O corte a laser se torna mais econômico do que os métodos de lâmina de diamante para o corte de tubos de quartzo quando o volume de produção ultrapassa 8.000 tubos por ano, as exigências de qualidade da borda atingem os padrões de polimento a fogo ou são necessárias geometrias complexas. Materiais de alta pureza e aplicações premium também impulsionam essa mudança, pois a redução de sucata e a automação diminuem os custos. O cruzamento econômico depende tanto de fatores mensuráveis quanto de necessidades específicas de aplicação, tornando o corte a laser de tubos de quartzo econômico em muitos ambientes de fabricação avançados.
Principais conclusões
O corte a laser torna-se econômico para o corte de tubos de quartzo quando a produção excede 8.000 tubos por ano, devido aos custos mais baixos por tubo e à redução da mão de obra.
A automação no corte a laser pode economizar até 75% em custos de mão de obra, permitindo que um operador gerencie várias máquinas, o que aumenta a produtividade e a eficiência.
A eliminação do acabamento secundário com o corte a laser economiza $8-$15 por tubo, melhorando a consistência e reduzindo o tempo total de produção.
O corte a laser atinge taxas de refugo mais baixas (2-3%) em comparação com os métodos de lâmina de diamante (8-12%), levando a uma economia significativa de custos de material ao longo do tempo.
A capacidade de criar geometrias complexas com o corte a laser abre novas oportunidades de mercado, tornando-o uma opção viável até mesmo para produção de baixo volume ou de protótipos.
Quando o volume de produção justifica o investimento em equipamentos de corte a laser em vez de sistemas de lâmina de diamante?
O volume de produção desempenha um papel fundamental na determinação do custo-benefício do corte a laser tubo de quartzo o corte se torna a melhor opção. Os fabricantes devem pesar o número de tubos produzidos por ano em relação ao investimento em equipamentos e à economia operacional. A compreensão do ponto de equilíbrio ajuda os tomadores de decisão a planejar o crescimento e a eficiência.
Análise do volume de equilíbrio: 8.000-12.000 tubos Cálculo do limite anual
O ponto de equilíbrio para o corte econômico de tubos de quartzo por corte a laser geralmente fica entre 8.000 e 12.000 tubos por ano. As instalações que produzem abaixo dessa faixa geralmente consideram os métodos de lâmina de diamante mais econômicos devido aos custos iniciais mais baixos. À medida que a produção aumenta, a economia com a automação e a redução das taxas de refugo começam a superar os investimentos iniciais.
Quando a produção anual de tubos atinge a faixa de 8.000 a 12.000, o custo total por tubo cai significativamente com os sistemas a laser. Por exemplo, as configurações de lâminas de diamante podem custar $17-23 por tubo nesses volumes, enquanto os sistemas a laser podem reduzir esse custo para $16-21 por tubo. Essa mudança resulta de menos mão de obra, menos tubos rejeitados e a eliminação do acabamento secundário.
Causa | Efeito |
|---|---|
Maior volume anual de tubos | Menor custo por tubo com o corte a laser |
Automação e economia de sucata | Retorno mais rápido do investimento em equipamentos |
Menor necessidade de mão de obra | Aumento da eficiência de custos em volumes maiores |
Economia de custos de mão de obra: Redução de 75% por meio da automação ($70.000-100.000 anuais)
O corte a laser de tubos de quartzo é econômico e proporciona uma redução de 75% na mão de obra direta em comparação com os métodos de lâmina de diamante. Os operadores passam menos tempo em cada tubo porque a automação cuida da maior parte do processo. Essa mudança permite que um trabalhador supervisione várias máquinas, multiplicando a produtividade.
A economia anual de mão de obra pode chegar a $70.000 a $100.000 para instalações que produzem 10.000 tubos ou mais. Essa economia resulta da redução do tempo de trabalho, menos ajustes manuais e menos necessidade de mão de obra especializada em acabamento. Em regiões com altos salários, o volume de equilíbrio para a adoção do laser cai ainda mais, tornando a automação atraente em níveis de produção mais baixos.
