Disques de quartz Les lentilles de précision à performance optique reposent sur les propriétés optiques exceptionnelles du verre de quartz. Ce matériau offre une grande pureté optique, une clarté optique exceptionnelle et une homogénéité constante de l'indice de réfraction. 0,3 ppm en valeur absolue. Le verre de quartz maintient une transmission élevée dans les longueurs d'onde visibles, infrarouges et ultraviolettes, et conserve ses propriétés optiques même à des températures élevées. La structure du verre de quartz garantit une résistance supérieure aux dommages causés par le laser et une biréfringence minimale, ce qui en fait un matériau idéal pour la fabrication d'instruments optiques. Ces qualités permettent d'améliorer les performances des instruments optiques modernes, en particulier pour les lentilles optiques exigeantes.
Principaux enseignements
Le verre de quartz offre une pureté et une clarté optiques élevées, essentielles pour produire des images nettes dans les systèmes optiques avancés.
Le maintien d'un indice de réfraction uniforme dans les disques de quartz empêche la distorsion du front d'onde, ce qui garantit une imagerie précise et une haute résolution.
Des techniques de fabrication avancées, telles que la fusion et le refroidissement contrôlés, améliorent l'homogénéité de l'indice de réfraction du verre de quartz.
Les normes ISO guident la mesure de l'homogénéité de l'indice de réfraction, garantissant que les lentilles de quartz répondent à des critères de performance stricts.
La faible dilatation thermique du verre de quartz permet aux lentilles de conserver leur mise au point et leurs performances à des températures variables.
Quelles performances d'homogénéité de l'indice de réfraction les lentilles à disque de quartz atteignent-elles ?

Les performances optiques des disques de quartz Les lentilles de précision dépendent de la capacité du verre de quartz à maintenir un indice de réfraction uniforme sur l'ensemble de la lentille. Cette propriété garantit que la lumière traverse la lentille sans distorsion, ce qui est essentiel pour la précision de l'imagerie dans l'optique moderne. L'homogénéité de l'indice de réfraction, ainsi que d'autres propriétés optiques telles que la transmission, la stabilité thermique, la résistance aux dommages causés par le laser et la biréfringence, définissent la valeur du verre de quartz dans la fabrication d'instruments optiques.
Comment la variation de l'indice de réfraction affecte la qualité du front d'onde et la résolution de l'image
Indice de réfraction La variation de l'indice de réfraction dans le verre de quartz peut provoquer une distorsion du front d'onde, qui a un impact direct sur la qualité des images produites par les instruments optiques. Lorsque l'indice de réfraction change dans une lentille, la vitesse de la lumière se modifie, ce qui déforme les fronts d'onde et crée des aberrations classiques. Ces distorsions peuvent conduire à une image molle, à un contraste réduit et à une résolution moindre, en particulier dans les optiques de haute précision.
Même de petites inhomogénéités peuvent introduire des front d'onde erreurs. Par exemple, à la jonction de coins de quartz cimentés, il se produit un fractionnement angulaire ou un cisaillement des fronts d'onde. Les ondes ordinaires et extraordinaires ont des indices de réfraction différents, ce qui entraîne une séparation et une distorsion spatiales. La différence de vitesse entre ces fronts d'onde contribue à l'erreur globale de front d'onde, qui peut dégrader le rapport Strehl et réduire la fonction de transfert de modulation (MTF) du système.
Points clés :
Distorsion du front d'onde résultats de la variation de l'indice de réfraction dans le verre de quartz.
Résolution de l'image diminue à mesure que les erreurs de front d'onde augmentent.
Imagerie précise nécessite une grande homogénéité de l'indice de réfraction.
Cette relation montre pourquoi disques de quartz Les performances optiques des lentilles de précision reposent sur un contrôle strict de l'homogénéité de l'indice de réfraction.
Méthodes de fabrication pour l'obtention d'une homogénéité supérieure dans le domaine de la physique des lentilles
Les fabricants utilisent des techniques avancées pour obtenir une homogénéité supérieure de l'indice de réfraction dans le verre de quartz. La température de fusion, la vitesse de refroidissement et le traitement thermique jouent tous un rôle essentiel dans la détermination des propriétés optiques finales du disque de lentille. Des températures de fusion plus élevées et des vitesses de refroidissement plus rapides peuvent augmenter l'indice de réfraction, tandis qu'un traitement thermique contrôlé permet de le stabiliser.
Silice fondue synthétique, produite par hydrolyse à la flammeLes boules de bière de qualité supérieure offrent la plus grande uniformité grâce au traitement d'un seul lot et à des gradients de composition minimes. Les fabricants sélectionnent des zones de boules présentant des gradients de température minimaux pendant la fusion afin de garantir une homogénéité constante. La cartographie interférométrique identifie les zones appropriées avant le broyage, ce qui permet de maintenir les performances optiques requises pour les optiques modernes.
