıda yer almaktadır:
Daha düşük bakım maliyetleri daha uzun ömürlü özellikleri nedeniyle
Azaltılmış arıza süresi daha az değişimden
Daha hızlı yatırım geri dönüşü gelişmiş optik sistemler için
Yansıma önleyici kaplamalara sahip UV sınıfı erimiş kuvars diskler zorlu ortamlarda olağanüstü optik performans sunar. Bu kuvars bileşenler, gelişmiş alt tabaka ve kaplama özelliklerini bir araya getirerek yüksek iletim, dayanıklılık ve maliyet etkinliğini korur. Mühendisler kuvarsı UV optik sistemlerinde hassasiyet, güvenilirlik ve uzun vadeli kararlılık için optimize eder.
Faktör | Açıklama |
|---|---|
Hassasiyet ve Tekdüzelik | Optimum optik özellikler için tutarlı kaplama kalınlığı ve bileşimi çok önemlidir. |
Yapışma ve Dayanıklılık | Kaplama ve kuvars substrat arasındaki güçlü yapışma, maliyetli arızaları önler ve özellikleri korur. |
Kirlenme Kontrolü | Temiz oda ortamları ve titiz yüzey hazırlığı kuvars özelliklerini kusurlardan korur. |
Süreç Optimizasyonu | Biriktirme parametrelerindeki uzmanlık, kuvars için istenen optik özellikleri sağlar. |
Üstün Dayanıklılık | Sertlik ve çevresel kararlılık için tasarlanmış formülasyonlar, kuvars özelliklerini zaman içinde korur. |
Optimize edilmiş özelliklere sahip kuvars diskler, gelişmiş UV uygulamalarında güvenilir optik performans ve hassasiyet için standardı belirler.
SSS
UV sınıfı erimiş kuvarsı derin UV uygulamaları için uygun kılan nedir?
UV sınıfı erimiş kuvars çok düşük hidroksil içeriği ve yüksek saflık içerir. Bu özellikler 300 nm'nin altındaki dalga boylarında yüksek iletim sağlar. Mühendisler, zorlu UV ortamlarında güvenilir performans için bu malzemeyi seçmektedir.
Yansıma önleyici kaplama kuvars diskler için ne işe yarar?
Yansıma önleyici kaplama yüzey yansımasını azaltır ve ışık geçirgenliğini artırır. Bu gelişme, optik sistemlerin hedeflerine daha fazla UV enerjisi göndermesine yardımcı olur. Kaplamalı kuvars diskler daha yüksek hassasiyet ve verimliliği destekler.
AR kaplamalı UV kuvars için 248nm'de tipik iletim oranı nedir?
AR kaplamalı UV kuvars diskler genellikle 248nm'de 99%'nin üzerinde iletim oranlarına ulaşır. Bu yüksek değer hem substrat saflığından hem de gelişmiş kaplama tasarımından kaynaklanmaktadır. Kullanıcılar gelişmiş verim ve ölçüm doğruluğundan faydalanır.
Hangi çevresel faktörler AR kaplama performansını etkileyebilir?
Nem, sıcaklık değişiklikleri ve yoğun UV maruziyeti AR kaplamalarını bozabilir. Nem emilimi artırabilir, termal döngü ise çatlaklara neden olabilir. Mühendisler stabiliteyi korumak için yoğun kaplamalar ve koruyucu önlemler kullanırlar.
İpucu: Düzenli temizlik ve kontrollü ortamlar UV AR kaplamalı kuvars disklerin ömrünü uzatmaya yardımcı olur.
Kaplanmış UV kuvars diskler için lazer hasar eşiği nedir?
Kaplamalı UV kuvars diskler genellikle 355nm'de 7 J/cm²'nin üzerindeki lazer akıcılığına dayanır. Bu eşik, yüksek güçlü lazer sistemlerinde güvenli çalışma sağlar. Sertifikasyon, güvenilirlik için ISO 21254-2 standartlarını takip eder.