Principais economias de mão de obra com o corte a laser:
75% redução na mão de obra direta
$70.000-$100.000 de economia anual em volumes ideais
Um operador pode gerenciar várias máquinas
Menor volume de equilíbrio em áreas com altos salários
Eliminação do acabamento secundário: $8-15 Economia por tubo nas bordas polidas a fogo
O corte de tubos de quartzo econômico por corte a laser elimina a necessidade de acabamento secundário ao produzir bordas polidas a fogo em uma única etapa. Os métodos com lâmina de diamante exigem de 8 a 15 minutos de acabamento manual por tubo para obter resultados semelhantes. Essa etapa extra acrescenta $8-$15 ao custo de cada tubo.
Ao remover o acabamento secundário, os sistemas a laser não apenas economizam dinheiro, mas também melhoram a consistência. O processo garante que cada tubo atenda aos padrões de qualidade da superfície sem mão de obra adicional. Em milhares de tubos, essas economias se acumulam rapidamente e contribuem para um retorno mais rápido do investimento.
Mudança de processo | Economias resultantes |
|---|---|
Eliminação do acabamento manual | $8-$15 economizado por tubo |
Bordas polidas a fogo consistentes | Maior qualidade do produto, menos retrabalho |
Processamento em uma única etapa | Mão de obra reduzida e produtividade mais rápida |
Retorno do investimento de capital: ROI de 18 a 24 meses com volumes de produção ideais
O corte a laser econômico de tubos de quartzo oferece um rápido retorno do investimento quando os volumes de produção são altos. As instalações que processam 10.000 ou mais tubos por ano geralmente registram períodos de retorno de 18 a 24 meses. Esse rápido retorno sobre o investimento resulta da economia combinada de mão de obra, sucata e acabamento.
Os custos operacionais dos sistemas a laser permanecem competitivos, especialmente com lasers de fibra com eficiência energética. Esses sistemas normalmente usam de 6 a 10 kWh, custando cerca de $100-$160 por mês, enquanto os lasers de CO2 podem custar $200-$400 por mês. Despesas menores com serviços públicos e manutenção aceleram ainda mais o retorno do investimento.
Destaques do retorno do capital:
ROI de 18 a 24 meses em volumes ideais
Custos operacionais mais baixos com lasers com eficiência energética
A economia de mão de obra, sucata e acabamento gera retornos rápidos
As instalações podem reinvestir a economia no crescimento ou em novas tecnologias
Quando os requisitos de qualidade da borda tornam o corte a laser superior, apesar do custo inicial mais alto?
Os requisitos de qualidade da borda geralmente determinam a escolha entre os métodos de lâmina de diamante e laser para o corte de tubos de quartzo. Muitos setores precisam de superfícies que atendam a padrões rigorosos de suavidade, planicidade e limpeza. O processo de corte a laser oferece vantagens exclusivas que o tornam a única solução prática para aplicações exigentes.
Qualidade da borda polida a fogo: Ra 0,3-0,5μm inatingível por meio de acabamento mecânico
O corte a laser cria bordas polidas a fogo com uma rugosidade de superfície entre Ra 0,3 e 0,5μm. O acabamento mecânico não consegue atingir esse nível de suavidade, mesmo com um esmerilhamento extenso. O processo de corte a laser aquece o tubo de quartzo até seu ponto de amolecimento, permitindo que a tensão superficial suavize a borda à medida que esfria.
Muitos fabricantes escolhem o laser para aplicações em que a qualidade da borda afeta o desempenho do produto. Os tubos com bordas polidas a fogo resistem a rachaduras e contaminação, o que é fundamental em ambientes de laboratório e semicondutores. O processo de corte a laser também elimina a necessidade de polimento manual demorado, economizando mão de obra e melhorando a consistência.
Principais vantagens das bordas polidas a fogo:
O acabamento Ra 0,3-0,5μm aumenta a durabilidade
Não é necessário polimento manual
Qualidade consistente em todos os tubos
Aplicações ópticas: λ/10 Requisitos de planicidade e transmissão UV (200-400nm)
As aplicações ópticas exigem padrões extremamente altos de planicidade e transmissão de UV. O processo de corte a laser atinge uma planicidade de λ/10 e uma rugosidade de superfície abaixo de 5 nm Ra, que os métodos mecânicos não conseguem igualar. Os tubos usados em óptica devem transmitir mais de 80% de luz UV a 185nm e mais de 85% a 250nm, com paralelismo abaixo de 3 minutos de arco.