Facteur de fabrication | Effet sur l'homogénéité | Performance optique résultante |
|---|---|---|
Température de fusion | Une température plus élevée augmente l'indice de réfraction | Peut provoquer une inhomogénéité si elle n'est pas contrôlée |
Taux de refroidissement | Un refroidissement plus rapide augmente l'indice de réfraction | Peut introduire des gradients |
Traitement thermique | Stabilise l'indice de réfraction | Améliore l'uniformité |
Ces méthodes permettent de garantir que le verre de quartz répond aux exigences élevées de la fabrication d'instruments optiques.
Normes de mesure : Protocoles de test d'homogénéité ISO 11455
Les fabricants utilisent les protocoles ISO 11455 pour mesurer l'homogénéité de l'indice de réfraction dans le verre de quartz. Cette norme exige des tests interférométriques précis, utilisant souvent l'interférométrie Mach-Zehnder à une longueur d'onde spécifique. Le processus permet de cartographier l'indice de réfraction sur l'ensemble de l'ouverture transparente et d'identifier les variations, même mineures, susceptibles d'affecter les performances optiques.
Les tests garantissent que les disques de quartz respectent des tolérances strictes, telles que Δn <2×10-⁶ pour les matériaux de qualité UV. Les résultats guident la sélection des ébauches de lentilles pour les optiques de haute précision, garantissant que seul le meilleur matériau passe à l'étape suivante de la production. L'application cohérente de ces normes renforce la fiabilité et les performances des disques de quartz et des lentilles de précision.
Résumé des points clés :
ISO 11455 fournit une méthode normalisée pour mesurer l'homogénéité de l'indice de réfraction.
Cartographie interférométrique détecte de petites variations dans le verre de quartz.
Tolérances strictes garantissent des performances optiques de haute qualité.
Ces protocoles permettent de maintenir les normes élevées requises pour une imagerie précise dans l'optique moderne.
Quelles sont les performances de transmission UV-IR offertes par les matériaux des lentilles à disque de quartz ?

Le verre de quartz se distingue en optique par sa capacité à transmettre la lumière depuis les ultraviolets profonds jusqu'aux longueurs d'onde infrarouges. Cette transmittance élevée en fait un choix privilégié pour les instruments optiques qui exigent clarté et efficacité sur une large gamme spectrale. Les sections suivantes examinent les performances des différentes qualités de verre de quartz, l'impact des impuretés et la manière dont la conception du système affecte la transmission globale.
Courbes de transmission spectrale : Disque de quartz de qualité UV, optique ou IR
Le verre de quartz offre une excellente transmission spectrale, mais les performances varient en fonction de la qualité. Le verre de quartz de qualité UV offre une transmission supérieure à 85% à 193nm, tandis que la qualité optique maintient plus de 80% de 260nm à 2500nm, et la qualité IR excelle à plus de 85% à 2800nm. Ces différences résultent du processus de fabrication et de la pureté des matières premières.
Les ingénieurs sélectionnent le grade approprié en fonction des exigences de l'application en matière de longueur d'onde. Par exemple, le verre de quartz de qualité UV permet la lithographie en UV profond, tandis que le verre de qualité IR convient à l'imagerie thermique. Le bon choix garantit une transmission élevée et des performances optimales dans des environnements exigeants.
Verre de quartz Qualité | Transmission UV (193nm) | Transmission dans le visible (589nm) | Transmission IR (2800nm) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Qualité UV (JGS1) | >85% | >92% | 60-75% | Imagerie UV profonde, lithographie |
Qualité optique (JGS2) | 45-60% | >92% | 50-65% | Optique générale, livraison de laser |
Classe IR (JGS3) | 30-50% | >91% | >85% | Spectroscopie NIR, imagerie thermique |
Ce tableau montre comment le choix de la qualité du verre de quartz affecte directement la transmission et l'adéquation à des instruments optiques spécifiques.
Comment les impuretés métalliques créent des bandes d'absorption dans la gamme des UV
Les impuretés métalliques dans le verre de quartz peuvent créer des bandes d'absorption, en particulier dans le domaine de l'ultraviolet. Même des traces d'aluminium ou de titane, souvent inférieures à 1 partie par million, peuvent réduire la transmission de 15-30% à des longueurs d'onde inférieures à 250 nm. Ces impuretés absorbent la lumière UV, ce qui entraîne une baisse de la sensibilité et de l'efficacité du système.