Parâmetro | Requisito |
|---|---|
Transmitância UV | >80% a 185nm (JGS1) |
>85% a 250nm (JGS2) | |
Rugosidade da superfície | <5nm Ra para aplicações ópticas |
Paralelismo | <3 minutos de arco |
Estabilidade térmica | Até 1.100°C |
O corte a laser permite que os fabricantes atendam a essas especificações rigorosas. Os tubos processados com o processo de corte a laser mantêm alta clareza óptica e geometria precisa. Essa capacidade abre portas para mercados avançados, como o de fotônica e instrumentos analíticos.
Processamento de contaminação zero: Padrões de qualidade para semicondutores e produtos farmacêuticos
Os setores farmacêutico e de semicondutores exigem tubos de quartzo com contaminação zero. O processo de corte a laser evita o contato com ferramentas de metal, impedindo a introdução de partículas metálicas. Os métodos de lâmina de diamante geralmente deixam resíduos que precisam ser removidos com limpeza ácida, o que aumenta o custo e o risco.
O corte a laser produz tubos prontos para uso em ambientes limpos. Os fabricantes se beneficiam da redução das etapas de limpeza e da maior segurança do produto. O processo de corte a laser também oferece suporte à documentação para padrões de qualidade, o que é essencial para a conformidade em setores regulamentados.
Resumo do controle de contaminação:
Nenhum resíduo metálico do corte a laser
Prontidão imediata para uso em salas limpas
Oferece suporte a uma documentação de qualidade rigorosa
Economia do mercado premium: margens mais altas do 40-60% justificam a adoção de volumes menores
Os mercados premium recompensam os fabricantes que oferecem qualidade superior de borda e controle de contaminação. O processo de corte a laser permite o acesso a esses mercados, atendendo a especificações que exigem margens mais altas. Mesmo em volumes de produção menores, o valor agregado justifica o investimento inicial em tecnologia a laser.
Os fabricantes podem oferecer tubos especializados para aplicações ópticas, de semicondutores e farmacêuticas. Esses produtos são vendidos a preços premium, compensando o custo mais alto do processo de corte a laser. A capacidade de atender a requisitos exigentes permite que as empresas expandam sua base de clientes e aumentem a lucratividade.
Causa | Efeito |
|---|---|
Qualidade superior das bordas | Acesso a mercados premium |
Contaminação zero | Preços mais altos dos produtos |
Processo de corte a laser | Justifica o investimento em volumes baixos |
Quando o corte a laser proporciona tempos de ciclo mais rápidos do que os métodos com lâmina de diamante para tubos de quartzo?
Corte a laser destaca-se por sua velocidade e eficiência no processamento de tubos de quartzo. Os fabricantes costumam comparar os tempos totais do fluxo de trabalho para determinar o melhor método para suas necessidades. As seções a seguir detalham a comparação, destacando onde os sistemas a laser oferecem resultados mais rápidos e maior produtividade.
Análise completa do fluxo de trabalho: 8-12 segundos de laser vs. 13-23 minutos de lâmina de diamante Total
Os sistemas a laser realizam um corte completo do tubo em apenas 8 a 12 segundos, enquanto os métodos de lâmina de diamante exigem de 13 a 23 minutos para a mesma tarefa. Essa diferença se torna ainda mais significativa quando se considera a configuração, o corte, o acabamento e a inspeção. A eficiência do corte a laser aumenta à medida que a automação reduz a intervenção manual e o processo elimina muitas etapas demoradas.
Uma comparação direta mostra que as operações com lâminas de diamante envolvem vários estágios. Os operadores devem configurar o equipamento, monitorar o corte e realizar o acabamento secundário. Os sistemas a laser, por outro lado, otimizam o fluxo de trabalho combinando corte e acabamento em uma única etapa.