Les fabricants contrôlent les niveaux d'impureté grâce à une sélection rigoureuse des matières premières et à des techniques de purification avancées. En minimisant la teneur en métaux, ils s'assurent que le verre de quartz conserve une transmission élevée, en particulier pour les optiques sensibles aux UV. Ce processus permet de produire des instruments optiques fiables et efficaces.
Points clés :
Impuretés métalliques provoquent des bandes d'absorption UV.
Faibles niveaux d'impuretés garantissent une transmission élevée dans le verre de quartz.
Purification est essentiel pour les optiques de qualité UV.
Comprendre le rôle des impuretés aide les ingénieurs à sélectionner le meilleur verre de quartz pour les applications UV de haute performance.
Calculs de transmission du système pour les assemblages de lentilles à éléments multiples
Les concepteurs de systèmes doivent tenir compte de l'effet cumulatif de chaque élément de la lentille sur la transmission globale. Dans un assemblage à plusieurs éléments, même de petites pertes par élément peuvent s'additionner, réduisant la lumière totale qui atteint le détecteur. Par exemple, un système de lentilles à six éléments utilisant un verre de quartz de qualité optique à 193 nm ne transmet qu'environ 26% de la lumière originale, alors qu'un verre de quartz de qualité UV avec des revêtements antireflets peut atteindre une transmission de système de 74%.
Ces calculs guident la sélection des matériaux et des revêtements pour les systèmes optiques complexes. Les ingénieurs utilisent les données de transmission pour optimiser les performances et s'assurer que l'instrument final répond aux exigences de sensibilité.
Facteur de conception du système | Effet sur la transmission | Résultat |
|---|---|---|
Nombre d'éléments | Plus d'éléments augmentent les pertes | Réduction de la transmission totale |
Qualité des matériaux | Une qualité supérieure améliore le rendement | Efficacité accrue du système |
Qualité du revêtement | De meilleurs revêtements réduisent les reflets | Meilleure diffusion de la lumière |
Une planification minutieuse et la sélection des matériaux permettent aux concepteurs d'optiques de maximiser les avantages du verre de quartz dans les instruments optiques avancés.
Quelles sont les performances de stabilité optique thermique qui permettent de concevoir des lentilles à disque de quartz athermique ?
Le verre de quartz offre une stabilité optique thermique exceptionnelle, ce qui en fait un choix de premier ordre pour la conception de lentilles athermiques. Cette stabilité garantit que les instruments optiques conservent leur mise au point et leurs performances même lorsque les températures changent. Les ingénieurs s'appuient sur ces propriétés pour construire des systèmes fiables dans des environnements exigeants.
Coefficient thermo-optique (dn/dT) Impact sur la stabilité de la longueur focale
Le coefficient thermo-optique (dn/dT) décrit la manière dont l'indice de réfraction du verre de quartz varie en fonction de la température. Une faible valeur de dn/dT signifie que la lentille conserve ses propriétés optiques même lorsque les températures fluctuent. Cette stabilité est cruciale pour les optiques utilisées dans des environnements soumis à de fortes variations de température.
Le verre de quartz a un dn/dT de +1,0×10-⁵ K-¹, ce qui est beaucoup plus bas que beaucoup d'autres matériaux optiques. Cette faible valeur se traduit par un décalage moindre de la longueur focale, ce qui permet de conserver des images nettes et claires. Par exemple, une lentille de 100 mm de longueur focale fabriquée en verre de quartz se décale de seulement 20 microns sur une plage de 100°C, alors qu'une lentille similaire fabriquée en verre BK7 se décale de 350 microns.
Points clés :
Faible dn/dT en verre de quartz maintient la longueur focale stable.
Des images nettes résultent d'un décalage minimal de la mise au point.
De meilleures performances en cas de changement de température.
Cette propriété permet aux concepteurs de créer des optiques qui fonctionnent de manière fiable dans des conditions chaudes et froides.
Conception de lentilles athermiques : Performance du quartz par rapport à d'autres matériaux optiques
La conception de la lentille athermique vise à maintenir la mise au point stable malgré les changements de température. Le verre de quartz se distingue par sa faible dilatation thermique et son faible dn/dT. Ces caractéristiques le rendent plus stable que de nombreuses autres solutions.
D'autres matériaux, tels que le verre BK7 et le saphir, présentent des valeurs de dilatation thermique et de dn/dT plus élevées. Cela entraîne des décalages de mise au point plus importants et des performances moins fiables dans les environnements où la température varie. Le verre de quartz permet aux systèmes de lentilles de maintenir la qualité de l'image sans mécanismes de compensation complexes.
Matériau | Dilatation thermique (α) | dn/dT | Décalage de la mise au point (100°C) | Performance athermique |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Verre de quartz | 0.5×10-⁶ K-¹ | +1.0×10-⁵ K-¹ | 20 μm | Excellent |
Verre BK7 | 7.1×10-⁶ K-¹ | +2.5×10-⁶ K-¹ | 350 μm | Modéré |
Saphir | 5.0×10-⁶ K-¹ | +1.3×10-⁵ K-¹ | 260 μm | Bon |
Ce tableau montre comment le verre de quartz surpasse les autres matériaux dans les applications de lentilles athermiques.
Résultats des tests de cyclage en température : Mesures de décalage de la mise au point selon MIL-STD-810
Les ingénieurs testent les lentilles en verre de quartz en les exposant à des cycles de températures extrêmes, conformément à des normes telles que MIL-STD-810. Ces tests font passer la lentille d'une température très basse à une température très élevée, en vérifiant les changements de performance optique. Le verre de quartz fait preuve d'une stabilité exceptionnelle au cours de ces cycles.
Lors d'un test, un métal en verre de quartz a supporté 15 cycles de -195,8°C à 200°C. La lentille n'a montré aucun changement significatif en termes de performances optiques ou de dommages physiques. Ce résultat démontre la capacité du matériau à maintenir la mise au point et la clarté, même dans des conditions difficiles.
Résumé des résultats :
Pas de changement d'orientation significatif après des cycles de température répétés.
Pas de dommages physiques observée dans les lentilles en verre de quartz.
Des performances fiables pour les instruments optiques dans des environnements extrêmes.
Ces résultats confirment que le verre de quartz est idéal pour les optiques qui doivent fonctionner dans de larges plages de température.
Quelle est la performance du seuil de dommage optique pour les applications laser de haute puissance ?
Le verre de quartz offre une protection exceptionnelle contre les dommages induits par le laser, ce qui en fait un matériau de choix pour les optiques laser de haute puissance. Les ingénieurs s'appuient sur sa résistance supérieure au laser pour garantir la fiabilité des instruments optiques dans des environnements exigeants. Comprendre comment la qualité de la surface, les dommages sous la surface et la sélection des matériaux affectent les performances aide les concepteurs à créer des systèmes laser plus sûrs et plus efficaces.
Mesure du seuil de dommage induit par laser (LIDT) selon ISO 21254
La LIDT définit l'énergie laser maximale qu'un matériau peut supporter avant d'être endommagé. La norme ISO 21254 définit la norme de mesure de ce seuil dans le verre de quartz, garantissant des résultats cohérents et fiables. Les ingénieurs utilisent ces données pour sélectionner les matériaux qui répondent aux exigences des optiques laser de haute puissance.
Les essais consistent à exposer des échantillons de verre de quartz à des impulsions laser contrôlées et à enregistrer le niveau d'énergie auquel les dommages apparaissent. Les résultats montrent que le verre de quartz de haute pureté atteint des valeurs LIDT supérieures à 20 J/cm² à 355 nm, ce qui est nettement plus élevé que de nombreux autres matériaux. Ce seuil élevé permet aux instruments optiques de fonctionner en toute sécurité à des puissances laser intenses.
Points clés :
LIDT mesure la limite d'énergie avant tout dommage matériel.
ISO 21254 garantit des tests précis et reproductibles.
Haut LIDT en verre de quartz pour une meilleure résistance au laser.
Ces résultats guident la sélection des matériaux pour les applications où la sécurité et la performance sont essentielles.
Comment la qualité de la surface et l'endommagement de la subsurface affectent le seuil d'endommagement
La qualité de la surface et les dommages sous la surface (SSD) jouent un rôle majeur dans la détermination de la LIDT du verre de quartz. Même des imperfections mineures peuvent créer des points faibles qui abaissent le seuil d'endommagement. Des dommages sous la surface plus profonds, souvent causés par des particules abrasives lors du polissage, entraînent une augmentation des signaux de détection et une réduction de la LIDT.
Une étude portant sur trois groupes d'échantillons a montré une relation claire entre la profondeur de la DSS et le signal de détection. Le groupe 1 avait un Profondeur du SSD de 1,96 μmLes profondeurs plus importantes produisent des signaux plus forts et des valeurs LIDT plus faibles. Les défauts à forte absorption peuvent réduire la LIDT de plus de 40%, ce qui limite considérablement la capacité du système.
Groupe d'échantillons | Profondeur du SSD (μm) | Relation entre les signaux de détection |
|---|---|---|
Groupe 1 | 1.96 | En rapport avec la taille des particules abrasives |
Groupe 2 | 7.28 | Une plus grande profondeur génère un signal de détection plus important |
Groupe 3 | 11.51 | Une plus grande profondeur génère un signal de détection plus important |
Le maintien de surfaces lisses et la minimisation de la SSD garantissent que le verre de quartz offre la plus grande résistance possible au laser.