Etapa | Tempo de laser | Tempo da lâmina de diamante |
|---|---|---|
Configuração | 1-2 min | 2-3 min |
Corte | 8-12 segundos | 5-8 min |
Acabamento | 0 | 8-15 min |
Inspeção | 2-3 min | 2-3 min |
Pontos principais:
Laser: 8 a 12 segundos por tubo
Lâmina de diamante: 13-23 minutos por tubo
O laser combina corte e acabamento
Eliminação do acabamento secundário: 8 a 15 minutos economizados com bordas polidas a fogo
O corte a laser elimina a necessidade de acabamento secundário, economizando de 8 a 15 minutos por tubo. Essa mudança resulta da borda polida a fogo produzida durante o processo a laser. O corte limpo e preciso significa que não é necessário nenhum tipo de esmerilhamento ou polimento adicional.
Os cortadores de tubos a laser oferecem alta precisão e flexibilidade, o que aumenta a eficiência.
O processo produz cortes que não requerem processamento adicional, reduzindo o tempo total do ciclo de produção.
Cortes limpos e precisos removem as sobras de materiais, agilizando o fluxo de trabalho e minimizando o desperdício.
Os fabricantes se beneficiam de um cronograma mais previsível e da redução dos custos de mão de obra. A eliminação das etapas de acabamento manual também melhora a consistência e a qualidade do produto.
Frases resumidas:
Não é necessário acabamento manual
Bordas polidas a fogo consistentes
Ciclos de produção mais curtos
Benefícios do carregamento automatizado: 85-90% Tempo de espera que permite a supervisão de vários sistemas
A automação nos sistemas de corte a laser permite que os operadores supervisionem várias máquinas ao mesmo tempo. O tempo de folga aumenta para 85-90%, liberando os trabalhadores qualificados para outras tarefas. Esse nível de automação contrasta com as operações de lâminas de diamante, que exigem ajustes manuais e supervisão constantes.
Os sistemas a laser podem funcionar fora do horário comercial, aumentando ainda mais a produtividade. Os operadores carregam os tubos brutos no sistema, e a máquina se encarrega do posicionamento, do corte e da descarga. Essa abordagem reduz a necessidade de supervisão contínua e permite maior rendimento.
Os operadores supervisionam várias máquinas
Intervenção manual mínima
Aumento da produtividade fora do horário de expediente
Os sistemas automatizados aumentam a eficiência e reduzem os custos de mão de obra. As instalações podem escalonar a produção sem adicionar mais funcionários, tornando o corte a laser uma escolha inteligente para operações em crescimento.
Multiplicação da produtividade: 2-2,5x a produção diária dentro das horas de trabalho existentes
Os sistemas de corte a laser multiplicam a produção diária de tubos em 2 a 2,5 vezes em comparação com os métodos de lâmina de diamante. Esse aumento é resultado de tempos de ciclo mais rápidos e redução do trabalho manual. As instalações podem atingir uma produção maior sem estender os turnos ou contratar mais funcionários.
Causa | Efeito |
|---|---|
Tempos de ciclo mais rápidos | Mais tubos produzidos por turno |
Menos trabalho manual | Os operadores gerenciam mais máquinas |
Automação | Maior eficiência e rendimento |
Os fabricantes observam ganhos imediatos em produtividade e economia de custos. A capacidade de aumentar a produção com as horas de trabalho existentes torna o corte a laser uma opção atraente para as instalações que desejam expandir a capacidade.
Pontos principais:
2 a 2,5 vezes mais tubos por dia
Não há necessidade de turnos extras
Maior eficiência com a equipe atual
Quando o corte a laser reduz as taxas de refugo o suficiente para compensar o custo mais alto do equipamento para tubos de quartzo?
As taxas de sucata desempenham um papel importante no custo total da produção de tubos de quartzo. Muitos fabricantes procuram maneiras de reduzir o desperdício, especialmente quando trabalham com materiais caros ou de alta pureza. A tecnologia a laser oferece uma clara vantagem ao minimizar os defeitos e melhorar a consistência.