Sélection des matériaux pour les systèmes de lentilles laser UV et IR de haute puissance
Le choix de la bonne qualité de matériau est essentiel pour les applications laser de haute puissance. Le verre de quartz UV-FS (KU-1) offre une grande transparence dans les régions UV et visible, sans bandes d'absorption entre 170 et 250 nm. UV-IR FS (Infrasil 302) offre d'excellentes propriétés de l'ultraviolet profond à l'infrarouge moyen, sans bulles ni inclusions.
Les ingénieurs sélectionnent ces qualités en fonction de la longueur d'onde et de la puissance requises pour leurs systèmes laser. Les deux matériaux offrent la durabilité et la clarté nécessaires aux optiques laser de pointe, garantissant ainsi des performances et une sécurité à long terme.
Qualité des matériaux | Caractéristiques |
|---|---|
UV-FS (KU-1) | Grande transparence dans l'UV/visible, pas de bandes d'absorption (170-250 nm), stable, sans bulles ni inclusions. |
UV-IR FS (Infrasil 302) | Excellentes propriétés, pas de bandes d'absorption à partir de 250 nm, absence de bulles/inclusions, convient pour le DUV jusqu'à l'IR moyen. |
Points clés :
Qualité des matériaux affecte la résistance au laser et la clarté.
UV-FS et UV-IR FS supportent les systèmes laser UV et IR de grande puissance.
Sélection appropriée garantit des performances fiables dans le domaine de l'optique laser.
Le choix d'une qualité de verre de quartz appropriée maximise la sécurité et l'efficacité des instruments optiques de grande puissance.
Quelle performance de biréfringence garantit un fonctionnement de la lentille indépendant de la polarisation ?
La biréfringence peut affecter les performances des optiques, en particulier dans les systèmes qui nécessitent un contrôle précis de la polarisation. Le verre de quartz présente une faible biréfringence de contrainte, ce qui le rend adapté à de nombreux instruments optiques. Comprendre comment mesurer, contrôler et appliquer la performance de la biréfringence aide les ingénieurs à concevoir des optiques laser fiables.
Méthodes de mesure de la biréfringence sous contrainte selon ASTM C1093
Les ingénieurs utilisent la norme ASTM C1093 pour mesurer la biréfringence des contraintes dans le verre de quartz. Cette norme s'appuie sur des techniques photoélastiques qui révèlent les schémas de contraintes internes en analysant la façon dont la lumière polarisée passe à travers la lentille. Ce processus permet d'identifier les zones où les contraintes peuvent avoir un impact sur les performances optiques.
La mesure photoélastique consiste à placer le disque de quartz entre des polariseurs croisés et à observer les motifs colorés qui en résultent. Ces motifs indiquent l'ampleur et la distribution de la contrainte résiduelle, qui peut être quantifiée en nanomètres par centimètre. Une mesure cohérente garantit que seuls les disques à faible biréfringence peuvent être utilisés dans des applications optiques de haute précision.
Méthode de mesure | Objectif | Informations clés |
|---|---|---|
Analyse photoélastique | Révèle le stress interne | Identifie les zones de biréfringence |
Polariseurs croisés | Visualisation des schémas de stress | Quantifie la contrainte en nm/cm |
Norme ASTM C1093 | Assurer la cohérence | Guide la sélection des matériaux |
Cette approche permet aux fabricants de maintenir un contrôle de qualité strict et de fournir des instruments optiques fiables.
Contrôle du processus de recuit pour minimiser les contraintes résiduelles dans les lentilles à disques de quartz
Le processus de recuit joue un rôle essentiel dans la réduction des contraintes résiduelles et la minimisation de la biréfringence dans le verre de quartz. Les fabricants contrôlent soigneusement la température et la vitesse de refroidissement pendant le recuit afin d'obtenir des résultats optimaux. Un processus de refroidissement lent et échelonné permet d'éviter la formation de contraintes internes susceptibles de dégrader les performances optiques.