Comparação da taxa de refugo: Laser 2-3% vs. Rejeição da lâmina de diamante 8-12%
Os sistemas a laser atingem consistentemente taxas de refugo entre 2% e 3%, enquanto os métodos de lâmina de diamante geralmente resultam em rejeição de 8% a 12%. Essa diferença significa menos tubos desperdiçados e menores custos de material. Ao longo de um ano, o impacto dessa redução torna-se significativo para qualquer operação.
Os operadores que usam lâminas de diamante enfrentam um risco maior de lascas, rachaduras e erros dimensionais. O corte a laser elimina a maioria desses problemas, pois utiliza métodos precisos e sem contato. Dados de várias instalações mostram que a mudança para o laser pode reduzir o refugo anual em até 75%.
Menores taxas de refugo com o laser: 2-3% vs. 8-12%
Menos defeitos e menos desperdício
Qualidade consistente em todas as execuções de produção
Cálculo da economia anual: $12.000-30.000 a uma produção de 5.000-10.000 tubos
O impacto financeiro das menores taxas de refugo aumenta rapidamente. Para instalações que produzem de 5.000 a 10.000 tubos por ano, a adoção do laser pode economizar de $12.000 a $30.000 por ano. Essa economia vem da redução da perda de matéria-prima e do menor tempo gasto com retrabalho.
Uma operação típica de lâmina de diamante pode perder 800 tubos a cada 10.000 devido a defeitos, enquanto um sistema a laser perderia apenas cerca de 250. Com um custo médio de material de $35 por tubo, essa diferença equivale a uma economia de $19.250. Os números aumentam ainda mais para tubos premium ou especiais.
Causa | Efeito |
|---|---|
Menor taxa de sucata | Redução dos custos de material |
Menos defeitos | Menos retrabalho e maior rendimento |
Precisão do laser | Economia anual de $12.000 a $30.000 |
Eliminação da variabilidade do operador: Consistência CNC reduzindo 60-75% de defeitos
Os sistemas a laser usam controles CNC para manter os mesmos parâmetros de corte para cada tubo. Essa abordagem elimina a variabilidade resultante da operação manual. Como resultado, de 60% a 75% de defeitos causados por erro humano desaparecem.
O corte manual com lâminas de diamante depende da habilidade e da atenção do operador. A fadiga ou pequenos erros podem levar a taxas de rejeição mais altas. A automação a laser garante que cada tubo atenda aos mesmos padrões, turno após turno.
O controle CNC elimina erros do operador
O processo estável reduz as taxas de defeitos
A qualidade confiável melhora os cronogramas de entrega
Economia de materiais premium: tubos de alta pureza que ampliam o impacto do custo da sucata
Os tubos de quartzo de alta pureza geralmente custam de $80 a $150 cada. As taxas de sucata têm um impacto financeiro muito maior nesses casos. A tecnologia a laser torna-se ainda mais valiosa porque protege materiais caros contra perdas desnecessárias.
Uma instalação que produz 3.000 tubos de alta pureza com uma taxa de sucata de 10% perderia $30.000 somente em material. Ao mudar para o laser e reduzir a sucata para 3%, a perda cai para $7.200. Essa diferença de $22.800 pode compensar os custos mais altos do equipamento e aumentar a lucratividade.
Fator-chave | Resultado |
|---|---|
Alto valor do tubo | Maior economia com a redução de sucata |
Precisão do laser | Protege materiais de primeira qualidade |
Menores taxas de sucata | Retorno mais rápido do investimento |
Quando o corte de geometria complexa torna o laser mais econômico do que a lâmina de diamante para tubos de quartzo?