Le programme de recuit le plus efficace consiste à chauffer le disque de quartz à 1100°C, puis à le refroidir par étapes : 15°C par heure de 1100°C à 950°C, 30°C par heure à 750°C, et 60°C par heure à 450°C, suivi d'un refroidissement naturel en dessous de 450°C. Cette méthode garantit un relâchement progressif des contraintes et une biréfringence uniforme sur l'ensemble de la lentille. Le tableau suivant résume les paramètres clés :
Stade | Plage de température | Taux de refroidissement |
|---|---|---|
Phase de chauffage | Jusqu'à 1100°C | 4,5/R²°C/min |
Phase de refroidissement | 1100°C à 950°C | 15°C/heure |
950°C à 750°C | 30°C/heure | |
750°C à 450°C | 60°C/heure | |
Stade de refroidissement naturel | Inférieur à 450°C | Isolation jusqu'à <100°C |
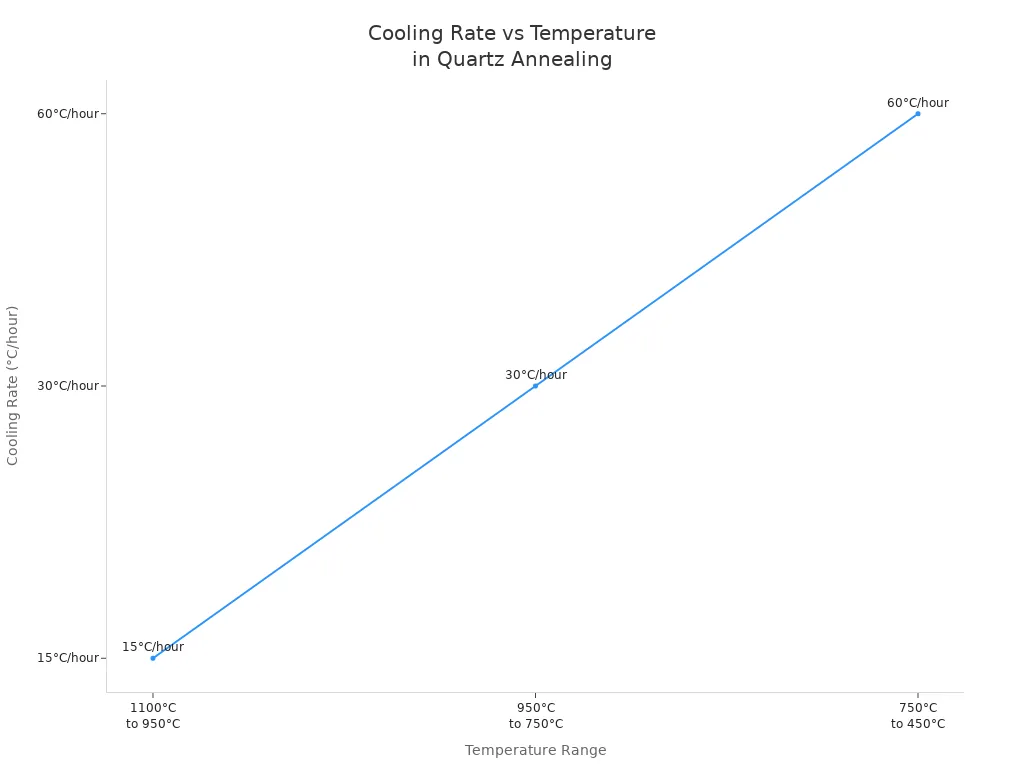
Points clés :
Recuit contrôlé réduit les contraintes résiduelles et la biréfringence.
Refroidissement par étapes empêche l'accumulation de stress interne.
Biréfringence uniforme est doté d'une optique de haute qualité.
Ce processus garantit que le verre de quartz répond aux exigences strictes de l'optique laser et des instruments optiques avancés.
Quand la biréfringence compte : Applications d'imagerie sensibles à la polarisation et applications d'imagerie standard
La biréfringence devient critique dans les optiques sensibles à la polarisation, comme la microscopie ou l'ellipsométrie. Dans ces systèmes, même de petites quantités de biréfringence de contrainte peuvent déformer les états de polarisation et réduire la précision des mesures. Les applications d'imagerie standard, cependant, tolèrent souvent une biréfringence plus élevée sans perte de performance significative.
Les concepteurs doivent adapter la performance de la biréfringence aux besoins de l'application. Pour les systèmes sensibles à la polarisation, ils spécifient une biréfringence de contrainte inférieure à 5 nm/cm, alors que l'imagerie standard peut accepter des valeurs allant jusqu'à 10 nm/cm. Cette sélection minutieuse garantit des résultats optimaux pour chaque type d'instrument optique.
Résumé :
Optique sensible à la polarisation nécessitent une faible biréfringence.
Imagerie standard peut tolérer des valeurs plus élevées.
Besoins de l'application guider la sélection et le traitement des matériaux.
En comprenant l'importance de la biréfringence, les ingénieurs peuvent choisir le bon verre de quartz pour chaque défi optique.
Quelles sont les normes de qualité qui valident les performances optiques des lentilles à disque de quartz ?
Les normes de qualité jouent un rôle essentiel pour garantir que les lentilles à disque de quartz répondent aux exigences des instruments optiques modernes. Les fabricants utilisent une combinaison de normes internationales et régionales pour valider chaque aspect de la performance des lentilles. Ces normes permettent de garantir que chaque lentille fournit des résultats fiables dans les applications optiques avancées.