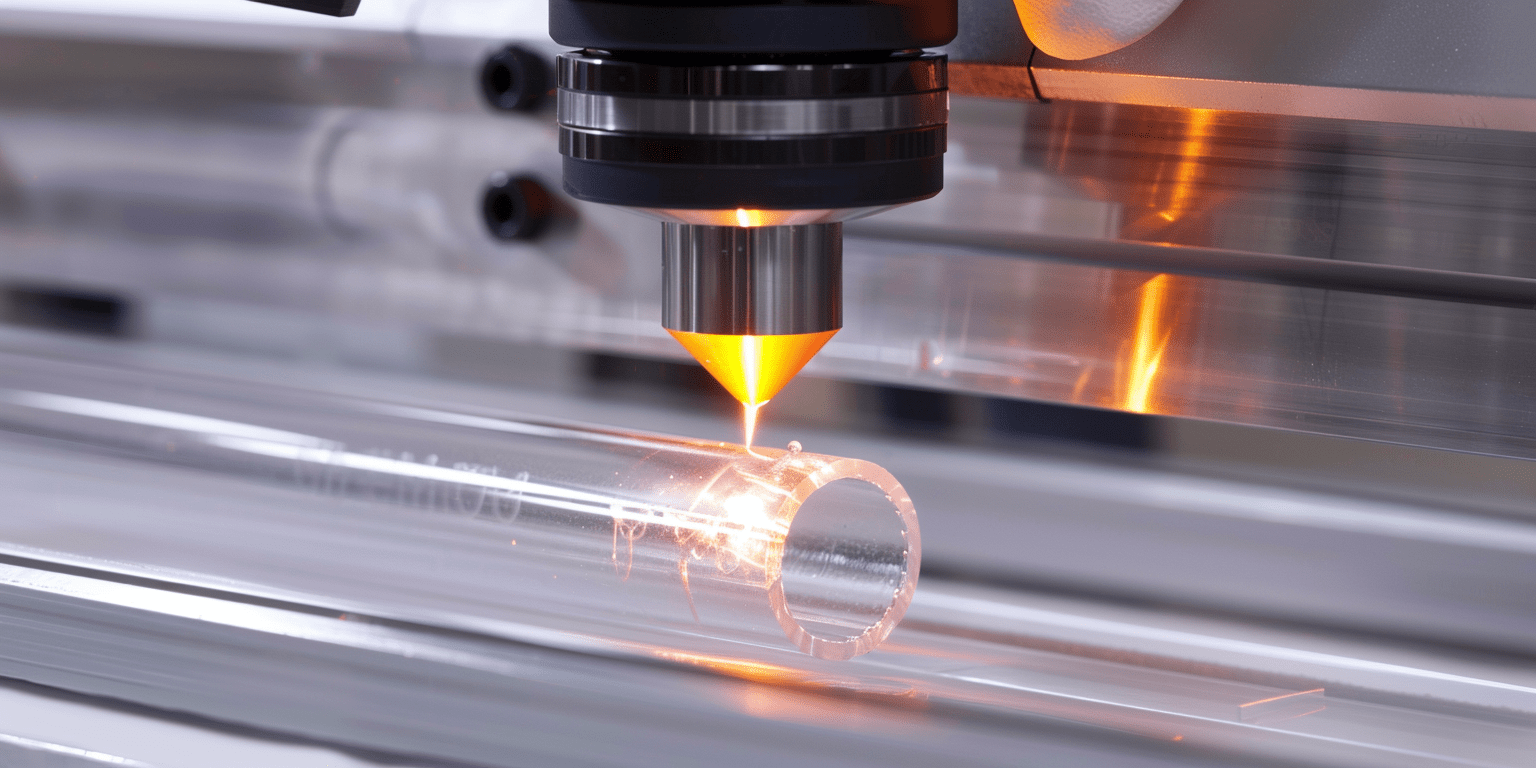

O corte de geometria complexa muitas vezes torna o laser a única opção prática e econômica para tubos de quartzo. Os fabricantes enfrentam desafios ao produzir recursos internos angulares, espirais ou intrincados que os métodos tradicionais de lâmina de diamante não conseguem alcançar. A capacidade de criar formas avançadas abre novas oportunidades para o design de produtos e a prototipagem rápida.
Capacidade de corte angular: cortes de 15 a 45° impossíveis de serem feitos com acessórios de lâmina de diamante padrão
Os sistemas a laser são excelentes na produção de cortes em ângulos entre 15 e 45 graus, que não podem ser realizados por dispositivos padrão de lâmina de diamante. Essa capacidade permite que os fabricantes atendam a requisitos exclusivos de projeto para aplicações como portas de visão de fornos ou janelas ópticas. A precisão do corte a laser garante que cada ângulo permaneça consistente em todos os ciclos de produção.