Approche d'essai multi-normes pour une validation complète des performances optiques
Les fabricants s'appuient sur une approche multi-normes pour valider les performances optiques des lentilles à disque de quartz. Ils utilisent des normes internationales telles que ISO et ANSI pour couvrir tous les paramètres critiques, y compris l'homogénéité de l'indice de réfraction, la transmission et le seuil d'endommagement du laser. Ces tests complets garantissent que chaque lentille répond à des exigences strictes pour une utilisation dans des instruments optiques de haute précision.
Les protocoles d'essai comprennent souvent la norme ISO 11455 pour l'indice de réfraction, la norme ASTM E903 pour la transmission et la norme ISO 21254 pour le seuil d'endommagement du laser. Ces normes fournissent des lignes directrices claires pour les critères de mesure et d'acceptation. En suivant ces protocoles, les fabricants peuvent identifier et corriger tout problème de performance avant que les lentilles n'arrivent sur le marché.
Points clés :
Normes multiples assurer une validation complète.
ISO et ANSI couvrir les besoins mondiaux et régionaux.
Tests complets permet de bénéficier d'une optique fiable.
Cette approche aide les fabricants à fournir des lentilles qui fonctionnent de manière constante dans des environnements exigeants.
Type standard | Description |
|---|---|
Normes ISO | Reconnues au niveau mondial, ces normes fournissent un cadre complet pour les essais optiques, couvrant des critères tels que la précision dimensionnelle et la qualité des matériaux. |
Normes ANSI | Importantes en Amérique du Nord, ces normes garantissent que les composants optiques répondent aux exigences régionales spécifiques, en se concentrant sur les mesures de performance et les directives de sécurité. |
Contrôle statistique des processus pour des performances optiques constantes
Le contrôle statistique des processus (CSP) aide les fabricants à maintenir une qualité constante pendant la production des lentilles. Ils surveillent les paramètres clés tels que l'indice de réfraction et la transmission à l'aide de données en temps réel. Ce processus permet de détecter rapidement tout écart par rapport aux valeurs cibles.
Le SPC utilise des cartes de contrôle et des indices de capacité pour suivre l'évolution des performances. Par exemple, une valeur Cpk de 1,33 ou plus indique que le processus produit régulièrement des lentilles dans les limites des spécifications. En analysant ces données, les fabricants peuvent ajuster les processus afin d'éviter les défauts et de maintenir des rendements élevés.
Un résumé de la relation de cause à effet entre la CPS et la qualité des lentilles est présenté ci-dessous :
Méthode SPC | Paramètre contrôlé | Effet de causalité |
|---|---|---|
Cartes de contrôle | Indice de réfraction | Détecte les décalages précoces, évite les lentilles hors normes |
Indices de capacité (Cpk) | Transmission | Assure la stabilité du processus et maintient un rendement élevé |
Données en temps réel | Seuil de dommages laser | Permet une réponse rapide, réduit les taux de défaut |
SPC veille à ce que chaque lot de lentilles à disque de quartz réponde aux normes élevées requises pour les instruments optiques de pointe.
Exigences de certification : Systèmes de métrologie optique traçables au NIST
La certification à l'aide de systèmes de métrologie traçables au NIST garantit la précision des mesures. Les fabricants utilisent des équipements calibrés pour vérifier les propriétés des lentilles telles que l'indice de réfraction, la transmission et la biréfringence. Cette traçabilité relie chaque mesure aux normes nationales, garantissant ainsi des résultats fiables.
Les laboratoires tiers effectuent souvent ces certifications à l'aide d'outils avancés tels que des interféromètres Mach-Zehnder et des spectrophotomètres à laser. Ces laboratoires délivrent des certificats qui confirment la conformité aux normes ISO, ANSI et ASTM. Les clients peuvent consulter ces certificats pour vérifier que chaque lentille répond aux spécifications requises.
Résumé :
Systèmes traçables au NIST garantissent la précision des mesures.
Certification par un tiers confirme le respect des normes.
Lentilles certifiées fournissent une assurance pour les applications optiques critiques.
La certification renforce la confiance et la fiabilité des performances des lentilles à disque de quartz.
Comment les concepteurs optiques doivent-ils spécifier les exigences de performance pour les lentilles à disque de quartz ?
Les concepteurs optiques jouent un rôle crucial en veillant à ce que les lentilles à disque de quartz répondent aux besoins des applications avancées. Ils doivent spécifier des exigences de performance claires et mesurables pour garantir des résultats cohérents. Des spécifications bien définies aident les fabricants à fournir des lentilles qui permettent de réaliser des optiques de haute précision et des instruments optiques fiables.
Création de spécifications basées sur les performances pour l'achat de disques de lentilles
Les concepteurs doivent se concentrer sur des spécifications basées sur les performances qui tiennent compte des paramètres les plus critiques pour les lentilles à disque de quartz. Ces paramètres comprennent la pureté et la transparence optiques, la stabilité thermique, la résistance mécanique et la faible dispersion. Chaque facteur influence directement la capacité de la lentille à transmettre efficacement la lumière, à résister aux changements de température, à conserver sa forme et à minimiser les aberrations chromatiques.
Les données d'essai de l'industrie montrent que la pureté optique garantit une transmission élevée, ce qui est essentiel pour une imagerie précise. La stabilité thermique permet aux lentilles de fonctionner dans des environnements extrêmes, tandis que la résistance mécanique empêche la déformation pendant l'utilisation. Une faible dispersion réduit les franges de couleur, ce qui améliore la clarté de l'image. Les concepteurs qui incluent ces exigences dans les documents d'achat aident les fabricants à sélectionner les meilleurs matériaux et processus pour chaque application.
Conseil :
Définir des objectifs mesurables pour chaque paramètre.
Demande de certification des propriétés optiques et mécaniques.
Inclure le contexte de l'application tels que la gamme de longueurs d'onde, la température et les besoins en matière d'imagerie.
En suivant ces étapes, les concepteurs peuvent s'assurer que chaque lentille répond aux exigences de l'optique moderne.
Le tableau ci-dessous résume les principaux paramètres de performance et leur impact sur la qualité de l'objectif :
Paramètres | Description |
|---|---|
Pureté optique et transparence | Garantit une transmission élevée et minimise l'absorption de la lumière, ce qui est crucial pour les applications d'imagerie précises. |
Stabilité thermique | Résiste aux fluctuations de température, ce qui le rend adapté aux conditions extrêmes. |
Résistance mécanique | Grande durabilité et résistance à la déformation, assurant la stabilité dimensionnelle dans les applications exigeantes. |
Faible dispersion | Atténue les aberrations chromatiques, améliorant la clarté et la netteté de l'image. |
Un processus de spécification clair permet d'améliorer la communication avec les fournisseurs et d'obtenir des instruments optiques plus performants.
Les lentilles de précision à disques de quartz offrent des avantages inégalés pour l'optique avancée. Le verre de quartz se distingue par sa grande pureté optique, sa stabilité thermique et sa résistance supérieure au laser. Le tableau ci-dessous présente les principaux avantages :
Avantage | Description |
|---|---|
Pureté optique élevée | Excellente transmission dans le spectre UV et visible. |
Stabilité thermique | Dilatation thermique extrêmement faible, stable à haute température. |
Excellente résistance chimique | Très résistant à la corrosion, il garantit une durabilité à long terme. |
Résistance supérieure au laser | Résiste à des densités d'énergie élevées, idéal pour les optiques laser. |
Les ingénieurs doivent toujours spécifier et valider les paramètres clés lorsqu'ils choisissent des lentilles de précision à disques de quartz pour des applications critiques.
FAQ
Pourquoi les disques de quartz sont-ils idéaux pour la fabrication de lentilles de précision ?
Les disques de quartz offrent une grande pureté optique, un indice de réfraction stable et une excellente transmission des UV aux IR. Ces propriétés permettent d'obtenir des images nettes et des performances fiables dans les systèmes optiques avancés.
Quelle est la plage de transmission typique des lentilles à disque de quartz ?
Les lentilles à disque de quartz transmettent la lumière de 185 nm dans l'UV à 3500 nm dans l'IR. Le quartz de qualité UV atteint une transmission supérieure à 85% à 193 nm, ce qui permet des applications dans l'UV profond et le visible.
Quelles sont les normes qui valident la qualité optique des lentilles à disque de quartz ?
Les fabricants utilisent la norme ISO 11455 pour l'indice de réfraction, la norme ASTM E903 pour la transmission, la norme ISO 21254 pour les dommages causés par le laser et la norme ASTM C1093 pour la biréfringence. Ces normes garantissent des performances optiques cohérentes et de haute qualité.
Quel est le seuil d'endommagement du laser pour les disques de quartz de haute pureté ?
Les disques de quartz de haute pureté résistent à une fluence laser supérieure à 20 J/cm² à 355 nm. Ce seuil élevé permet un fonctionnement sûr dans les systèmes laser de haute puissance.
Que doivent spécifier les concepteurs optiques lorsqu'ils commandent des lentilles à disque de quartz ?
Les concepteurs doivent spécifier l'homogénéité de l'indice de réfraction, la transmission aux longueurs d'onde de l'application, le seuil d'endommagement du laser, la biréfringence sous contrainte et la stabilité thermique. La demande de certification et de données d'essai permet de s'assurer que la lentille répond à toutes les exigences.