O corte a laser suporta projetos complexos, cantos afiados e recursos fora do eixo. Os operadores podem programar o sistema para obter detalhes finos e bordas chanfradas, que são difíceis ou impossíveis com métodos mecânicos. Os lasers de tubo também oferecem alta precisão para perfis complexos, o que os torna ideais para necessidades avançadas de engenharia.
Cortes angulares de 15 a 45° obtidos com laser
Cantos nítidos e detalhes finos são possíveis
Resultados consistentes em todos os lotes
Os fabricantes ganham uma vantagem competitiva ao oferecer produtos com geometrias avançadas. As vantagens do corte a laser incluem flexibilidade, velocidade e a capacidade de atender a especificações exigentes.
Prevenção de custos com acessórios personalizados: $2.000-8.000 economizados com a programação CNC
A tecnologia a laser elimina a necessidade de dispositivos personalizados caros, que podem custar entre $2.000 e $8.000 por configuração para sistemas de lâmina de diamante. Em vez disso, os operadores usam a programação CNC para ajustar os caminhos de corte para novas geometrias. Essa abordagem reduz o tempo de espera e o investimento inicial.
Com o laser, os fabricantes podem alternar entre os projetos rapidamente, atualizando as instruções do software. Essa flexibilidade permite a criação rápida de protótipos e a produção de pequenos lotes sem os atrasos da fabricação de acessórios. Os dados mostram que a mudança para o laser economiza milhares de dólares por projeto, especialmente para pedidos de baixo volume ou personalizados.
Ponto-chave | Causa | Efeito |
|---|---|---|
Não é necessário nenhum acessório | A programação CNC substitui o hardware | Menores custos de instalação |
Mudanças rápidas no design | Ajustes orientados por software | Retorno mais rápido |
Economia de custos | Nenhum investimento em instalações | $2.000-$8.000 economizados por projeto |
Os métodos e as técnicas de corte a laser oferecem um claro benefício econômico para trabalhos complexos. Os fabricantes podem responder às solicitações dos clientes mais rapidamente e com menos risco de capital.
Geometria curva e em espiral: Aplicações impossíveis com corte mecânico
O corte a laser permite a criação de características espirais, curvas e internas que os métodos mecânicos não conseguem igualar. Os lasers de tubo podem cortar perfis complexos com alta precisão, o que os torna adequados para reatores farmacêuticos, tubos de mistura e equipamentos de laboratório personalizados. Essas formas geralmente exigem curvas contínuas ou defletores internos que as lâminas de diamante não conseguem produzir.
Os designers se beneficiam da liberdade de criar contornos intrincados e micro-recursos. Os sistemas a laser oferecem precisão excepcional para cortes muito finos, dando suporte à pesquisa e ao desenvolvimento avançados. O processo também permite a produção de recursos exclusivos, como recortes chanfrados ou elípticos, em uma única operação.
Cortes em espiral e curvos possíveis somente com laser
Recursos internos e microdetalhes obtidos
Oferece suporte ao desenvolvimento avançado de produtos
A capacidade de produzir essas geometrias amplia a gama de produtos que um fabricante pode oferecer. Esse valor estratégico ajuda as empresas a entrar em novos mercados e atender a setores especializados.
Economia de uma única unidade: Laser justificado mesmo para quantidades de protótipos
O corte a laser é econômico mesmo para a produção de uma única unidade ou de protótipos. Ao contrário dos métodos de lâmina de diamante, que exigem fixações e configurações caras, os sistemas a laser podem produzir peças únicas com preparação mínima. Essa capacidade de prototipagem rápida leva a uma inovação mais rápida e a um menor tempo de colocação no mercado.
Os fabricantes obtêm vários benefícios com essa abordagem. O corte a laser oferece uma operação muito rápida, liberdade de design e eficiência de custos ao otimizar o uso do material. O retorno rápido, incluindo a entrega durante a noite para pedidos urgentes, torna-se possível para formas personalizadas e geometrias complexas.
Benefício | Descrição |
|---|---|
Operação muito rápida | Tempos de resposta mais curtos em comparação com a usinagem tradicional |
Liberdade de design | Geometrias complexas e recursos internos facilmente produzidos |
Eficiência de custos | Várias peças cortadas de um único tubo, economizando tempo e material |
Embora algumas pessoas possam considerar as desvantagens do corte a laser, como os custos iniciais mais altos do equipamento, a capacidade de fornecer protótipos e peças personalizadas com rapidez geralmente supera essas preocupações. Essa capacidade apoia a inovação e fortalece os relacionamentos com os clientes.
O corte a laser se torna mais econômico do que os métodos de lâmina de diamante quando o volume de produção, a qualidade da borda e os requisitos de geometria se alinham com seus pontos fortes. As instalações obtêm os maiores benefícios do laser quando precisam de alto rendimento, acabamentos de borda premium ou formas complexas. O processo a laser também reduz o refugo e dá suporte a aplicações premium.
Os tomadores de decisão devem usar essas etapas para avaliar suas próprias operações:
Compare os custos totais, a precisão e a eficiência de cada método de corte.
Analise as necessidades do projeto, como a qualidade do corte, a espessura do quartzo e a quantidade de tubos.
Avalie os benefícios exclusivos do laser e da lâmina de diamante para determinar a melhor opção.
O laser se destaca por sua capacidade de fornecer resultados consistentes, reduzir o trabalho manual e abrir o acesso a novos mercados. Ao avaliar esses fatores, os fabricantes podem decidir se o laser é o investimento certo para suas necessidades de corte de tubos de quartzo.
PERGUNTAS FREQUENTES
Por que o corte a laser reduz as taxas de refugo na produção de tubos de quartzo?
O corte a laser utiliza métodos precisos e sem contato. Isso reduz a formação de lascas e rachaduras, que geralmente ocorrem com ferramentas mecânicas. Taxas de refugo mais baixas significam menos desperdício de material e maior rendimento geral.
O processo preciso reduz os defeitos
A qualidade consistente aumenta o rendimento
Menos desperdício economiza dinheiro
Por que os fabricantes escolhem o corte a laser para geometrias complexas?
Os sistemas a laser podem cortar ângulos, espirais e características internas que as lâminas de diamante não conseguem obter. A programação CNC permite mudanças rápidas sem acessórios caros. Essa flexibilidade permite a criação rápida de protótipos e projetos personalizados.
Motivo | Efeito |
|---|---|
Programação CNC | Mudanças rápidas no design |
Não é necessário nenhum acessório | Menores custos de instalação |
Formas avançadas | Oportunidades de novos produtos |
Por que o corte a laser é preferido para aplicações ópticas ou de alta pureza?
O corte a laser evita o contato com o metal, o que impede a contaminação. O processo cria bordas polidas a fogo com Ra 0,3-0,5μm, atendendo a rígidos padrões ópticos e de limpeza. Isso permite o uso nos setores de semicondutores e farmacêutico.
Sem resíduos de metal
Atende aos padrões ópticos
Pronto para uso em salas limpas
Por que a automação a laser reduz os custos de mão de obra no corte de tubos?
A automação do laser reduz o tempo de trabalho em até 75%. Um operador pode gerenciar várias máquinas ao mesmo tempo. Essa eficiência reduz os custos de mão de obra e aumenta a produtividade.
Fator | Resultado |
|---|---|
Automação | Menos trabalho manual |
Uso de vários sistemas | Maior produtividade |
Menos operadores | Menores despesas com mão de obra |
Por que o corte a laser oferece tempos de ciclo mais rápidos do que os métodos de lâmina de diamante?
Os sistemas a laser cortam e fazem o acabamento dos tubos em 8 a 12 segundos. Os métodos de lâmina de diamante levam de 13 a 23 minutos, incluindo configuração e acabamento. Tempos de ciclo mais rápidos significam mais tubos produzidos por dia.
8-12 segundos por tubo
Sem acabamento secundário
Maior produção diária





